IT incident management is the process whereby the different IT-related problems are evaluated in a short period in order to be prioritized. In the past, this process was a labour-intensive endeavour that especially put pressure on IT operations teams, given the always-rising alert rates. Automated solutions, however, have emerged as a key positive factor in assisting organizations through intelligent products that help cater to wise incident segregation and enable organizations to decrease the number of cases managed manually while enhancing response time.
How Automation Helps in Incident Triage
Retrospective incident triage was previously highly dependent on manual work as IT security teams filter through many alerts, categorise them and decide on responses. This process is critical, but batch size can be time-consuming and cumbersome, which results in alert fatigue most of the time. Automation shifts this paradigm by offering analytical tools that analyze and sort incidents according to some measures. These automated solutions rely on Machine Learning and analytics to selectively eliminate false positives, connect multiple unrelated alerts as related events, and route the incidents to the team that should handle them.
How Automated Incident Triage Works
In automated triage systems, all information from different monitoring tools, security systems, and logs is provided to the system. Alerts are then correlated and analyzed in real time. Based on predefined rules and artificial intelligence, automation tools help qualify the levels of incidents and categories, tag them, and prioritize them. Incidents or events of importance to an organization may set off prescheduled actions such as sending notifications to stakeholders, creating tickets, or correcting some system actions.
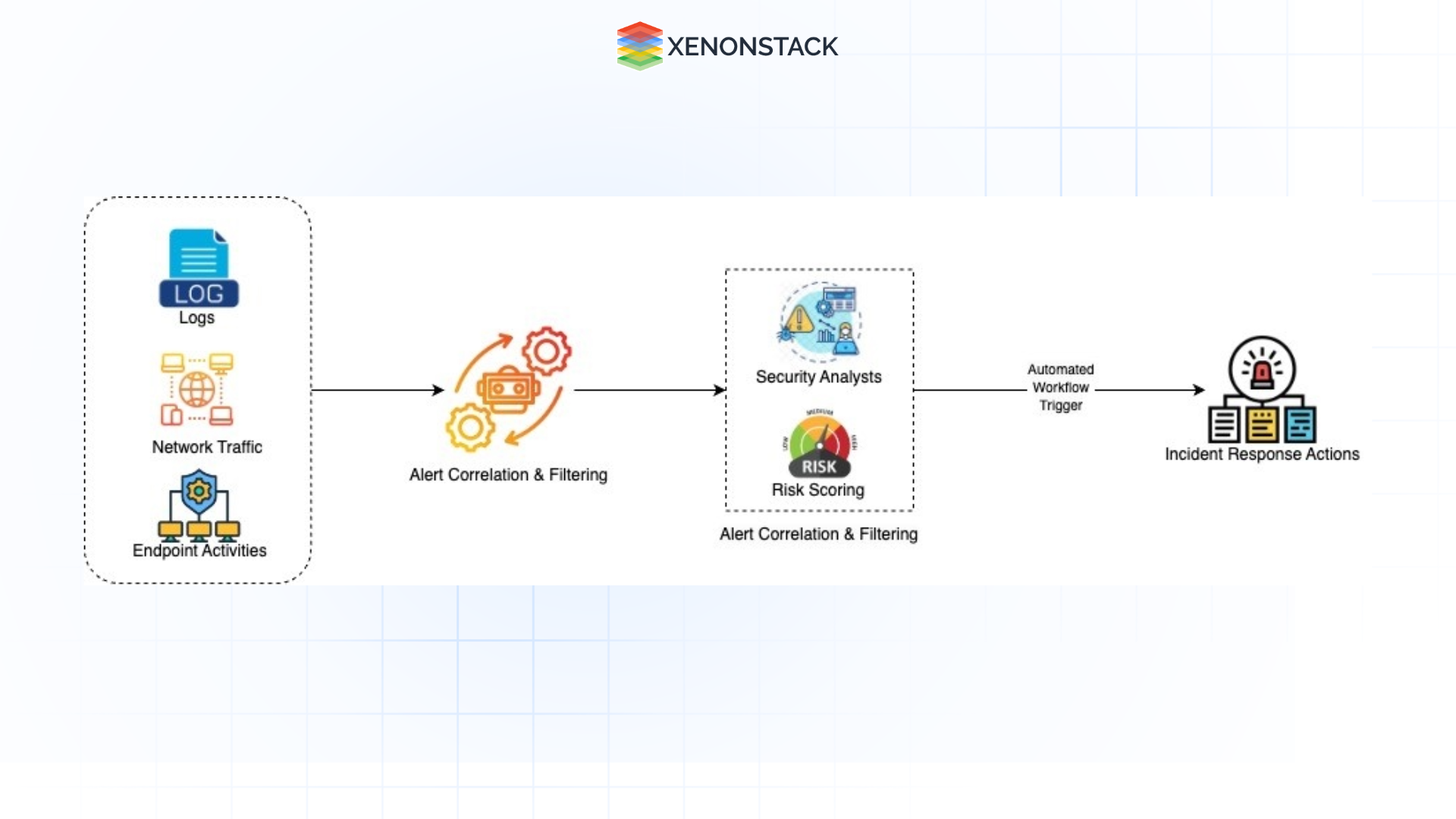 Figure 1: Automated Incident Triage System
Figure 1: Automated Incident Triage SystemExplanations:
-
Data Ingestion: Information is gathered from sources such as application logs, firewalls, IDS, IPS, and any other monitoring tools used.
-
Alert Correlation & Filtering: The automation tools then help review the obtained data by grouping related alerts and excluding noise alerts.
