
During a time when sustainability demands have reached an urgent level, artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming a seismic force that is changing the way energy is consumed in homes and industries. AI is not just cutting costs but helping deliver more brilliant, efficient energy management systems while lowering your company’s environmental footprint. In this blog, we take a deep look at the trenches of how AI is powering its way into the energy consumption world, as well as its mechanisms, benefits, drawbacks, and potential prospects.
The Energy Challenge: A Call for Innovation
World energy demand keeps increasing, fueled by rising population and industrial growth. By 2050, the International Energy Agency (IEA) says global energy consumption will nearly double. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is critically essential to combat climate change. Bridging this gap requires an innovative approach to optimizing energy use, and AI is the leader in this field.
AI in Smart Energy Management
Energy usage in a building is optimized in real-time using advanced algorithms, machine learning (ML), and data analytics applied by AI. By analyzing large amounts of data from sensors, smart meters, and other IoT devices, AI systems can find patterns, predict demand, and make real-time decisions to improve energy efficiency responsible AI in retail.

Let’s explore the critical ways AI is making an impact:
-
Real-Time Energy Monitoring
AI-powered energy management systems use IoT-enabled smart meters to collect real-time data on electricity consumption. This data is analyzed to provide insights into usage patterns and identify areas of inefficiency. For instance:
- In homes, smart thermostats like Nest Learning Thermostat use AI to learn user preferences and adjust heating and cooling for optimal energy use.
- AI tools like GE’s Predix platform monitor industry equipment performance to ensure energy-efficient operations.
2. Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting
AI’s predictive capabilities enable accurate energy demand forecasting, helping utilities and industries plan more effectively. By analyzing historical data and external factors like weather conditions, AI can:
- Prevent energy wastage by adjusting supply to match demand.
- Optimize grid operations to reduce strain during peak hours.
3. Energy Storage Optimization
Energy storage systems like batteries are critical in balancing supply and demand. AI enhances these systems by:
- Predicting optimal charging and discharging cycles.
- Ensuring maximum efficiency and lifespan of energy storage units.
4. Integration with Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are inherently variable, posing challenges for consistent energy supply. AI addresses these challenges by:
- Predicting renewable energy generation based on weather forecasts.
