Today, as more businesses rely on network infrastructure to keep operations running smoothly, we must ensure these systems' reliability, performance, and security. As network infrastructures' breadth and scale increase, established monitoring and debugging methods illustrate big challenges. But in this case, Computer Vision exists, a very new technology with the potential to change network infrastructure monitoring.
But computer vision, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), lets systems see and interpret the world around them. Using such technology, network administrators can automatically identify, classify, and even resolve infrastructure network problems (hardware faults, security breaches, or performance degradation).
This blog focuses on how Computer Vision could be leveraged to drive automation through network infrastructure monitoring and the advanced use cases, benefits, and future potential.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer Vision is an interdisciplinary field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data from the environment. It involves extracting meaningful information from images, videos, and real-time visual inputs, emulating the human ability to see, understand, and react to visual stimuli. In essence, it equips machines with the ability to process and analyze visual data, which is increasingly being applied in various industries, from healthcare to retail and now to network infrastructure management.
Components of Computer Vision
Image Processing
The foundation of computer vision deals with enhancing, transforming, and extracting features from images.

Object Detection and Recognition
Identifying and classifying objects within an image or video stream.
Pattern Recognition
Identifying recurring patterns, trends, or anomalies in visual data.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks
Advanced techniques for training systems to recognize complex patterns from large datasets.
In the context of network infrastructure, Computer Vision can provide real-time visual monitoring to detect issues like hardware failures, connectivity problems, or unauthorized access to network components. Biomedical Image Analysis and Diagnostics.
The Need for Automated Network Infrastructure Monitoring
Modern enterprises rely on network infrastructure comprising many components, including routers, switches, servers, cables, and access points. Ensuring this infrastructure is healthy often requires human intervention, involving troubleshooting, inspecting, and maintaining systems. Essential Insights into Self-Supervised Learning for Computer Vision.