-
Incident Classification & Prioritization: According to the set parameters and AI models, incidents are differentiated based on their priority level and the degree of their seriousness and urgency.
-
Automated Workflow Trigger: There are alarm cases involving high priorities with default response procedures: creating tickets, notifying related teams, or performing prescribed actions.
-
Incident Response Actions: The incident response workflow is activated, and other teams/systems with roles in this incident start engaging/dragon.
-
Resolution & Closure: Afterward, the report is cased and archived, and key statistics are captured to review performance indicators.
Alert Correlation & Filtering
 Figure 2: Flow diagram of Alert Correlation & Filtering
Figure 2: Flow diagram of Alert Correlation & Filtering -
Raw Alerts from Multiple Sources: Information regarding alerting involves material from application logs, network traffic data, security systems, and other endpoint protection devices.
-
Alert Normalization: Alerting often creates large files that take time to process, hence the need to transform the format of alert data into a universal structure.
-
Alert Deduplication: Filtering of alerts to eliminate duplicate alerts, which contribute to alert noise.
-
Alert Correlation: Categorizing alerts from various sources into a more coherent set of ‘things that could be going wrong’.
-
Priority Assignment: Prioritize it according to its severity level, the business effect it might have, and any other criteria.
-
Relevant Alerts for Triage: Prioritized relevant alerts only reach the second stage, which is referred to as a triage alert, where they are further sorted and sent for handling.
Key Features of Automation in Incident Triage
In incident triage, automation improves identifying issues based on a large amount of information collected at the speed of light. This leads to enhanced availability of applications and services since the average time to detect and fix an incident is reduced, thus reducing MTTR. Companies such as InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG), a hotel company, for instance, have recorded a great availability of 99.8% by integrating automated triage solutions while containing costs.
As basic and routine triage work is largely automated, IT and SecOps can remain on high-value work. This workload redistribution has a dual benefit: it cuts out aspects of manual input that come with many mistakes and inefficient work output. Automated triage by itself reduces alert fatigue as it buries all the false-positive alerts, allowing the teams to handle critical issues.
Automated triage solutions enable analysts to have a single pane of glass through which one can get the required information about an incident aggregated from disparate sources. This lets teams see and sort incidents and set priorities in one central location, enhancing intergroup unity and effort.
Traditional vs. Automated Incident Triage
Traditional Incident Triage
-
Miss detections, several levels of analysis with key details passed up the chain and time-consuming response.
-
Currently, incident classification and prioritization are performed manually, using knowledge and best practices, and thus are vulnerable to errors.
-
Increased probability of alert fatigue due to an overload of unfiltered or low-signal relevance alerts.
-
Heavy use of people to route incidents to the right teams.
-
Its ability to address tracking and management of incidents that are spread across various tools and platforms unsuccessfully.
Automated Incident Triage
-
Another advantage of alerts is that they are interrelated, filtered, and categorized automatically, thanks to technologies such as SIEM and SOAR.
-
By automatically prioritizing a case according to a set of specific business rules, the chances of errors are also minimized.
-
Optimize alert fatigue and reduce noise by turning off false positives and unimportant alerts automatically.
-
It helps to seamlessly assign the correct teams and sends incidents to appropriate teams in the shortest time possible.
-
A more centralized dashboard gives an overall picture for real-time reporting and tracking of the incident.
Components of Automated Incident Triage
Flexible Custom Tags
Flexible tagging allows IT teams to include all the necessary business context in incidents. Special tags supplement information about incidents and help the system sort incidents by context, priority, and relation.

Automatic Tag Population
Tag auto-complete reduces the work required to categorize incidents by automatically assigning tags to them according to some given conditions. This auto-population of tags guarantees the right teams’ examination.
Implementing Automation in Incident Triage
-
Select Appropriate Tools
It is important to pick the automation tools to use wisely. Products like SIEM and SOAR can correlate alerts and automate tasks. -
Integrate Multi-Source Data
Effective triage involves data from logs, firewalls, and endpoints. Application logs are important in inferring endpoint security. These sources can be integrated to provide a complete look at an incident and, as a result, more expedite root cause determination. -
Fine-Tune the System Regularly
As the name implies, it is not a one-time implementation. Periodic runtime tag updates and new tags, workflow adjustments, and priority level changes guarantee that the systems are always relevant to the dynamic security and operational environment. -
Implement Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
On the same note, feedback loops with the automated incident triage system should be created to track performance metrics like MTTD and MTTR. Supervisory use of performance data enables a team to implement correctives on the system that would enhance efficiency and productivity.
Challenges and Opportunities
Adopting automation for incident triage comes with its share of challenges, which organizations must address to unlock its full potential. Integration complexity often arises, as automated tools may not align seamlessly with legacy systems or diverse data sources. To overcome this, businesses should prioritize solutions with open APIs and seamless interoperability. High initial costs for advanced tools, infrastructure, and training can be another deterrent; however, starting with small-scale implementations and scaling based on ROI can make the transition more manageable. False positives and noise remain persistent, as improperly tuned systems can generate redundant alerts.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by automation in incident triage are significant. Automated systems dramatically improve response times by quickly identifying, categorizing, and resolving incidents, reducing the mean time to resolution (MTTR) and ensuring better service availability. These solutions also provide scalability, enabling IT teams to handle growing alert volumes without increasing headcount. By addressing these challenges, businesses can fully leverage the transformative potential of automated incident triage systems.
Next Steps with Automation in Incident Triage
Talk to our experts about implementing automation in incident triage and how industries and different departments leverage AI to streamline incident detection, classification, and resolution. By automating IT support and operations, organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce response times, and improve overall decision-making.