In the ever-dynamic field of manufacturing, robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) are leading the way to a new way of mass customization. This paradigm shift allows manufacturers to offer customized products within mass production without incurring high costs. Glossing over the interaction of Robotics and AI, this blog analyses how integrating the two is changing the face of mass customization in manufacturing through smart automation, intelligent decision-making, and the application of adaptive systems.
Introduction to Mass Customization
Mass customization refers to the operations of making products or providing services that engage customization and customization of mass production. It is somewhere between arts and crafts and industrial production using modularity, adaptable systems, and big data. Consumers increasingly expect specific, better-quality goods to be available at shorter turnaround times.
Key Drivers of Mass Customization

Consumer Demand
The growth of customer needs for more individualized products.
Technological Advancements
It manufactures technologies and advances in system automation.

Competitive Advantage
Customization as a means of differentiation.

Data Availability
Improved data gathering and data analysis capacities.
The Role of Robotics in Mass Customization
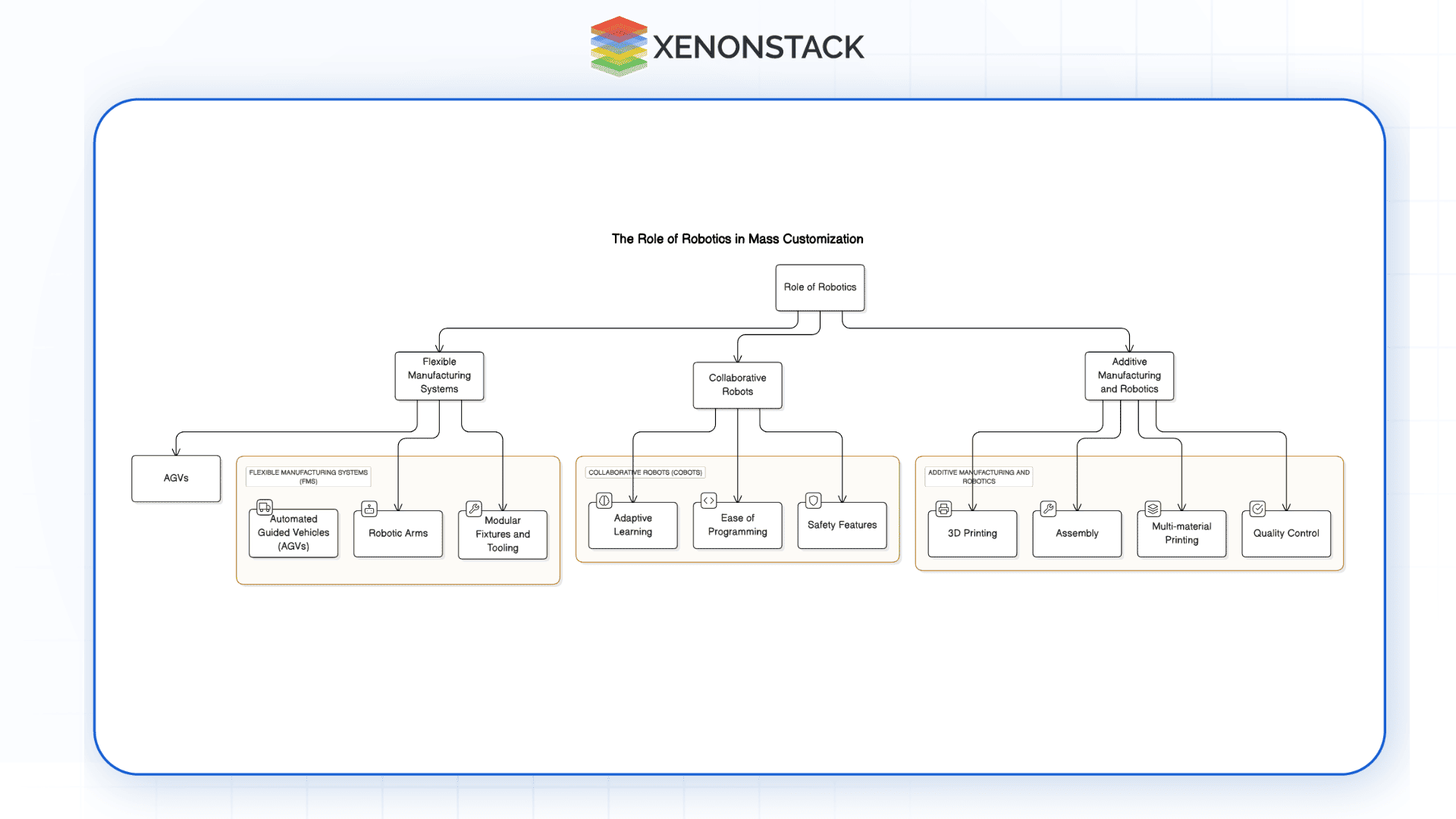 Fig 1.0: Role of Robotics in Mass Customisation
Fig 1.0: Role of Robotics in Mass Customisation Robotics plays a pivotal role in achieving the flexibility and precision required for mass customization. Advanced robotic systems offer adaptability, scalability, and consistency, enabling manufacturers to handle diverse product specifications without significant reconfiguration.
