Digital transformation has touched virtually every aspect of our lives. We've witnessed books evolve into e-readers, music transition from physical media to streaming services, and photographs move from albums to cloud storage. While these examples represent digitization in its simplest form, Digital Twin Technology takes this concept to an entirely new level.
This article explores the fascinating world of Digital Twin Technology, unpacking how this revolutionary approach creates virtual replicas that do far more than simply exist in digital space—they evolve, predict, and provide unprecedented insights into their physical counterparts.
What is a Digital Twin?
A Digital Twin is a virtual replica of a physical object, system, or process that allows real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization. It leverages IoT sensors, AI, big data, and cloud computing to provide a dynamic digital counterpart.
Why Digital Twins Are More Relevant Today
The adoption of Digital Twin technology has accelerated in recent years due to a combination of global disruptions, technological advancements, and industry-specific challenges. Businesses and governments increasingly leverage Digital Twins to improve decision-making, enhance operational efficiency, and build resilience against uncertainties. Below are the key factors driving this surge in relevance:
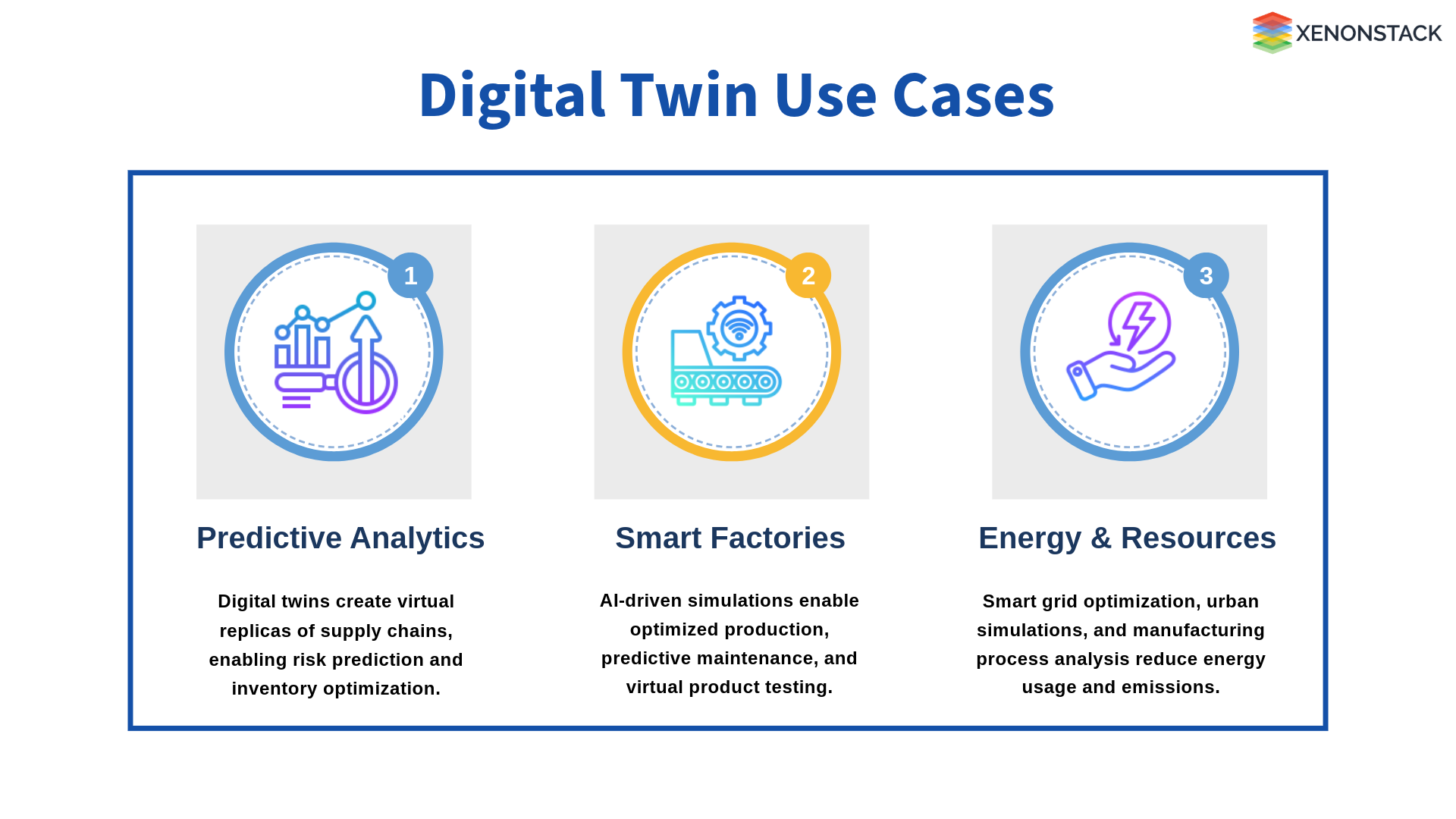
Fig - Use Cases of Digital Twin
Need for Predictive Analytics
The COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical conflicts, and economic fluctuations have severely impacted global supply chains. Businesses face:
-
Supply chain bottlenecks: Delays in raw materials, production, and logistics.
-
Unpredictable demand fluctuations: Consumer behaviour shifts rapidly.
-
High transportation costs & inefficiencies: Rising fuel prices and trade restrictions.
-
Lack of end-to-end visibility: Companies struggle to monitor supply chain risks in real-time.
How Digital Twins Solve This Issue:
End-to-End Supply Chain Visibility
-
Digital Twins create real-time virtual replicas of global supply chains, allowing businesses to simulate scenarios and detect risks before they escalate.
Predictive Analytics for Risk Management
-
By integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Digital Twins analyze historical and real-time data to forecast supply chain disruptions—allowing companies to make data-driven decisions.
