In the ever-changing landscape of today's business environment, where customer expectations are continuously evolving, the role of efficient and personalized customer relationship management (CRM) cannot be overstated. Microsoft Dynamics Co-pilot stands out as a transformative tool that leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to redefine how sales, customer service, and marketing teams engage with customers and manage interactions. This blog provides an in-depth exploration of Co-pilot's capabilities, highlighting its impact, the challenges it addresses, key concepts, and more.
Microsoft Dynamics Co-pilot represents a paradigm shift in CRM technology, integrating AI capabilities directly into the Dynamics 365 ecosystem. Co-pilot serves as an intelligent assistant that augments the capabilities of sales, customer service, and marketing professionals by automating routine tasks, providing data-driven insights, and facilitating personalized interactions.
Introduction to Microsoft Dynamics Copilot
Microsoft Dynamics Co-pilot integrates AI seamlessly into the Dynamics suite, offering intelligent assistance across sales, customer service, and marketing functions. It enables professionals to automate mundane tasks, enhance customer interactions with personalized insights, and streamline operational workflows. Co-pilot represents a leap forward in leveraging AI to drive efficiency and effectiveness in managing customer relationships.
Challenges Addressed by Copilot
In today's competitive environment, organizations face several challenges that hinder productivity and customer satisfaction. These challenges include:
-
Time-consuming Administrative Tasks: Sales professionals often spend significant time on administrative duties such as drafting emails and summarizing meetings, diverting focus from core activities like client engagement and closing deals.
-
Customer Service Efficiency: Customer service agents juggle between multiple queries, often needing to provide quick and accurate responses tailored to individual customers' needs. This requires access to extensive knowledge bases and historical data, which can be overwhelming to navigate in real-time.
-
Personalized Marketing: Marketers strive to deliver targeted campaigns that resonate with specific customer segments. This demands deep insights into customer behavior and preferences, which can be challenging to gather and analyze comprehensively.
Microsoft Dynamics Co-pilot addresses these challenges by automating routine tasks, providing contextual insights, and facilitating personalized interactions across the entire customer journey.
Importance of Microsoft Dynamics Copilot
The importance of Co-pilot is to enhance both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction simultaneously:
-
Enhanced Productivity: Automating repetitive tasks such as email drafting and meeting summaries, Co-pilot frees up valuable time for sales professionals to focus on strategic activities that drive revenue.
-
Improved Customer Service: Co-pilot empowers customer service agents with AI-generated responses that are contextually relevant and timely, thereby improving service delivery and customer satisfaction.
-
Personalized Marketing Campaigns: Marketers leverage Co-pilot to analyze customer data and preferences, enabling them to create highly targeted campaigns that resonate with specific audience segments.
By harnessing AI capabilities, co-pilot not only optimizes operational workflows but also enables organizations to deliver exceptional customer experiences, fostering long-term loyalty and business growth.
Key Concepts and Features of Copilot
Microsoft Dynamics Co-pilot encompasses several key features and functionalities tailored to different business needs:
1. Sales and Viva Sales:
-
Automated Email Responses: Co-pilot utilizes AI to draft personalized email responses, enabling sales professionals to engage with prospects more effectively.
-
Meeting Summaries: It generates concise summaries of team meetings, helping sales teams capture key action points and insights without manual effort.
2. Customer Service:
-
Contextual Answers: Co-pilot assists customer service agents by suggesting contextual answers to customer queries, drawing insights from knowledge bases and case histories.
-
Interactive Chat Support: It enhances customer service interactions by providing real-time support and information retrieval through interactive chat capabilities.
3. Customer Insights:
-
Personalized Segmentation: Marketers use Co-pilot to segment customer data effectively, enabling them to create personalized marketing strategies based on individual preferences and behaviors.
-
Natural Language Dialogue: Co-pilot facilitates natural language interactions with customer data platforms, allowing marketers to derive actionable insights and make informed decisions.
4. Marketing:
-
Segment Description: Co-pilot assists marketers in defining customer segments using natural language queries, simplifying the process of targeting specific audience groups.
-
Campaign Content Generation: It provides inspiration and suggestions for fresh campaign content based on identified topics and trends, enhancing the creativity and effectiveness of marketing initiatives.
