What is AWS Data Catalog?
AWS Data Catalog is a prospering metadata management service nowadays. It offers two forms:
1. Comprehensive
2. Hive Metastore
The two may exist in parallel. Using a comprehensive Data Catalog, we can search for all our assets in the lake.
There has always been a no-man's land between IT and business. IT knows how to work with inputs, but the business knows what it represents. This creates a conflict as neither knows enough about it to use it strategically. Hence, a tribal behavior emerges where each guards its pockets of expertise. At a certain point, every company has suffered from this condition over the years.
Top 5 Use Cases of Data Catalog in Enterprises
What is a Data Catalog?
It can be compared to retailer catalogs, but instead of providing information about the product, it provides information about the organization's elements. The consumers of this are present all over the hierarchy. They want to use it to its full potential.
Hence, it gives the data catalog a heavy dose of automation to collect meaningful information about the element imported into the solution. This acts as a bridge between consumers; hence, emitting tribal behavior is essential to understanding that it does not conform. Still, instead, it plays to identify its uses. The application of conformity is what lives inside the warehouse.
1. Comprehensive AWS Data Catalog
Standard AWS services like AWS Lambda, Amazon ES, and Amazon DynamoDB can create a comprehensive catalog. At a glance, triggered Lambda functions populate the DynamoDB table with metadata and object names. When saving it and the object name into Amazon S3, the Amazon ES may search for desired assets. It contains all information about the assets ingested into the S3 lake.
2. HCatalog with AWS Data Catalog
Hive-compatible Metastore can be created using AWS Amazon Glue for the assets stored in an Amazon S3-based lake. Building your data catalog is a piece of cake with the help of AWS glue. To begin with, go to the AWS management console and register your asset source with AWS glue. The crawler crawls over the S3 bucket, searches your input sources, and devises a catalog using classifiers.
You can choose from many classifiers, such as CSV, JSON, and Parquet, or add your classifiers or choose classifiers from the AWS glue community to add them to the Crawler to recognize different types. AWS glue then spawns a data catalog that can be used by various AWS services, such as Amazon Athena, Amazon EMR, Amazon Redshift Spectrum, and Amazon Redshift, as third-party analytics tools that use a standard Hive Metastore.
A good Catalog helps the user in understanding the data. Click to explore about, Guide to Data Catalog Tools and Architecture
3. Connections in AWS Glue Data Catalog
It stores connection information for a particular data store. Creating a connection takes the burden off the shoulder to specify connection details every time you create a crawler or job. Different types of connections are available with it, such as JDBC, Amazon RDS, Amazon Redshift, MongoDB, and Amazon DocumentDB. While creating a crawler or ETL job for any source, specify the connection to use.