Inventory Optimization
-
Digital Twins help businesses balance stock levels, ensuring they avoid overstocking or understocking critical components.
Real-Time Logistics Monitoring
-
Companies use Digital Twins to track shipments, predict delays, and reroute transportation dynamically to reduce downtime.
Smart Factories & AI-Driven Workflows
With the rise of Industry 4.0, companies face pressure to:
-
Increase automation and reduce manual intervention.
-
Improve manufacturing efficiency and reduce costs.
-
Optimize machine performance to prevent unexpected failures.
-
Create smart factories that adapt to changing production demands dynamically.
How Digital Twins Solve This Issue:
Smart Manufacturing & AI-Driven Optimization
-
Digital Twins allow factories to run AI-driven simulations before making real-world changes, reducing downtime and ensuring maximum productivity.
-
AI-based models can predict machine failures and recommend preventive maintenance—avoiding costly breakdowns.
Virtual Prototyping & Product Design Optimization
-
Engineers can test multiple product designs in a Digital Twin environment before manufacturing them, reducing wastage and R&D costs.
AI-Driven Quality Control
-
Digital Twins analyze sensor data from manufacturing lines to detect defects and inconsistencies, ensuring high product quality.
Optimizing Energy & Resources
With increasing concerns over climate change, carbon emissions, and energy consumption, companies and governments must:
-
Reduce carbon footprints and optimize energy usage.
-
Enhance sustainable practices in production and logistics.
-
Implement smart energy management in cities and buildings.
-
Monitor and reduce waste in industrial processes.
How Digital Twins Solve This Issue:
Energy Consumption Optimization in Smart Grids
-
Energy companies use Digital Twins to simulate power grids, optimizing electricity distribution and minimizing energy losses.
-
Predictive analytics can forecast energy demand and dynamically adjust power generation.
Sustainable Urban Development
-
Cities use Digital Twins to simulate traffic patterns, water usage, and air quality to design greener urban spaces.
-
Smart buildings use Digital Twins to reduce heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) costs, cutting energy usage.
Waste & Emission Reduction in Manufacturing
-
Digital Twins analyze manufacturing processes and suggest ways to reduce waste, material consumption, and CO₂ emissions.
