Introduction to Quality Assurance and Quality Control
In this blog, we cover all aspects of Quality Assurance and Quality control. The focus is on what one looks for while purchasing any product. If the quality of the product is useful, then the outcome will also be reflected via quality only. In a software field, when a user refers to the product's quality, the user means it to fulfil the requirement earlier given by the user.
The developer team gives confidence that the user will be satisfied with the product delivered, as it is according to his requirements. Trust helps in feedback and end-user testing. In this blog, we focus mainly on software quality assurance and software quality control.
A successful business that develops software, software quality must be the requirement- cannot be an exception. Click to explore about our, Software Quality Management Techniques
What is Software Quality Assurance (SQA)?
Testing is a phase in which a set of activities are performed and ensures the ultimate quality during the software engineering process, which provides self-assurance and sureness to the user as well. Its primary focus is on fulfilling the user’s requirements. The main focus within the Management Review is on processing the software rather than the work products.
It provides various umbrella activities, and several tasks are included in them as well. Also, the function of a test manager is to check whether he is doing the work correctly or not. Audit regularly checks whether the product works according to the information to evaluate whether the customary process can be followed.
Need for Software Quality Assurance in Test Management Process
Let’s go through the various phases: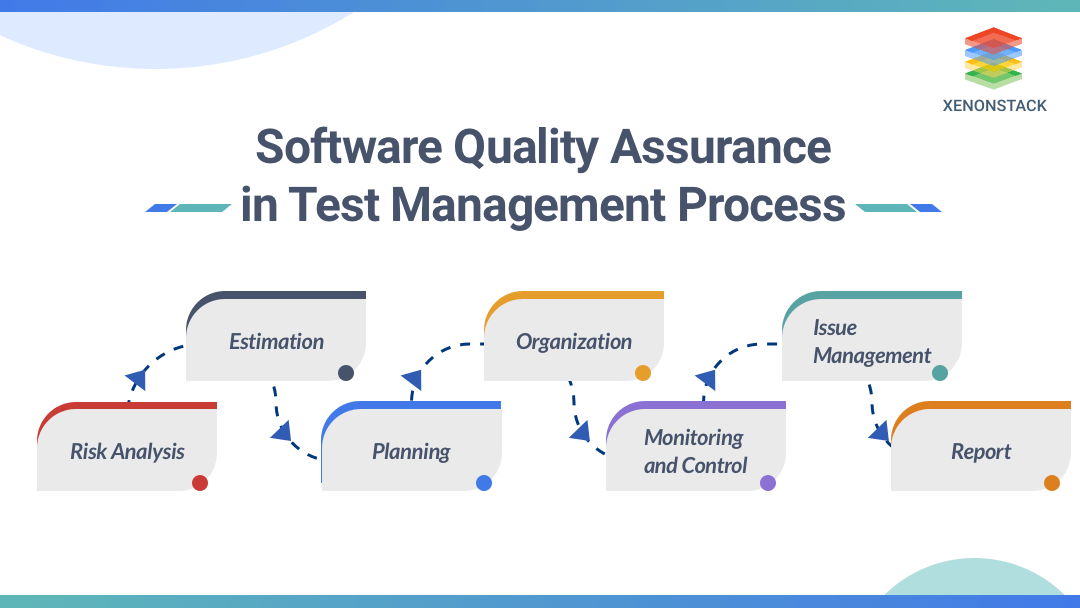 Well, here, two persons perform their tasks: one, a Test Manager, and the other, an SQA Auditor. The test manager takes charge of such jobs, and the SQA auditor reviews and keeps track of the project with the help of the review reports. With the help of the review reports, the Management Board evaluates the project’s handling quality. Because of this, there is only a need for a management board or SQA.
Well, here, two persons perform their tasks: one, a Test Manager, and the other, an SQA Auditor. The test manager takes charge of such jobs, and the SQA auditor reviews and keeps track of the project with the help of the review reports. With the help of the review reports, the Management Board evaluates the project’s handling quality. Because of this, there is only a need for a management board or SQA.