Architecture of Copilot 365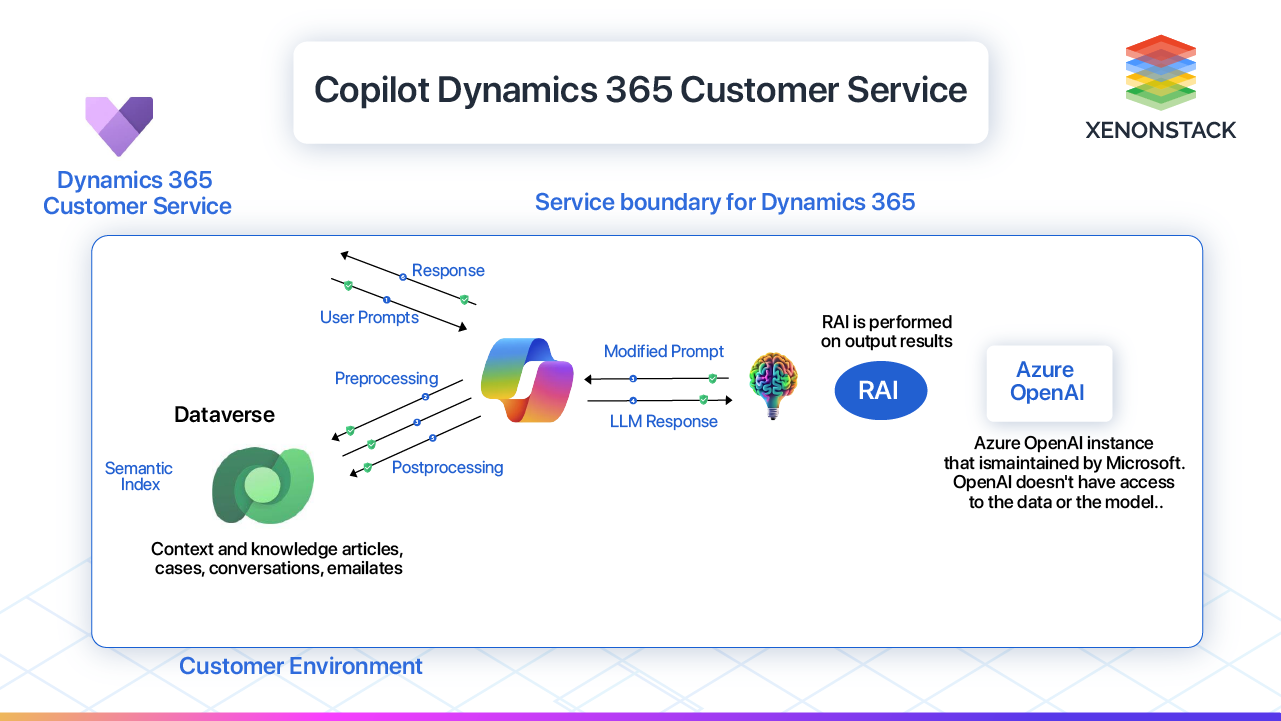
1. User Prompt Submission
The interaction begins when a user within Dynamics 365 Customer Service submits a prompt to Co-pilot. This prompt typically consists of a query or request for information related to customer support, service inquiries, or troubleshooting.
2. Preprocessing: Accessing Dataverse and Semantic Index
Upon receiving the user prompt, Co-pilot initiates a preprocessing phase. It accesses two key components: the Dataverse and Semantic Index.
-
Dataverse: This is the foundational data repository within Dynamics 365, containing structured data related to customer profiles, service histories, case details, and more. Co-pilot leverages this data to contextualize the user's query within the specific customer service context.
-
Semantic Index: The Semantic Index complements the Dataverse by providing a semantic understanding of the user prompt. It helps Co-pilot identify relevant keywords, intents, and context that inform the subsequent interaction with the Large Language Model (LLM).
3. Sending Data to Large Language Model (LLM)
Armed with the user prompt, meta prompt (additional contextual information), and relevant data from Dataverse and Semantic Index, Co-pilot transmits this enriched dataset to a Large Language Model (LLM). The LLM serves as the core AI engine responsible for generating a response based on the input it receives.
4. Receiving LLM Response
The LLM processes the input from Co-pilot, employing natural language processing (NLP) techniques to generate a coherent and contextually appropriate response. This response is tailored to address the user's query or fulfill their request effectively.