Discover how Digital Twin simulations and AI agents are transforming manufacturing by optimizing operations, enhancing predictive maintenance, and improving efficiency.
The Digital Twin Ecosystem
A Digital Twin is not just a static model but a dynamic, data-driven system that continuously evolves alongside its real-world counterpart. To function effectively, a Digital Twin consists of multiple interdependent components that collect, process, analyze, and visualize data in real-time.
 Fig - Digital Twin Ecosystem
Fig - Digital Twin Ecosystem
Physical Asset: The Real-World Object or Process Being Replicated
The foundation of any Digital Twin is the physical entity it represents. This could be:
-
A machine (e.g., an aircraft engine, a wind turbine, a robotic arm).
-
A process (e.g., a production line, a logistics workflow).
-
An environment (e.g., a city, a smart grid, an oil refinery).
The Digital Twin continuously receives real-time updates from its physical counterpart, allowing engineers and decision-makers to monitor and optimize operations remotely.
IoT Sensors & Data Feeds: Capturing Real-Time Data
To replicate a physical entity digitally, real-time data collection is essential. IoT sensors and connected devices gather information on key parameters such as:
-
Temperature, pressure, and humidity (e.g., in manufacturing plants).
-
Speed, vibration, and torque (e.g., in industrial machinery).
-
GPS and location tracking (e.g., in logistics and supply chains).
-
Energy consumption and emissions (e.g., in smart buildings and power plants).
These sensors continuously transmit data to the Digital Twin, ensuring that the virtual model remains accurate and up to date.
Data Integration & Analytics: AI/ML Models for Optimization
Once data is collected, it must be processed and analyzed. AI and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms play a crucial role in:
-
Detecting anomalies and predicting failures before they occur.
-
Identifying optimization opportunities (e.g., reducing energy consumption, improving workflow efficiency).
-
Providing actionable insights to human operators or triggering automated response
Data integration platforms consolidate structured (sensor readings, logs) and unstructured (video, audio) data, enabling holistic decision-making.
Visualization & Simulation Tools: AR/VR, 3D Models, and Dashboards
To interact with a Digital Twin effectively, businesses rely on visualization and simulation tools such as:
-
3D CAD Models → Creating virtual representations of physical assets.
-
Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR) → Enabling immersive real-time interaction.
-
Interactive Dashboards & Control Panels → Providing real-time operational insights.
These tools help engineers, operators, and decision-makers understand complex systems, test scenarios, and make informed decisions without disrupting real-world operations.
Automation & Decision-Making: AI-Driven Recommendations and Action
Digital Twins are not just passive monitoring tools—they enable autonomous decision-making through:
-
AI-driven recommendations → Suggesting actions based on predictive analytics.
-
Automated responses → Adjusting machine parameters in real time.
-
Human-in-the-loop decision-making → Alerting operators for manual interventions when necessary.
By integrating Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI, Digital Twins can optimize operations without human intervention, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
Types of Digital Twins
Digital Twins can be categorized based on the scope and complexity of the system they replicate.