- Optimizing energy distribution to maximize the use of renewable sources.
5. Automated Energy Management Systems
AI-powered automation enables homes and industries to operate with minimal human intervention. Smart appliances and industrial equipment can:
- Automatically adjust energy consumption based on real-time data.
- Coordinate with energy grids to optimize energy use during off-peak hours.
Transforming Energy Consumption in Homes
AI’s role in residential energy management rapidly expands, making homes smarter and more sustainable. Key applications include:
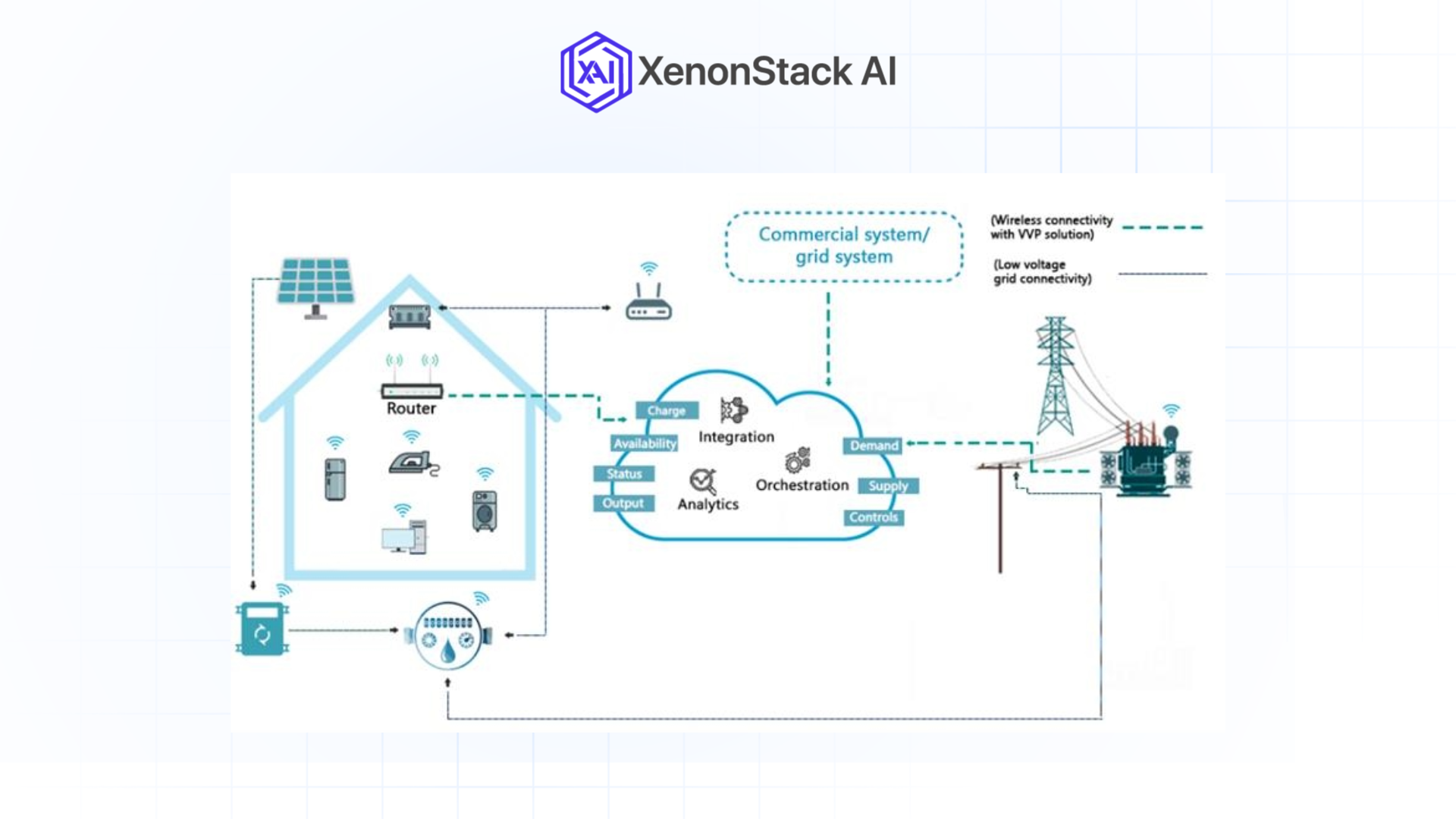 Fig1.2. Energy Consumption Management at Home
Fig1.2. Energy Consumption Management at Home Smart Home Automation
AI-driven smart home systems integrate appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems to optimize energy use. For example:
-
Intelligent lighting systems like Philips Hue adapt brightness based on natural light availability.
-
AI-enabled water heaters heat only the required amount of water, reducing unnecessary energy consumption.
Personalized Energy Insights
By analyzing individual usage patterns, AI provides homeowners with actionable insights to reduce energy waste. Platforms like Sense Energy Monitor can identify energy-hungry devices and suggest energy-saving measures responsible ai principles.
Dynamic Energy Pricing
AI facilitates real-time adjustments to energy consumption based on dynamic pricing models. This enables homeowners to:
-
Schedule high-energy tasks, like laundry, during off-peak hours to save on costs.
-
Integrate with time-of-use energy tariffs for maximum savings.
Revolutionizing Energy Consumption in Industries
Industries account for nearly 38% of global energy use. AI’s ability to optimize complex operations makes it a game-changer in industrial energy management.
Key applications include:
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Integration
AI-powered IIoT systems connect machinery and equipment to enable seamless energy optimization. Benefits include:
-
Real-time monitoring of energy-intensive processes.
-
Automated adjustments to minimize energy waste.
Predictive Maintenance
AI-driven predictive maintenance ensures that industrial equipment operates efficiently. By analyzing sensor data, AI can:
-
Detect anomalies and predict equipment failures.
-
Schedule maintenance to avoid energy loss due to inefficiencies.
Energy-Efficient Supply Chains
AI optimizes supply chain operations to minimize energy consumption. For example:
-
Route optimization for logistics reduces fuel consumption.
-
Inventory management systems minimize energy used in warehousing
AI-Powered Microgrids
Industries are increasingly adopting microgrids—localized energy systems that can operate independently. AI enhances microgrid performance by:
-
Balancing energy supply and demand within the grid.