5. Post-processing: Accessing Dataverse and Semantic Index Again
Upon receiving the response from the LLM, Co-pilot engages in post-processing activities. It revisits the Dataverse and Semantic Index to refine and enhance the generated response:
-
Data Validation: Co-pilot verifies the accuracy and relevance of the LLM-generated response against the latest data in the Dataverse. This ensures that the information provided aligns with current customer profiles and service contexts.
-
Semantic Enrichment: By leveraging the Semantic Index again, Co-pilot enriches the response with additional contextual insights and refinements. This step enhances the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the information conveyed to the user.
6. Sending the Final Response
Once the post-processing phase is complete, Co-pilot sends the finalized response back to the user within Dynamics 365 Customer Service. This response is presented in a format that is easy to understand and actionable, thereby facilitating efficient resolution of customer inquiries or issues.
Implementing Microsoft Dynamics Copilot
1. Assessment and Planning
-
Evaluate Current Processes: Begin by assessing existing workflows and identifying areas where automation and AI-driven insights could streamline operations and enhance productivity.
-
Identify Use Cases: Determine specific use cases for Co-pilot across sales, customer service, and marketing teams. For instance, automating email responses, improving customer service response times, or optimizing marketing campaign targeting.
2. Integration and Deployment
-
Integration with Dynamics 365: Ensure seamless integration of Co-pilot with your existing Dynamics 365 environment, including Dataverse and other relevant modules such as Customer Insights.
-
Customization and Configuration: Customize Co-pilot to align with your organization’s unique processes and requirements. Configure AI models and workflows to maximize efficiency and accuracy.
3. Training and Adoption
-
User Training: Provide comprehensive training sessions for employees across departments to familiarize them with Co-pilot’s capabilities and functionalities.
-
Change Management: Implement effective change management strategies that promote adoption and mitigate resistance to AI-driven technologies.
4. Monitoring and Optimization
-
Performance Monitoring: Continuously monitor the Co-pilot’s performance metrics, such as response times, accuracy of recommendations, and user feedback.
-
Optimization Strategies: Regularly optimize AI models and workflows based on real-time data insights and user feedback to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
Potential Effects on Your Organization
1. Enhanced Productivity
-
Automated Task Execution: By automating routine administrative tasks such as data entry, email drafting, and meeting summaries, Co-pilot frees up employees’ time to focus on high-value activities
2. Improved Customer Experience
-
Personalized Interactions: Co-pilot leverages AI to provide personalized responses and recommendations based on historical customer data and preferences. This enhances customer satisfaction by delivering timely and relevant solutions to queries and issues.
-
Faster Response Times: Customer service teams can respond to inquiries more quickly and accurately, leading to improved service levels and reduced resolution times.
3. Data-Driven Insights
-
Predictive Analytics: Co-pilot employs machine learning algorithms to analyze extensive customer data, offering predictive insights. This enables proactive decision-making, such as anticipating customer needs and identifying potential sales opportunities.
4. Strategic Decision Support
-
Business Intelligence: Co-pilot generates actionable insights and recommendations that support strategic decision-making processes. For example, it can suggest optimal marketing strategies based on customer behavior patterns or recommend personalized upsell opportunities.
5. Competitive Advantage
-
Innovation and Agility: By leveraging AI-driven technologies like Co-pilot, organizations can innovate faster, adapt to market changes more effectively, and maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
6. Cost Efficiency
-
Operational Efficiency: Automating repetitive tasks and optimizing workflows with Co-pilot can lead to cost savings through reduced manual labor and improved resource allocation.
Conclusion
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Co-pilot represents a paradigm shift in how businesses leverage AI to streamline operations and enhance customer engagement. By automating tasks, providing personalized insights, and facilitating intelligent interactions, Co-pilot empowers organizations to achieve greater efficiency, drive innovation, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Embrace the transformative potential of Co-pilot within your Dynamics 365 environment to stay ahead in today's dynamic marketplace. As AI continues to evolve, Co-pilot will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of CRM, enabling organizations to unlock new opportunities and achieve sustainable growth.
Explore the possibilities with Microsoft Dynamics 365 Co-pilot and embark on a journey towards enhanced productivity, personalized customer interactions, and lasting success in your business endeavors. Stay connected for more insights and updates on how Co-pilot is redefining the future of CRM and business operations globally.
-
Read more about Generative AI for Infrastructure Management
-
Know more about Generative Adversarial Network Architecture
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