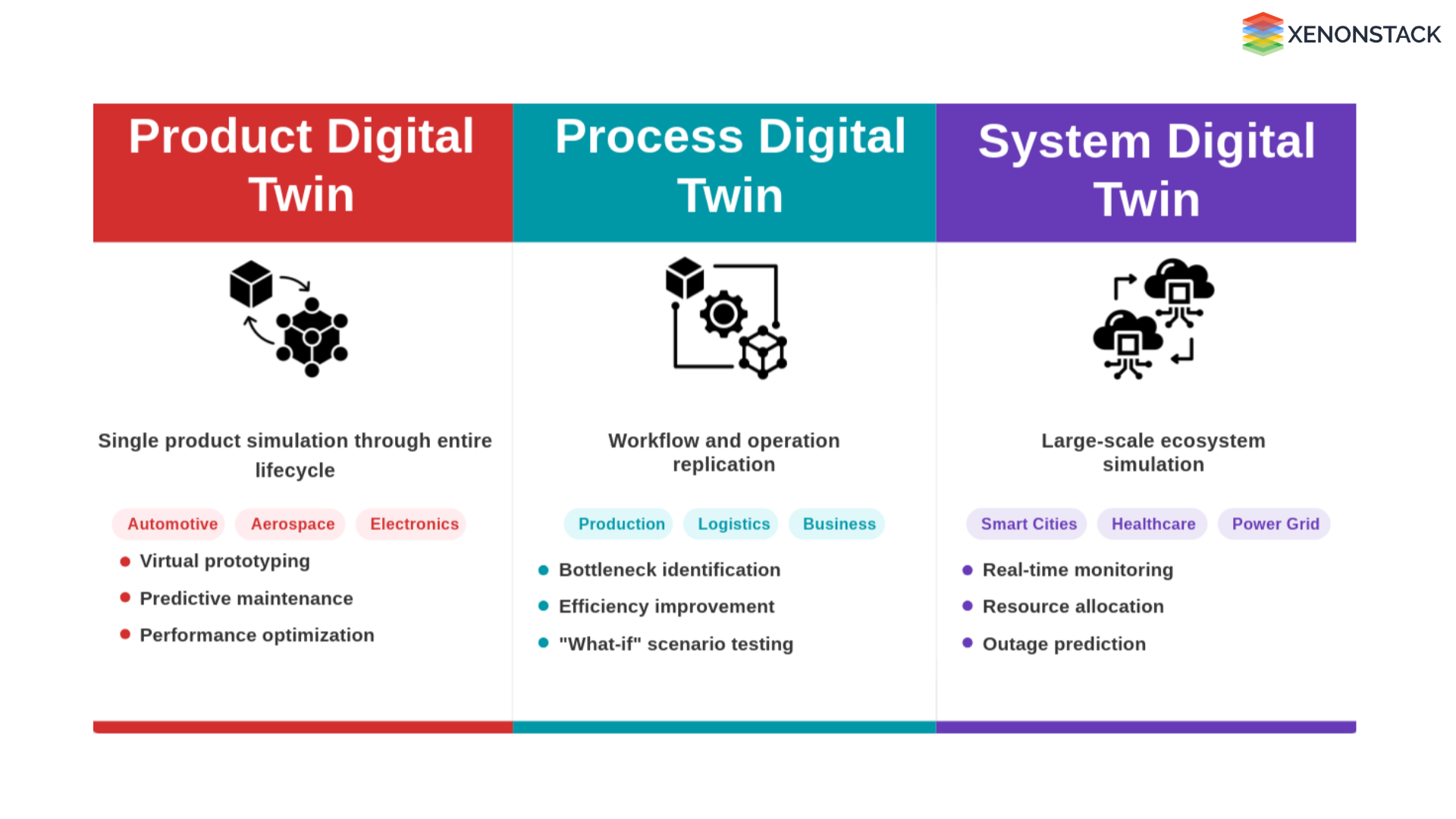
Fig - Digital Twin Types
Product Digital Twin: Tracking Product Design, Testing, and Performance
-
These Digital Twins simulate individual products across their lifecycle, from design to production to usage.
-
Used in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries to optimize product performance.
-
Helps in virtual prototyping before manufacturing, reducing R&D costs.
-
Monitors real-time product performance for predictive maintenance and over-the-air updates.
Process Digital Twin: Modeling Complex Workflows
Instead of a single product, this Digital Twin replicates an entire workflow or operation, helping industries:
-
Simulate and optimize production lines, logistics, and business processes.
-
Improve efficiency by identifying bottlenecks and streamlining operations.
-
Reduce operational risks by testing “what-if” scenarios before implementation.
System Digital Twin: Replicating Interconnected Environments
These Digital Twins simulate large-scale ecosystems involving multiple interconnected components, such as:
-
Smart Cities → Monitoring traffic, pollution, energy grids, and infrastructure in real time.