Error-prone traditional solutions for monitoring include manual inspections or software-based network monitoring tools that cannot and do not necessarily observe things in real-time. Network monitoring requires automation to the degree that there is increasing demand for higher network uptime, security, and efficiency.
However, Computer Vision provides a proactive and automated solution that allows for proactive elimination of existing problems; rather, it forces the issue before it becomes too dangerous.
How Computer Vision Transforms Network Infrastructure Monitoring
Real-Time Visual Monitoring of Hardware Components
Network infrastructure often involves large physical setups—data centres, server racks, switches, routers, and cables. These components need constant monitoring to ensure they are in proper working condition.
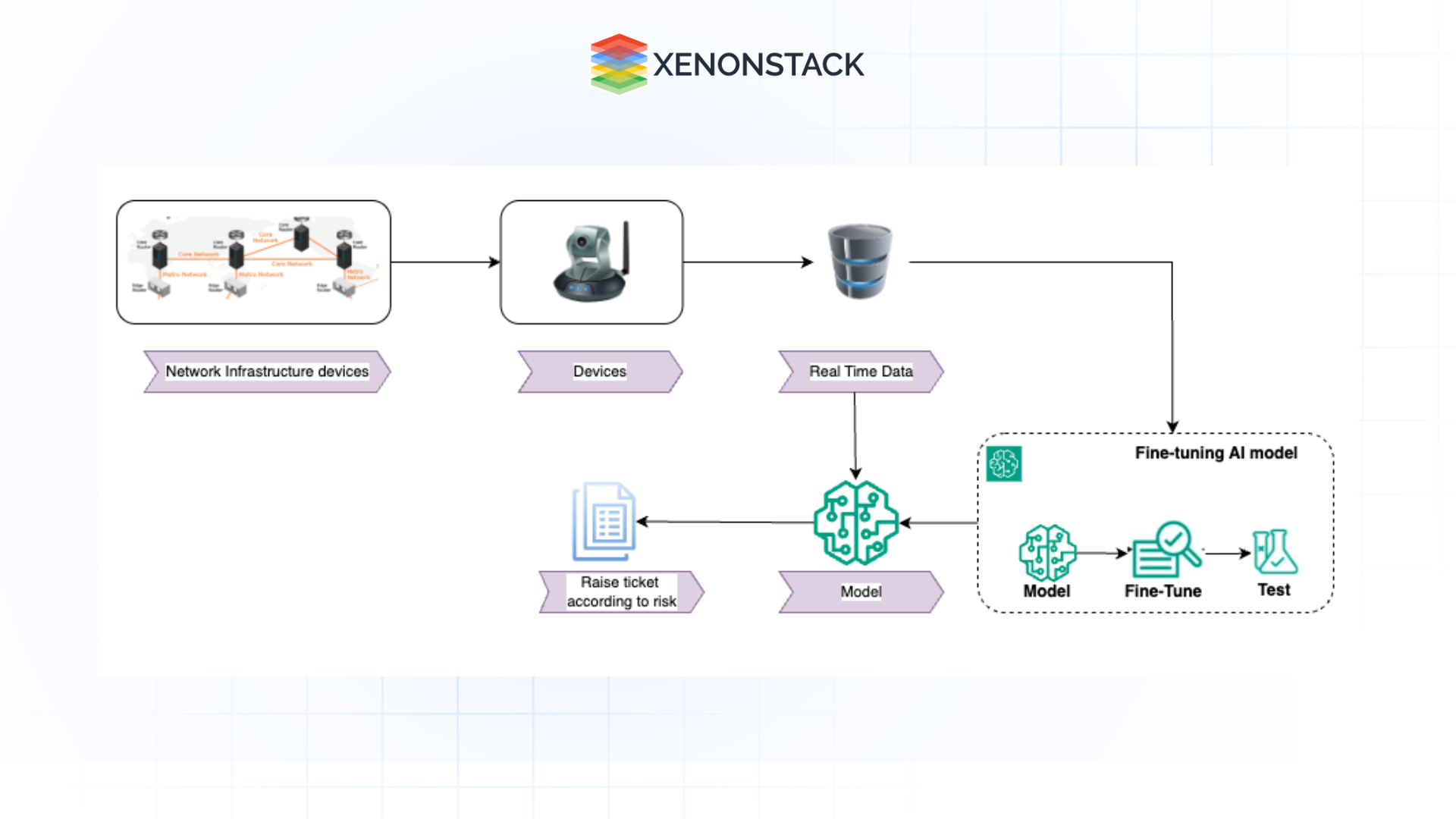
Computer Vision can help automate this process by using cameras and image recognition algorithms to inspect network equipment in real time. These systems can detect anomalies such as:
-
Loose cables: The AI can visually identify improperly connected or disconnected cables, reducing network downtime.
-
Damaged components: Visual inspection can detect physical damage to hardware, such as broken ports, frayed cables, or malfunctioning switches.
-
Overheating devices: Cameras with temperature-sensing capabilities can identify overheated network equipment, triggering automated alerts or cooling systems.
Automated Fault Detection and Diagnosis
When a network failure occurs, time is of the essence. Network administrators need to diagnose and fix the problem to minimize disruptions quickly. Traditionally, identifying the root cause involves extensive manual testing and diagnostics. With Computer Vision, automated systems can rapidly analyze visual data to identify issues like:
-
Network cable faults: Computer Vision algorithms can examine the physical state of network cables and detect faults such as wear, bending, or broken fibres.
-
Hardware failures: Computer Vision can detect error indicators on network devices, like LEDs or screens that display failure codes.
-
Obstructions and hazards: Objects or debris can block airflow or damage network equipment. AI-powered systems can scan for such obstructions, triggering automated alerts for maintenance teams.
Predictive Maintenance
Network infrastructure management is poised to take a predictive maintenance tack, enabling businesses to predict when a piece of equipment will fail before it does. With AI-driven predictive analytics, Computer Vision can be a game changer by continuously analyzing network hardware’s visual data. For example:
-
Wear-and-tear detection: Network devices wear out over time, developing things like rust, corrosion or physical deformation. Instead, Computer Vision can spot these signs early and replace parts preemptively or trigger maintenance.