Implementation of Software Quality Assurance
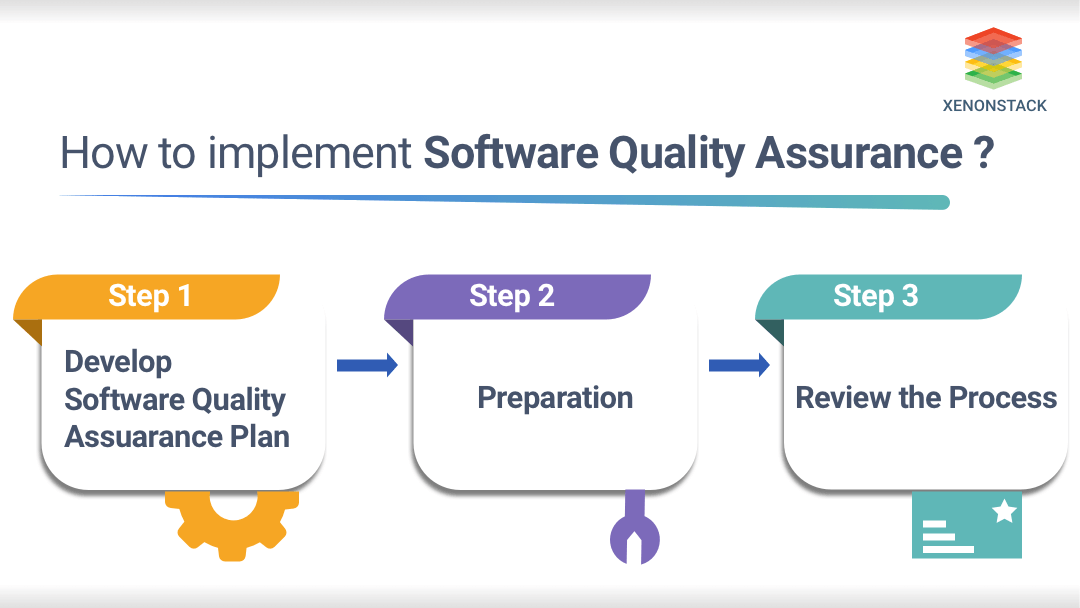
- Develop the Software Quality Assurance (SQA) Plan: Testing activities are planned just as SQA planning is complete. The main motive of the SQA plan is to create a planning procedure that considers exceptional services and quality. A test Manager creates an SQA plan, and SQA auditing is programmed sporadically. Various tasks are carried under it:
- Define the standards/methodology: The following steps are being implemented under this phase
- To review the process: In this phase, the main motive is to examine the activities of the particular project to verify the passivity as per the explanation given by the management process. In this SQA, members perform 5 SQA reviews as follows:
In each SQA phase, the SQA members follow all the organisational protocols and policies by providing consultancy and regular project reviews. After all three aspects of assurance, the result is the Tey Management Review and Audit, which provides a guarantee to the investors about the management quality.
Machine learning targets on the advancement of computer models that can admission datasets and use it train for themselves. Click to explore about our, ML Model Testing Training and Tools
What is Software Quality Control (SQC)?
Various organisations use various procedures and protocols to ensure that software products will meet all their requirements according to the values and goals of the customer. It specifies multiple non-functional and functional requirements. In this, only the reviewing and testing phases occur, just as in the Software Development Life Cycle, and the goal is to meet all the needs according to the specifications given during the requirement phase.
Activities in Software Quality Control
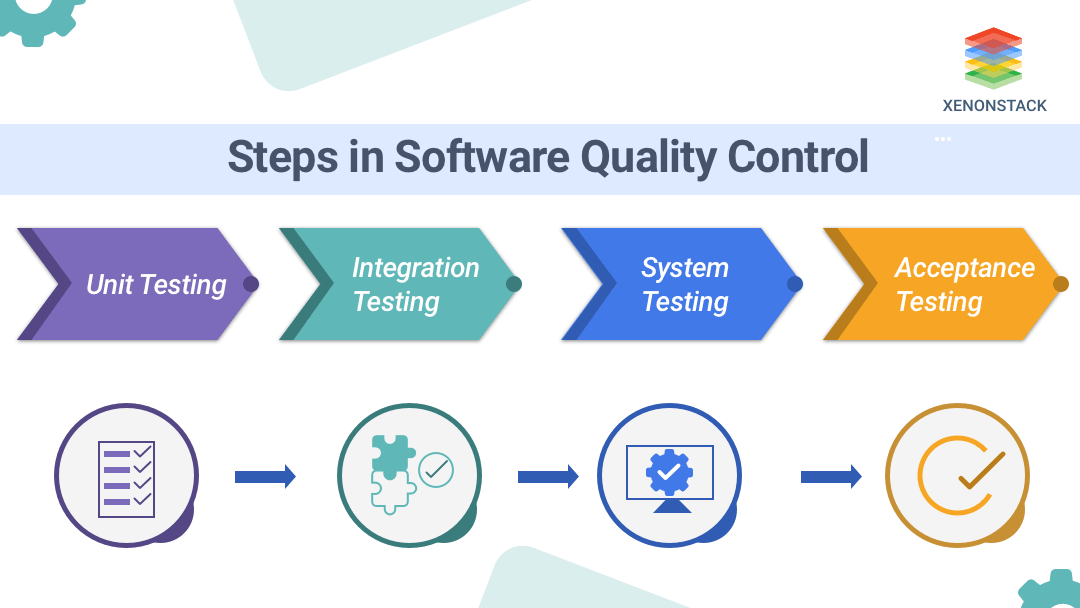 Various activities include this:
Various activities include this:
-
Reviews: In this phase, one goes through multiple reports:
-
Requirement review: All the requirements are reviewed to check whether all the elements are satisfied.