-
Healthcare Systems → Simulating hospital operations, patient care, and resource allocation
-
Power Grids → Optimizing energy distribution and predicting outages.
The Role of IoT, AI, and Cloud in Digital Twins
IoT Sensors: Capturing Real-Time Performance Data
-
IoT devices continuously collect, transmit, and process real-world data for the Digital Twin.
-
Enables real-time monitoring of equipment, vehicles, and supply chains.
-
Ensures seamless connectivity between the physical and digital worlds.
IoT is the backbone of Digital Twins, enabling real-time data flow between physical assets and their digital replicas.
AI & ML: Predicting Failures and Optimizing Processes
-
AI-driven analytics identify patterns, detect anomalies, and optimize system performance.
-
Machine Learning (ML) models improve over time, enabling better predictions and decision-making.
-
AI helps in self-healing systems, where the Digital Twin can autonomously fix problems.
Cloud & Edge Computing: Ensuring Scalability and Real-Time Processing
-
Cloud computing provides scalable storage and computational power to process vast amounts of IoT data.
-
Edge computing enables real-time decision-making by processing data closer to the source (e.g., within a factory or on a wind turbine).
-
Hybrid models leverage both cloud and edge computing for low-latency, high-efficiency operations.
Core Technology Stack of Digital Twins
.png?width=1920&height=1080&name=Xenon%20Daily%20Work-80%20(1).png)
Fig - Technology Stack of Digital Twins
IoT Sensors & Data Feeds
Types of Sensors:-
RFID & LiDAR: Track location and movement.
-
Smart Meters & Environmental Sensors: Measure energy consumption, temperature, and humidity.
-
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Sensors: Monitor vibrations, pressure, and machine performance.
-
Sensors generate structured data (e.g., temperature, pressure) and unstructured data (e.g., images, audio).
-
Integrated with telemetry systems, enterprise applications, and historical databases.
IoT has a significant impact on the Industrial sector too. Several industries are accepting this change to increase productivity and efficiency. Click to explore about, IoT Data Analytics for Intelligent Maintenance
Data Integration & Analytics
Real-time Data Processing: Using Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, and Spark Streaming.
AI & ML Models:
-
Predictive maintenance using anomaly detection.
-
Optimization models for energy efficiency and workflow automation.
-
Reinforcement learning for decision-making in complex environments.
Visualization & Simulation Tools
Augmented Reality (AR) & Virtual Reality (VR): Helps operators interact with the digital twin in an immersive environment.
3D Modeling & Simulation:
-
Unity & Unreal Engine: Advanced 3D environments.
-
Siemens NX, Ansys, and Dassault Systèmes: Physics-based simulations for engineering applications.
-
Interactive Dashboards: Power BI, Grafana, and Tableau for real-time monitoring.
Automation & Decision-making
AI-Driven Recommendations: Digital twins analyze real-time data and suggest adjustments.
Closed-Loop Automation:
-
AI models trigger automatic responses in industrial systems (e.g., adjusting robotic arm speed in manufacturing).
-
Digital twins integrate with ERP and MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) for process automation.
Challenges and Limitations of Digital Twins
While Digital Twins offer transformative benefits across industries, they also come with significant challenges. These challenges range from technical complexities to financial constraints, security risks, and ethical concerns. Below is an in-depth analysis of these limitations and their possible solutions.
Data Integration & Interoperability Issues
Challenge:
-
Digital Twins rely on multiple data sources such as IoT sensors, enterprise applications (ERP, MES, SCADA), and cloud platforms. These data sources often use different formats, protocols, and standards, making integration complex.
-
Legacy systems may lack APIs or use proprietary communication protocols that are incompatible with modern cloud-based architectures.
-
Interoperability issues arise when different vendors provide incompatible Digital Twin solutions, preventing seamless data exchange.
Solution:
Adopting Open Standards
-
Implementing OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) ensures a standardized way to exchange industrial data.
-
ISO/IEC 30173 defines best practices for Digital Twin interoperability.
