Overview of Kubernetes
Kubernetes is open-source software that allows the user to deploy and manage containerized applications on a scale. AWS manages clusters of EC2 compute instances and runs containers on those instances with deployment, scaling, and maintenance processes. Using it, we can run containerized applications using the same toolset on-premises and in the Cloud. AWS makes running them in the Cloud easy with highly available and scalable virtual machine infrastructure, EKS services, community-backed service integrations and managed Kubernetes service.
An open-source container orchestration engine and also an abstraction layer for managing full-stack operations of hosts and containers. Click to explore about, Architecture and its Components
How does Kubernetes work?
It is used to maintain a cluster of compute instances and programming containers to operate on the cluster based on the accessible computing resources and the fundamentals of each container. Containers are run in a logical grouping called Pods, and we can scale and run one or many containers together as a pod. It decides when and where to run the pods, manages traffic routing, and scales the pods based on utilization or other metrics that define. It automatically starts pods based on the cluster's support requirements and automatically restarts pods if they or the instances they are running fail. Each pod is given a single DNS name and an IP address, which is used to connect users' services and external traffic.
Why use it?
Kubernetes is an open-source project with large communities. It allows us to run containerized applications anywhere without changing our operational tooling. Additionally, many additional open-source projects and vendors build and maintain Kubernetes-compatible software that we can use to improve and extend the application architecture.What is Amazon EKS?
It is a managed service by Amazon that makes it straightforward to administer it on AWS without requiring them to stand up or manage their control plane. Amazon EKS runs its control plane instances across availability zones to implement high availability. Amazon EKS automatically detects and replaces unhealthy control plane instances and provides automated version upgrades. Amazon EKS also has other AWS services integrated to provide Security and Scalability for user's applications, including the following -
-
Amazon VPC for isolation
-
Elastic Load Balancing
-
IAM for authentication
-
Amazon ECR for container images
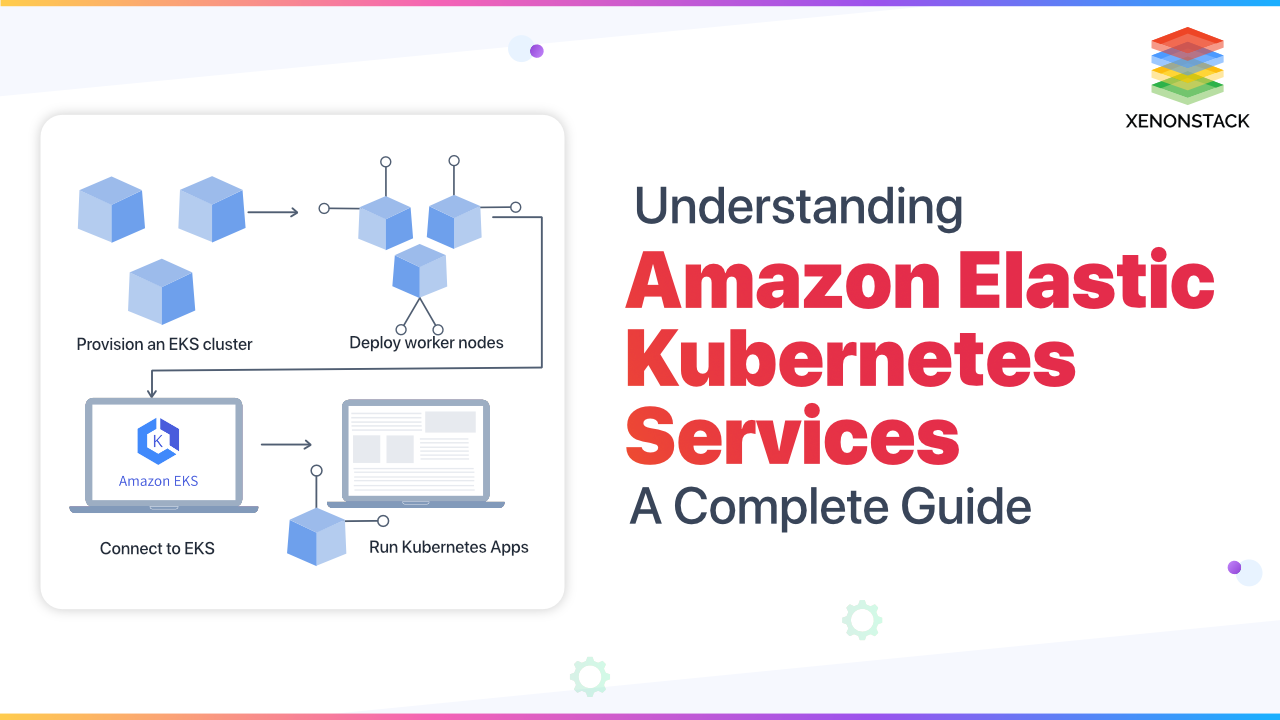
Amazon EKS runs up-to-date versions of open-source software so that we can use all the existing plugins and tools from the community. Applications running on Amazon EKS are fully compatible with applications running on any standard environment. This means we can easily migrate any standard application to Amazon EKS without any code modification required. Getting started with Amazon EKS is as easy as a piece of cake; follow the below steps to deploy a Kubernetes application in the EKS cluster.
-
First, create an Amazon EKS cluster in the AWS Management Console or with one of the AWS SDK or AWS CLI.
-
Then, launch worker nodes that register with the Amazon EKS cluster. AWS provides an AWS CloudFormation template that automatically configures the nodes.
-
When the cluster is ready, configure your favourite tools(Kubectl, for example) to communicate with it.
-
Finally, Deploy and manage applications on the Amazon EKS cluster as you would with any other Kubernetes environment.
How does Amazon EKS work?
EKS clusters have two main components: a control plane and worker nodes. Every cluster runs in its own fully managed Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). The control plane comprises three master nodes running in a different AZ to ensure AWS's high availability. Incoming traffic leads to its API passing through the AWS network load balancer Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling.
Worker nodes run on Amazon EC2 instances found in a VPC, which AWS does not manage. You can control and configure the VPC allocated for worker nodes. You can access your existing automation or provision worker nodes using an SSH. There are two main deployment options. You can deploy one cluster for any environment or application. You can also define IAM security policies and Kubernetes namespaces for deploying one cluster for multiple applications, such as Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling.
Xenonstack helps Enterprises in Kubernetes adoption for modernizing applications - Consult Now
A Comprehensive Approach
What is the Amazon EKS cluster?
An Amazon EKS cluster consists of two primary components:
-
The Amazon EKS control plane
-
Amazon EKS nodes that are registered with the control plane
What is the difference between EC2 and EKS?
Amazon EC2 Container Service lets you launch and stop container-enabled applications with API calls, inquire about the state of your cluster from a centralized service, and access many Amazon EC2 features. On the other hand, Amazon EKS is a managed service that makes it easy for you to run it on an AWS-managed cloud without installing and operating your clusters Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling.
What is the difference between AWS ECS and AWS EKS?
Amazon ECS is a scalable managed service that lets you run and orchestrate many containers. In contrast, Amazon EKS enables you to run Kubernetes on AWS as a managed service while retaining compatibility with the open-source K8s project.
To know more about the deployment and management of containerized applications using it, we suggest reading:
Next Steps with Amazon EKS Kubernetes
Connect with our experts to explore Amazon EKS Kubernetes Service solutions. Learn how industries and various departments leverage Agentic workflows and Decision Intelligence to build decision-centric operations. Utilize AI-powered automation to optimize IT support, streamline Kubernetes management, and enhance efficiency and responsiveness across cloud-native environments.