-
Design Review: In this, analyse the building phase of the software.
-
Code Review: Every code is reviewed and tested by using all the testing techniques.
-
Deployment Plan Review: The plan for the deployment is being reviewed.
-
Test plan Review: Before testing, create plans to test every field by performing various tests.
-
Test cases Review: Before performing testing, create multiple test cases that are reviewed by creating the most suitable ones.
-
Testing: Once the software product goes through all the phases before this one, it derives through all the aspects of testing. Here are various testing techniques under the testing phase:
Unit Testing
The first testing stage involves individually testing all the components. Usually, it provides one output on a single or few inputs. In Object-Oriented Programming, the smallest unit to test is a method that belongs to any of the base class, derived class, or abstract class. This testing is usually performed by developers' peers or the developers themselves. Various independent software testers may also perform this testing.
In this, first, a unit test is planned, then test cases are prepared, and finally, the phase of the unit test comes. The main advantage of unit testing is that it increases the maintenance of code and makes it independent code testing. In this, one needs to insulate the development environment from the testing environment.
Integration Testing
All the individual units are combined and tested within a group. The main motive of this testing is to check interaction within the module and with other modules. In component integration testing, complete testing to remove all the defects within the interfaces and further interaction between the integrated modules.
Then comes the system integration testing, complete testing to check the system integration and packages. Like unit testing, testing is being done by developers or by independent testers. Use various approaches such as top-down, bottom-up, big-bang, and sandwich/hybrid approaches. The main motive of this testing is to ensure that one has a proper detailed design document that lets us know about each interaction between modules.
System Testing
A phase at which complete integrated software is tested. The main motive of this testing is to check the entire system after each module is evaluated with each other. In this integration, testing is verified to ensure all requirements are met. Usually, a black box testing technique is performed in this phase. Various tasks are performed under it, such as a system test plan, system test cases, and system tests. Unlike other testing, it is performed by independent testers.
Acceptance Testing
Finally, the phases from developing to the testing mode come where the acceptance is being tested, which is called acceptance testing. In this, user requirements and business processes are conducted to check the user's satisfaction, as well as the authorised unit. As an example, this test is done until the pen's ballpoint, and none of the sections are left untested.
Because it is end-user testing, black box testing is being done as a user may not know all the components. It can be driven by testers, users, or employees who are not from the same organisation. For the above reasons, customer or user acceptance testing is part of it. Mostly, it is being thought that SQC is all about testing, but it is a base for QC (quick check) as well. SQC has been used many times by software quality assurance companies.
The most potent and environment-friendly software testing technique that ensures that developed software is filling all requirements to flow into the market. Click to explore about our, User Acceptance Testing Types and Best Practices
What is the difference between Software Quality Assurance and Software Quality Control
| Sl. No. | Software Quality Assurance | Software Quality Control |
| 1 | It assures that no compromise will be made with the quality. | It focuses on giving quality requests to the end-user |
| 2 | It manages quality. | It verifies the quality. |
| 3 | In this, the program is not executed. | The execution of the program is included in this. |
| 4 | It acts as a decision-making tool. | It acts as a remedial tool. |
| 5 | Its main aim is to prevent defects. | Its main aim is to identify and remove the defects. |
| 6 | It is a process-oriented and preventive technique. | It is a product-oriented and corrective technique. |
| 7 | The primary responsibility of this technique is the full software development life cycle. | Its responsibility is the software testing life cycle |
| 8 | It is a verification technique. | It is a validation technique. |
| 9 | It is a technique for creating or controlling the product’s issues. | It is a technique responsible for reactive dealings. |
Quality Assurance and Quality control are different, but both are part of the quality management process. They should not be used interchangeably or misunderstood. This blog aims to point out all the differences to avoid any confusion. Quality assurance is a process-focused, preventive technique, while Quality Control is a product-focused, corrective technique.
Next Steps with Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
Talk to our experts about implementing compound AI system, How Industries and different departments use Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence to Become Decision Centric. Utilizes AI to automate and optimize IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness.