Cloud computing has become a game changer in society as it has brought huge changes in the way organizations tackle issues of scalability, flexibility, and costs. However, it also means that protecting against risks only grows more complicated as the digital transformation advances. Unfortunately, most traditional SOCs, designed and embedded in the old infrastructure models, cannot handle the constant and decentralized nature of cloud-attracted platforms. As a result of this challenge, a new approach has emerged in the market known as Cloud-native Autonomous SOC, which is the new generation solution for the new world of threats.
A Cloud-native Autonomous SOC encompasses a collection of technologies, including Artificial intelligence (AI), Machine learning (ML), and automation to detect, analyze and counter threats in real time. The solution is engineered on a cloud-native architecture, allowing it to be flexible and highly available while fitting into the cloud environment. About the Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs, this blog offers insights into key characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages and a breakdown of the practical application of Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs, highlighting why this is the future of cybersecurity.
What is a Cloud-native Autonomous SOC?
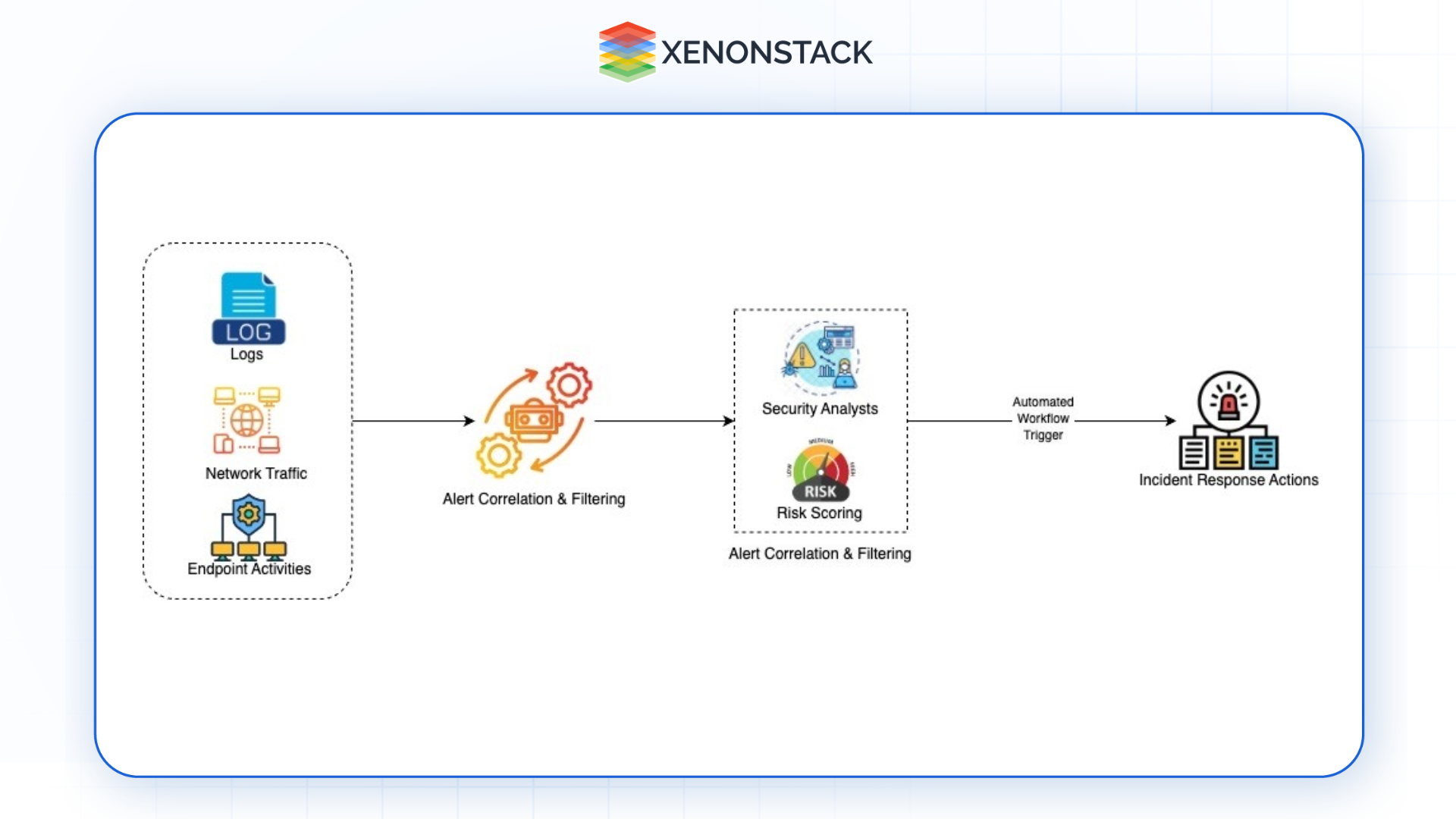
Figure 1: Cloud-native autonomous SOC security model
An Autonomous SOC is an advanced security model incorporated in cloud environments, and Cloud-native Autonomous SOC embodies an improved security model that is entirely congruent with the cloud environment. Unlike traditional SOCs that rely on static infrastructure and human intervention, this system is built with the following characteristics:
-
Cloud-native Design: This solution is well suited for cloud deployment since it will easily scale in large organizations.
-
Autonomous Operations: Randomizes the check-ups to a level that includes reduced human intervention as the AI/ML systems focus on detecting threats swiftly.