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)
A Flex Manufacturing System is a manufacturing system through which a robotic manufacturing system is implemented together with computer numerical control to implement changes in the manufacturing line. Key components include:
-
Robotic Arms: They can move and manipulate in a multiple axes pattern and for different operations.
-
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Promote the movement of material and goods around the manufacturing plant.
-
Modular Fixtures and Tooling: Allow for change in setups as products change to capture other aspects that may be required in the product.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots can be integrated with human workers, making production more efficient and safe. Their features include:
-
Adaptive Learning: Use sensors and visioning to work in changing environments.
-
Ease of Programming: Simplified interfaces allow for quick reprogramming for different tasks.
-
Safety Features: Innocuous interaction with human workers is kept safe by the existence of sensor and compliance components.
Additive Manufacturing and Robotics
Additive manufacturing, specifically 3D printing, can now accompany a robot to build complex, unique parts. Robot arms can manage multi-material printing, quality control, and assembly processes, diversifying potential individualistic production. Manufacturing Process Automation.
Artificial Intelligence in Mass Customization
AI improves robotic systems and procedures by introducing intelligent decision-making processes, accurately predicting equipment failure, and improving production process sequences. Artificial intelligence efforts actively work to understand large data sets to enhance suitability, productivity, and performance in manufacturing processes.
-
Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Depending on the data received from multiple sources, such as IoT Sensors, ML models predict equipment failures, scheduled maintenance, and control downtime. Predictive analytics makes it possible to keep manufacturing systems running while catering to customization needs.
-
Computer Vision and Quality Control
Computer vision systems driven by Artificial Intelligence inspect products in real time to conform to individual specifications. These systems identify defects, check dimensions, and confirm material characteristics and the sort to ensure that future production runs of small items are not compromised.
-
Generative Design and AI Optimization
On the other hand, generative design algorithms develop an optimized product design given some parameters and basic guidelines. This way, flexible customer-specific buildings can be made, and the architectural, functionality, form, and esthetics can improve distinctly.
-
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
AI enhances supply chain management in the following ways: demand forecasting of the rather complex customised products, inventory management and logistics. Computer programs guarantee the delivery of the correct materials at the right time, shortening the time taken and enhancing the manufacturing of custom goods.
AI Integration of Robotics and AI in Mass Customization
To achieve the mass customization goal, prime importance is devoted to the combined application of robotics and AI. Integrated systems intelligently use both technologies to design responsive manufacturing plants.
Case Studies: Robotics and AI in Action
Example 1: Automotive Industry
Car makers use artificial intelligence to assemble individual cars from robots. Industrial robots with vision technology mount tailored parts and paint application systems that guarantee every car leaves the production line with unique customer requirements.
Example 2: Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics industry, AI Robots manufacture fixed products and install specific arrangements according to the required models. When an assembly sequence is optimized using machine learning algorithms, manufacturing time and production quality are cut short.
Example 3: Apparel Manufacturing
Fashion companies use AI and robotics to create customized garments. AI-developed smart cutting systems produce patterns from measurements specific to each fabric needed, and smart sewing systems program robots to stitch garments properly and uniformly.