Populating the AWS Glue Data Catalog
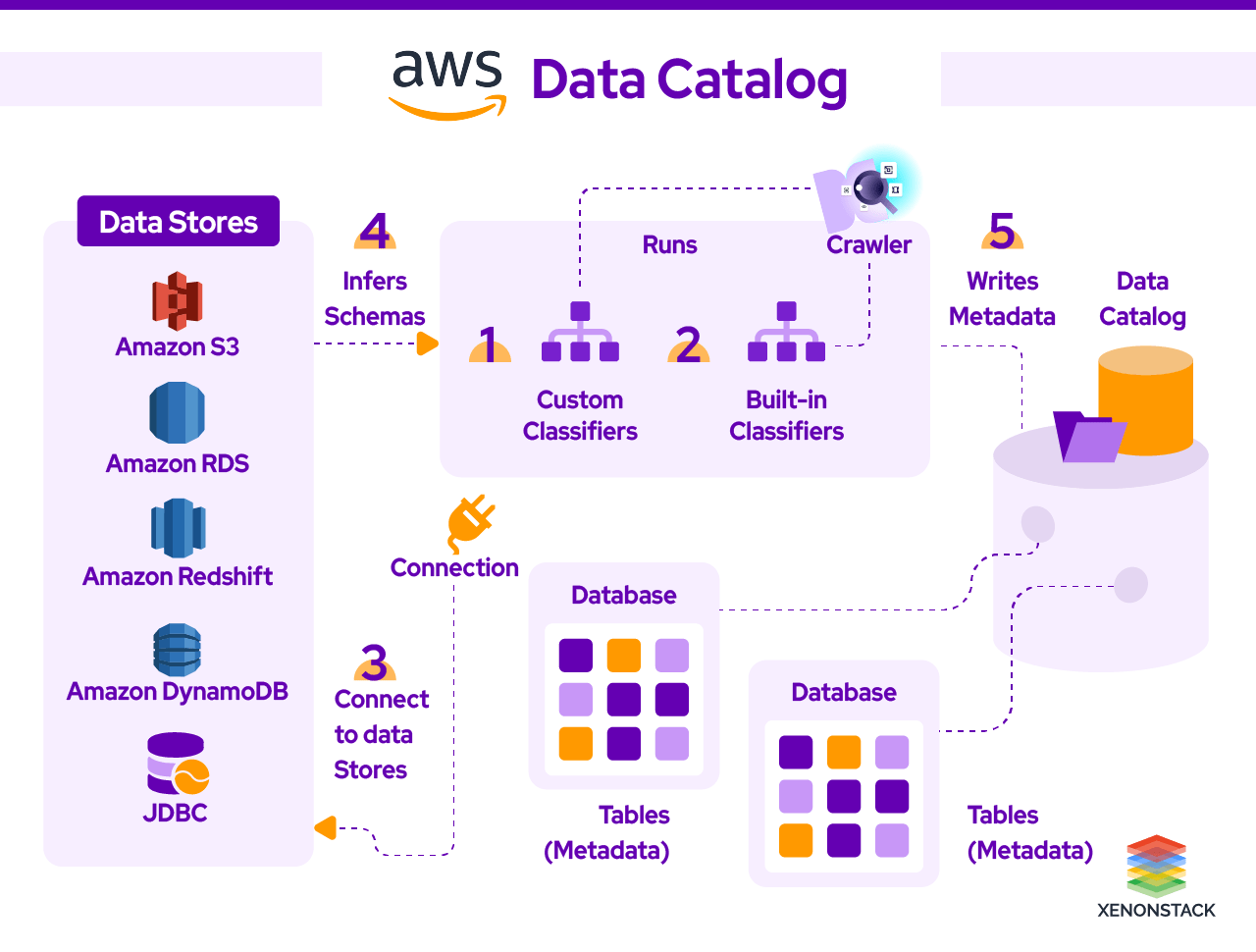
It references data used as a source and target for your ETL (extract, transform, and load) jobs. It must be cataloged to create your warehouse. The information is used to monitor ETL jobs. Each metadata table specifies a single where we store our information.
1. Tables
A table in AWS Data Catalog is a definition representing a store that may hold the object of Amazon S3 service and relational tables in Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service). We can create Tables manually or by using the AWS Data Catalog Crawlers. While defining a table in AWS glue, it provides you with the option of a partitioning key that allows you to partition the table to improve query performance. While partitioning the table, these conditions must be proper. The schemas of the files must be similar. As determined by AWS Glue, the data and the file compression format are the same.
2. Databases
Once a table is added in AWS Glue, it is subsequently incorporated into a database. The AWS Data Catalog organizes tables into various categories. This can be achieved by utilizing a crawler or accessing the AWS Glue console. In AWS Glue, a database functions as a container for the defined tables, which are created either manually or through a column run. The entire structure can be visualized as an interconnected chain. It may encompass objects from Amazon S3 service and relational tables from Amazon RDS, all of which are contained within the data catalog.
3. Steps to Work with Database
Various functions can be performed from the database tab in the AWS glue console:
-
To create a new database, select Add and provide the description.
-
To edit action allows you to edit the database.
-
To delete action allows you to delete it.
-
The View Tables action allows you to view the list of tables.
AWS cloud formation service can create many AWS resources. Cloudformation can automate the creation of an object, making it convenient to define and create AWS Glue objects and other related AWS resources. AWS Cloud Formation provides a simplified syntax in JSON/YAML to create AWS resources.
Cloud Formation can provide templates that may be used to define Data Catalog objects, databases, tables, partitions, crawlers, classifiers, and connections. AWS CloudFormation provides a simplified syntax in JSON/YAML to create AWS resources. It helps in provisioning and configuring resources described by the template.
It should now be evident how the AWS Data Catalog has facilitated the strategic utilization of assets by both business and IT, leveraging a serverless environment that simplifies the data catalog's population. Users are now familiar with the various AWS Data Catalog services (Comprehensive and HCatalog) and the methods for populating them. This underscores the rationale behind the Future Workspace initiative.