-
Real-time Analytics: This technique analyzes large volumes of security data in near real-time, leading to faster decision-making and lower dwell time.
-
Seamless Integration: It integrates with AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and other clouds and can be used for hybrid and multi-cloud computing.
Benefits of an Adoption of Cloud-native Autonomous SOC
 Figure 2: Some benefits of cloud-native architecture
Figure 2: Some benefits of cloud-native architecture Scalability and Resilience
Organizational growth is as follows: The SOC's architecture needs to be cloud-native to guarantee that the entity’s requirements can be met and addressed as the organization's scale increases. An organization’s environment can accommodate spikes in traffic through the network or even heavy volumetric loads of log data without the effects of decreased throughput.
AI and ML-driven Automation
Automating SOCs mainly involves the liberal use of AI and ML models to look for patterns, flag threats, or suggest threats that are likely to happen. For instance:
Continuous Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of all cloud resources means threats are identified and dealt with as they occur. This includes virtual machines, containers, serverless environments, and APIs.
Integration with DevSecOps
Modern cloud-native SOCs are fully synchronized with DevSecOps, allowing security to be an integral part of the SDLC. Tools utilized in the procedure guarantee that risks are consistently counteracted before the application programs are shipped.
Proactive Threat Hunting
In contrast to some less advanced forms of autonomous SOCs that might limit action to reactive measures, it employs artificial intelligence to scout advanced threats by finding risks that other tools are unlikely to discover.
Availability and Use of Compliance and Governance Automation
Compliance automation is mandatory regarding laws and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Cloud-native SOCs apply security policies and have built-in features that create Compliance reports.
Pros of Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs
-
Threat Identification and Response in Less Time
Automation lessens the time needed to detect and contain breaches, thus limiting their detrimental impact on the company.
-
Reduced Human Workload
Tasks, including log analysis and alert sorting, are time-consuming and can be eliminated by an autonomic system so SOC analysts can engage in higher tasks such as hunting for threats and planning.
-
Improved Cost-efficiency
Organizations prevent spending on hardware input and decrease numerous operational expenses through cloud structure and automation.
-
Scalability to Meet Business Needs
The cloud-native method helps SOCs to get thorough flexibility in bandwidth so that, during rush hour, it could easily accommodate the additional workload while, in low demanding time, allowing itself to shrink down.
-
Broadened Exposure in Each Cloud Sector
Traditional SOCs, on the other hand, are cloud-native and designed to offer visibility for multi-cloud and hybrid environments to facilitate cohesive security orchestration.
Challenges in Implementing a Cloud-native Autonomous SOC 
Figure 3: Challenges faced by Cloud-native Autonomous SOC
-
Complexity of Cloud Environments
Organizations normally have complex, hybrid, or multi-cloud setups. This can make ensuring seamless integration across diverse platforms challenging.
-
Data Overload
The vast amount of security data generated in cloud environments can be overwhelming. Misconfiguration models can lead to undetected threats or an excess of false positives.
-
Skill Gaps
Managing and optimizing an autonomous SOC requires cloud security and automation capability, skills in high demand but scarce.
-
Initial Implementation Costs
Moving to a cloud-native SOC necessitates a considerable upfront investment in tools and training of existing processes.
-
Regulatory Challenges
Cross-border data flows in cloud environments may complicate compliance with regulations, requiring careful attention to data governance.
The solutions that are enabling Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs
-
Autonomous SOCs also rely on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning AI/ML models for predictive analytical outcomes, Anomaly detection, and an automated response to threats.
-
Big Data Analytics The effectiveness of handling large volumes of data in real-time provides useful information to security teams.
-
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) is a set of tools for scanning cloud configurations for compliance issues and security concerns and then “fixing” them.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Current generation cloud SIEM solutions process security logs to detect threats.
-
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms combine with SOC tools to automate processes such as incident management and threat management.
-
Security Identity and Access Management (IAM) Strong IAM solutions implement zero-trust principles, so nobody but an authenticated user can access cloud resources.
 Popular Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs Cases
Popular Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs Cases
Live Ransomware Thwarting
Real-time threat hunting in a cloud-native SOC identifies when files are encrypted and the infrastructure shuts down the infected computers.
Information Lifecycle
The SOC guarantees that an organization's data is stored and processed only in permitted areas under GDPR; it also prepares compliance reports.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)
The SOC identifies long-term reconnaissance or lateral movements characteristic of APT Detection. Using AI, the SOC triggers anti-APT measures.
DevSecOps Integration
A financial institution brings the SOC with CI/CD pipelines to scan source code for vulnerabilities before the app release.

Popular Cloud-native Autonomous SOCs Cases
Live Ransomware ThwartingReal-time threat hunting in a cloud-native SOC identifies when files are encrypted and the infrastructure shuts down the infected computers.Information LifecycleThe SOC guarantees that an organization's data is stored and processed only in permitted areas under GDPR; it also prepares compliance reports.Advanced Persistent Threat (APT)The SOC identifies long-term reconnaissance or lateral movements characteristic of APT Detection. Using AI, the SOC triggers anti-APT measures.DevSecOps IntegrationA financial institution brings the SOC with CI/CD pipelines to scan source code for vulnerabilities before the app release.
 Figure 2: Some benefits of cloud-native architecture
Figure 2: Some benefits of cloud-native architecture 