-
Environmental monitoring: Such visual systems can be powered by AI to monitor environmental conditions like dust accumulation or water exposure and alert (or automatically protect) them if such environmental factors are neglected.
Integrating the information obtained from visual data with predictive models allows network managers to perform maintenance activities ahead of time, thereby improving uptime and prolonging the use of hardware.
Network Security Surveillance
Security is a top priority for any network infrastructure, especially with the increasing frequency of cyber-attacks and physical security breaches. Traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software are essential but are not always sufficient. Computer Vision can be used to monitor physical access to network infrastructure, providing an additional layer of security by:
-
Intruder detection: Using surveillance cameras, computer Vision can identify unauthorized personnel attempting to access secure areas, like data centres or server rooms. AI can recognize faces, detect abnormal movements, or identify individuals not wearing proper access badges.
-
Surveillance of critical equipment: Continuous monitoring can ensure that devices and network components are not tampered with or sabotaged. AI can instantly flag any unusual activity.
Enhanced Network Visibility
Computer vision also adds visibility into the network by making available more complete real-time insights into the physical layout of the infrastructure with which it is used. By mapping out the physical placement of equipment and monitoring their operational status, Computer Vision systems can offer:
-
Interactive visualizations: Interactive maps or diagrams can have real-time visual data on the network manager’s infrastructure to determine its health.
-
Integration with network monitoring tools: They begin with visual data collected via Computer Vision that can be integrated into existing network monitoring platforms to give us a complete picture of network performance.
Key Benefits
-
Reduced Downtime: With real-time visual monitoring and automated issue detection, network managers can respond to problems faster, minimizing downtime and improving overall system reliability.
-
Cost Efficiency: By automating routine inspections and diagnostics, businesses can save on the labour costs associated with manual monitoring. Predictive maintenance also helps reduce the frequency of costly emergency repairs.
-
Improved Accuracy: Computer Vision eliminates the potential for human error in monitoring tasks, ensuring that issues are detected more accurately and consistently.
-
Scalability: As businesses expand, their network infrastructure becomes more complex. Computer Vision can scale easily to monitor larger and more distributed network environments without requiring significant additional resources.
-
Security Enhancements: Besides monitoring network performance, computer vision can play a critical role in physical security by providing surveillance capabilities that deter unauthorized access and infrastructure tampering.
Use Cases of Computer Vision
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of Computer Vision in network infrastructure monitoring is immense, there are certain challenges to consider:
-
Data Privacy and Security: The deployment of cameras and surveillance systems must be carefully managed to avoid privacy breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive visual data.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating Computer Vision systems with existing network monitoring and management tools can be complex and may require customization.
-
Cost of Deployment: Initial setup costs, including camera installation and AI model training, can be significant. However, the long-term savings from improved network uptime and maintenance efficiency can offset these costs.
-
Real-Time Processing: To be effective, Computer Vision systems must process visual data in real-time, which can place demands on computational resources and infrastructure.
Conclusion
Network infrastructure monitoring can be revolutionized using Computer Vision, thus providing an automated, accurate, and proactive method to handle these complex networks. Organizations can reduce downtime, enhance network security, and reduce operations costs through AI-based visual data analysis. Also, regarding network infrastructure, as technology evolves, we can assume that there will be even better and more effective tools for monitoring and maintaining it.
Computer Vision is not just a trend—it’s a future step towards smarter, more efficient, and more resilient networks. By embracing this technology, businesses can ride the crest of the curve and continue to operate smoothly in an increasingly digital world.
Next Steps in Computer Vision
Connect with our experts to explore implementing advanced AI systems and how industries and departments leverage Decision Intelligence to become more decision-centric. Harness the power of AI and computer vision to automate and optimize network infrastructure monitoring, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness.