-
Facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources.
Use Cases
Use Case 1: Reducing Energy Wastage in Commercial Buildings
-
Problem Statement: Commercial buildings often experience significant energy wastage due to inefficient HVAC systems and lighting operations, especially during non-peak hours.
-
Solution: AI-powered building management systems (BMS) analyze real-time occupancy data and adjust lighting, heating, and cooling accordingly. Systems like Siemens’ Desigo CC integrate IoT and AI for optimal energy use.
-
Reduced energy costs by up to 30%.
-
Enhanced occupant comfort through personalized climate settings.
-
Lower carbon footprint for sustainable operations.
Use Case 2: Optimizing Renewable Energy Utilization in Manufacturing
-
Problem Statement: Manufacturing facilities struggle to integrate variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind into their energy mix without affecting operational stability.
-
Solution: AI systems predict renewable energy generation and match it with production schedules. Platforms like Tesla’s Autobidder optimize energy storage and usage for maximum efficiency. Automating Administrative Processes in Schools with AI.
Key Impacts:
-
Increased reliance on renewable energy by 40%.
-
Improved operational stability through predictive energy management.
-
Significant reduction in fossil fuel dependency.
Use Case 3: Enhancing Grid Stability in Urban Areas
-
Problem Statement: Urban energy grids face challenges in maintaining stability due to fluctuating demand and the growing integration of decentralized energy sources.
-
Solution: AI-driven grid management systems, such as those offered by ABB, monitor grid conditions in real-time and adjust to balance supply and demand dynamically.
- Reduction in power outages by 25%.
- Improved energy efficiency across the grid.
- Greater integration of distributed energy resources.
Benefits of AI-Driven Energy Management
The integration of AI into energy management systems offers a multitude of benefits:
-
Cost Savings: Identifying inefficiencies and helping cut half the energy spent in households and businesses helps address energy waste reduction and results in significant cost savings.
-
Environmental Impact: Energy usage becomes increasingly optimized, and carbon emissions decrease, which is suitable for sustainability goals.
-
Enhanced Reliability: AI predicts and reduces the downtime of grid stability by mitigating potential issues.
-
Scalability: For AI systems, scaling from one house to many houses or even from an entire industrial complex is trivial.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, the adoption of AI in energy management faces several hurdles:
-
Data Privacy and Security: The widespread use of IoT devices and data collection raises concerns about privacy and cybersecurity. Robust data protection measures are essential.
-
High Initial Investment: Implementing AI-driven energy management systems requires substantial upfront costs for infrastructure and technology.
-
Complexity of Integration: Integrating AI systems with existing infrastructure can be challenging, especially in legacy industrial setups.
-
Dependence on Data Quality: AI’s effectiveness depends on the quality and quantity of data it receives. Inconsistent or incomplete data can hinder performance.
Future Prospects of AI in Energy Management
The future of AI-driven energy management looks promising, with technological advancements and growing adoption rates. Emerging trends include:
-
AI-Enabled Decentralized Energy Systems: Decentralized systems, such as peer-to-peer energy trading, will leverage AI for efficient user energy exchange.
-
Enhanced Renewable Energy Integration: AI will play a crucial role in maximizing the potential of renewable energy sources by improving forecasting and storage capabilities.
-
Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS): AI will enable businesses to adopt EaaS models, where energy management is outsourced to specialized providers.
-
Collaboration with Blockchain: AI and blockchain technologies will combine to enhance transparency and security in energy transactions.
Conclusion for Smart Energy Consumption
AI is revolutionizing energy consumption in homes and industries, offering unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, sustainability, and cost savings. By harnessing the power of AI, we can pave the way for a brighter, greener future. However, addressing challenges like data security and integration complexities will be crucial to realizing AI’s full potential in energy management. As technology evolves, the role of AI in shaping our energy landscape will only grow, driving us closer to a sustainable energy future.
Next Steps with Smart Energy Consumption
Talk to our experts about implementing AI-driven solutions for smart energy consumption. Explore how industries and various departments leverage agentic workflows and decision intelligence to become more energy-efficient and decision-centric. Utilize AI to automate and optimize energy management systems, improving sustainability, operational efficiency, and responsiveness.