Challenges and Solutions
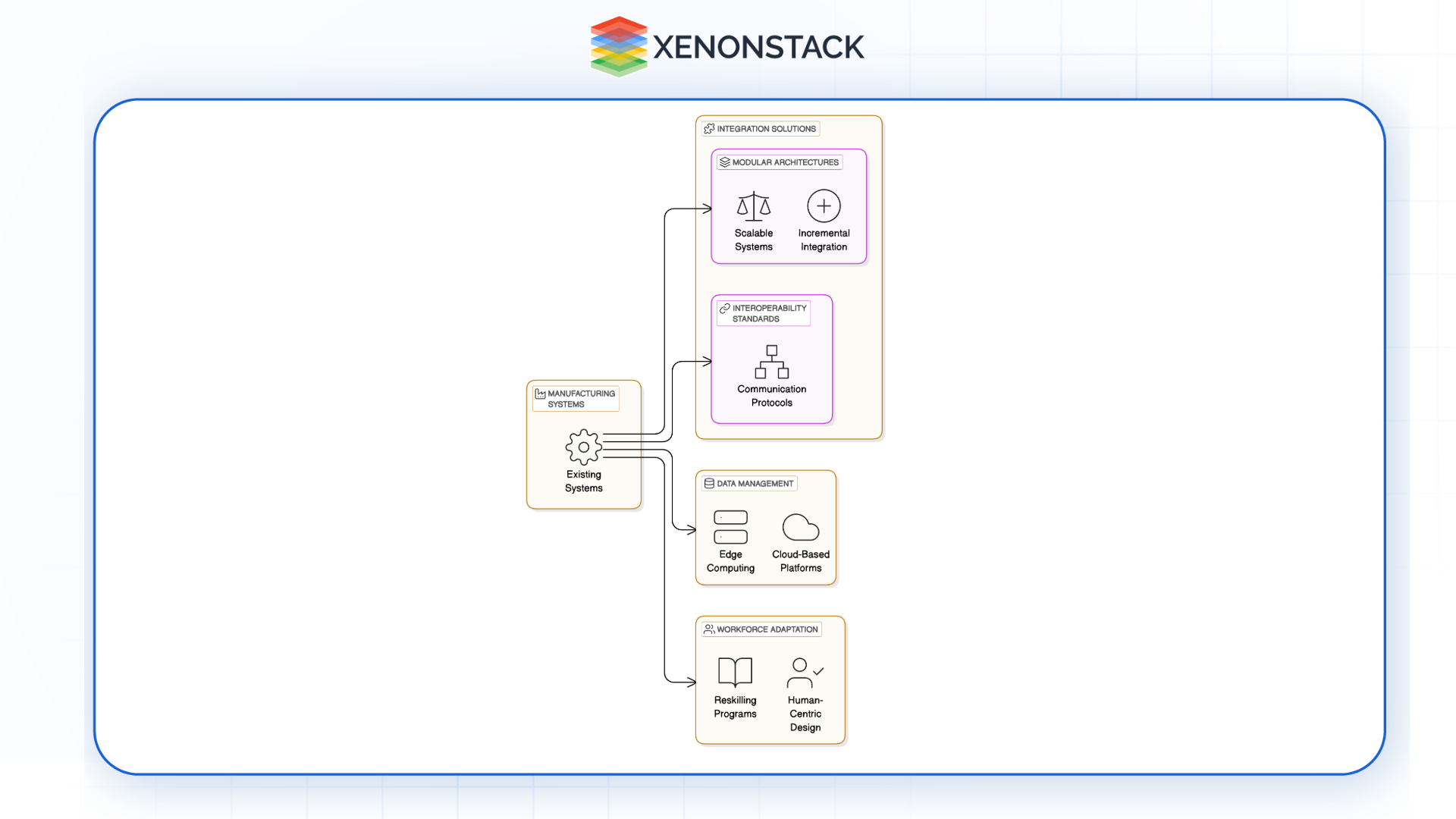 Fig 3.0: Challenges and Solutions
Fig 3.0: Challenges and Solutions Complexity of Integration
Integrating robotics and AI into existing manufacturing systems can be complex. Solutions include:
-
Modular Architectures: Implementing scalable, modular systems that allow incremental integration.
-
Interoperability Standards: Adopting common communication protocols to facilitate seamless data exchange.
Data Management
Handling vast amounts of data generated by AI and robotic systems requires robust data management strategies:
-
Edge Computing: Processing data locally to reduce latency and bandwidth usage.
-
Cloud-Based Platforms: Leveraging cloud infrastructure for scalable storage and advanced analytics.
Workforce Adaptation
The shift towards robotics and AI necessitates workforce training and adaptation:
-
Reskilling Programs: Providing training for employees to operate and maintain advanced systems.
-
Human-Centric Design: Designing systems that complement human skills and enhance collaboration.
Future Directions
-
Autonomous Manufacturing Systems
AI and Robotics integration will result in smart manufacturing systems with autonomous optimization and repair, improving mass customization.
-
Enhanced Personalization through AI
AI will help manufacturers better understand and address consumers' needs and wants, thus better serving individual needs more accurately, as has never been done before.
-
Sustainability and Efficiency
As mentioned above, mass customization through Robotics and AI will enhance environmental variations by optimizing resource consumption and reducing wastage and energy required in manufacturing.
-
Integration with Emerging Technologies
Industries can encourage greater integration and transparency in manufacturing by combining robotics and AI with other up-and-coming technologies that embrace IoT, blockchain, and AR in mass customization.
In conjunction with AI, robotics is at the core of driving change in mass customization in manufacturing due to the high flexibility, speed, and accuracy achieved. By integrating advanced automation, intelligent analytics, and adaptive systems, the implication is that through mass customization, manufacturers can be in a position to meet this growing demand for personalized products and still reap the features of the concept of mass production.
Next Steps with Robotics and AI
Talk to our experts about implementing advanced AI systems and how industries and departments leverage Robotics and Decision Intelligence to become decision-centric. Harness AI to automate and optimize robotic processes, enhancing efficiency, precision, and responsiveness.


