
Introduction Empathy Mapping
Products and services are made for the people, and a good understanding of our customer base psychology will help build successful products. Many techniques help get a deep understanding of user needs and goals, and Empathy mapping is one of them. Empathy Mapping helps build Empathy with customers so that designers and user researchers can think from the user perspective and build user-centric products design.
Empathy is the ability to understand another person's feelings. Empathy has a very famous quote attached to it which is “ walking in someone else’s shoes .” Empathy is a very important skill set for designers because it helps designers to think about the way users use and interact with products.
User experience design is a user-product interaction, and improve the product, and users experience by addressing all perspectives of a product by the user's feedback & requirements.Taken From Article, What is User Experience Design, Tools and Principles
What is an Empathy Map?
An empathy map helps to map what a design team knows about the potential audience. This tool helps to understand the reason behind some actions a user takes deeply. This tool helps build Empathy towards users and helps design teams shift focus from the product to the users who are going to use the product. As the team learns more about the users, they place that information on the chart and gain an in-depth view of the user behavior, problems, opportunities.
The benefits includes are below:
- More understanding of the Target Audience
- More Organized Information in easy to understand format
- Fast and Inexpensive
- Easy Customization
- Common Understanding and same mindset of whole team members
- It describes what users think, say, feel, do
How to create an Empathy Map?
For creating an empathy, map gathers qualitative data, quantitative data, personas, and your team.
- Quantitative data can be gathered from websites, blogs, books, and many other resources. They help to gain knowledge of a particular scenario or story but not give insights specific to users.
- Qualitative data can be gathered by taking user interviews, shadowing the users, card sorting, Ethnographic research, and many other techniques help to gather qualitative data.
- Personas are created after analyzing the data. It is a virtual character of a person stating its goals, pains, gains, lifestyle, and tasks they perform.
- It can also be created using a whiteboard, sticky notes, and markers in a group activity. One can also freehand sketch the empathy map. These are of various formats, but core elements remain the same. A large sheet or board is bifurcated into 4 sections, and a large circle or empty head represents the user at the center of the 4 sections.
Build empathy for your users through a conversation informed by your team’s observations. Taken From Article, Empathy Map
Say
What customers speak about the product and service. This section should always contain Real Quotes from customers recorded or written during the interview sessions for deeper understanding.
Think
What is a customer thinking when interacting with a product and service in a particular environment? How are the users distracted and occupied by various thoughts? What is the most important thing to customers?
Feel
Feels tell us about the Emotional state of the user. What are the things that make the user worried? When does a user get excited? How is the overall feeling and experience of the user while using the product or service?
Do
What are the actions of the user? What actions and behaviors does the moderator notice of a participant?
A digital strategy to identify and understand another person’s situation and feelings.Taken From Article, Tips to Develop Empathy Maps
The Refined Empathy map
While the empathy map explained above is helpful during the initial stages, it’s a bit too generalized for brainstorming sessions focusing on the core experience of the product. To make it more specific to the user and product needs, we used another version of it called the refined empathy map.
Feelings
How does the user feel while using the product or service? What is the most important thing to the user?
Tasks
What tasks are users trying to complete?
Influences
What environment and factors influence the user's actions?
Pain Points
What are the difficulties faced by the user, which they want to overcome? What are their fears, stress, anxiety-causing things?
Goals
The ultimate purpose of the user, The reason why they are performing a particular task.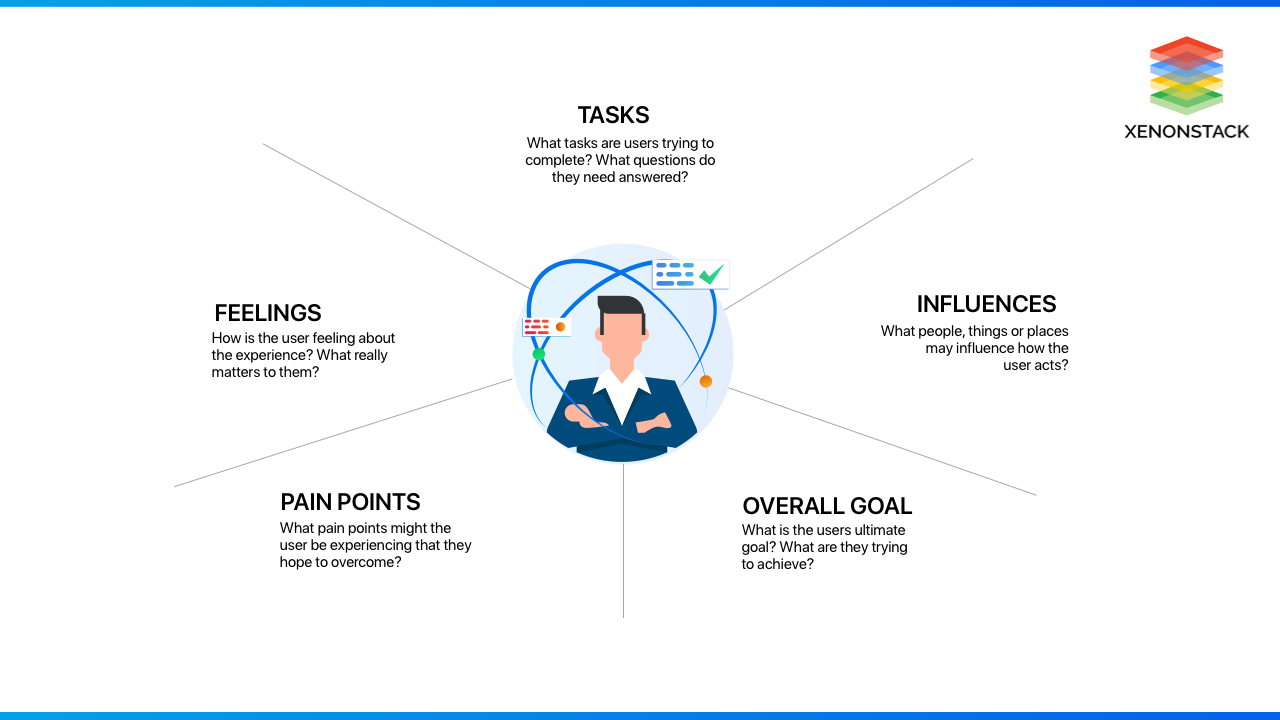
Since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, one of the most commonly heard words in sales thought leadership is "empathy."Taken From Article, Selling With Empathy
Points to remember
- Always be clear with the core objective of creating empathy maps. There could be multiple scenarios for which it is built. The activity conductor should modify the basic structure of it into a task-based on it or for decision making.
- The real customer data is the key to it which generates results. Make sure every team member is familiar with the Research data, only then start creating empathy maps.
- NEVER do it alone, it is a team sport. Each team member must think about the user using the product. Involve stakeholders, business managers, marketing teams so that from design to the business, every aspect should be considered.
- Always conduct a session with an experienced moderator. So that every team member should be able to participate and every point should be heard, and no point should be missed.
- Always remember that it is not an activity log for every emotional aspect of the user. It’s about focusing on the user's tasks and how they are affecting our product or service. A broader approach will destroy the purpose of making it

.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