-
FIWARE & Digital Twin Consortium promote open-source frameworks for Digital Twin standardization.
Middleware Solutions
-
Middleware like Apache Kafka or Mulesoft can bridge the gap between incompatible systems by acting as a universal data translator.
APIs & Data Lakes
-
Creating standardized APIs enables seamless data exchange between Digital Twins and third-party applications.
-
Data lakes (AWS S3, Azure Data Lake, Google BigQuery) can store raw, structured, and unstructured data for centralized processing.
Scalability & Real-Time Processing
Challenge:
-
High Computational Costs: Running AI models for predictive maintenance and real-time simulations requires massive computing power.
-
Latency Issues: Large-scale Digital Twins generate petabytes of data daily, making real-time analysis challenging.
-
Bandwidth Constraints: Transmitting raw sensor data to the cloud in real time can overload networks, leading to delays.
Solution:
Edge Computing for Localized Processing
-
Processing data closer to the source reduces latency and network congestion.
-
NVIDIA Jetson, Intel OpenVINO, and Google Coral enable AI inferencing on edge devices.
Cloud-Native Architectures
-
Serverless computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) allows on-demand scalability.
-
Containerized Digital Twins using Kubernetes ensure flexible deployment across cloud and edge environments.
Data Compression & Filtering
-
AI-powered data filtering can pre-process raw data at the edge, only sending relevant insights to the cloud.
5G & LPWAN Connectivity
-
5G networks provide ultra-fast, low-latency data transmission for real-time analytics.
-
LPWAN (LoRaWAN, NB-IoT) ensures long-range, low-power connectivity for industrial IoT sensors.
High Initial Investment & ROI Concerns
Challenge:
-
Implementing Digital Twins requires significant upfront investment in IoT sensors, cloud infrastructure, AI models, and simulation tools.
-
ROI (Return on Investment) is difficult to quantify because Digital Twins generate long-term benefits rather than immediate cost savings.
-
SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) may find full-scale adoption financially unfeasible.
Solution:
Modular Digital Twin Adoption
-
Instead of building a full-scale Digital Twin, businesses can start with a basic model (e.g., for predictive maintenance) and gradually expand.
Cloud-Based Digital Twin Services
-
Leveraging subscription-based Digital Twin platforms (Azure Digital Twins, AWS IoT TwinMaker) can reduce capital expenditure (CAPEX).
Government & Industry Grants
-
Many governments provide funding incentives for Digital Twin adoption, particularly in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities.
Proof of Concept (PoC) Before Full-Scale Deployment
-
A small-scale pilot project can help businesses estimate ROI before committing to large investments.
Ethical & Privacy Concerns
Challenge:
-
Human Digital Twins (HDTs) used in healthcare, sports science, and workforce simulations raise ethical and privacy concerns.
-
Unauthorized access to biometric, medical, and behavioral data could lead to data breaches or identity theft.
-
AI-driven Digital Twins could make biased decisions (e.g., in predictive hiring or medical diagnostics).
Solution:
Compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and Other Regulations
-
Ensuring data anonymization and encryption to comply with:
-
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation - EU)
-
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act - US)
-
ISO/IEC 27001 (International Standard for Information Security Management)
Ethical AI Governance
-
Implementing bias-detection algorithms ensures Digital Twins make fair and transparent decisions.
-
Explainable AI (XAI) models help users understand how Digital Twins arrive at conclusions.
Zero Trust Security Model
-
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures only authorized users can interact with sensitive Digital Twin data.
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security.
Blockchain for Secure Digital Twins
-
Decentralized identity verification prevents unauthorized data access.
-
Smart contracts can automate data-sharing agreements between Digital Twin stakeholders.
Next Steps for Implementing Digital Twin Technology
Talk to our experts about implementing Digital Twin technology and discover how industries and various departments leverage virtual replicas to enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Digital Twins integrate AI, real-time data, and predictive analytics to optimize IT support, streamline workflows, and improve responsiveness, driving smarter and more proactive business strategies.