Industries have enhanced the uptake of IoT devices with the increasing uptake of IoT devices. IoT has transformed industries enhanced by Internet real-time data and smarter automated information and sophisticated manufacturing, healthcare, transport, and even manufacturing Information health and Transportation homes. Yet, IoT’s growth also brings dangerous security threats into the cybersecurity domain. It can be noted that, unlike more conventional IT systems, IoT devices do not have strong inherent security protection and can thus be easily hacked. Security Operations Centers (SOCs) are accountable for overseeing the security and watching over security events, but to control the increasing and diverse intensity of IoT security threats, a broader solution is needed. To this end, SOC automation comes in handy by applying AI, machine learning and more advanced orchestration to IoT security. In this article, we will discuss SOC automation for IoT security and its usefulness, methods, advantages, disadvantages, and scenarios.
 Figure 1: Evolution of Security Operation Center
Figure 1: Evolution of Security Operation Center
Why Automating SOC in IoT is Essential?
Given the fact that there are millions of IoT devices connected internationally, the threat landscape of potential cyber threats has increased. Many SOC operations anchored in manual analysis are overwhelmed by the variety of IoT and the number and rate of threats they face.
Several key factors driving the need for SOC automation in IoT security include:
-
The volume of IoT Devices: Thousands of devices mean an effective solution must be found to detect and manage threats successfully.
-
Device Heterogeneity: IoT devices are equipped with dissimilar hardware, software, and communication technologies, so implementing security measures is not easy for all machines.
-
Resource Constraints: Current security solutions often cannot be directly implemented on IoT devices because most of them possess limited computational abilities.
-
Low-Latency Requirement: Security for critical IoT use cases like self-driving cars and remote health monitoring requires threats to be positively identified in milliseconds and then acted on—something that legacy SOC approaches fail to deliver.
Key Components of SOC Automation for IoT Security
 Figure 2: Components of SOC Automation for IoT Security
Figure 2: Components of SOC Automation for IoT Security
-
Automated threat detection: SOC automation incorporates machine learning techniques for scanning large IoT data streams for patterns that help detect threats. Malware is effectively prevented by applying behavioural analytics, all this without any interference from the SOCs.
-
Incident Response Orchestration: SOC automation platforms can connect with security systems such as firewalls, SIEM systems and IDS. During threat identification, there are automated programs that may include initiating actions such as quarantining infected gadgets or limiting access to the network.
-
Threat Intelligence Acquisition: Automated SOCs collect threat intelligence data through threat feeds from global and local sources, vulnerability databases, and previous event data. This reduces false positives and enhances the tactics used to address incidents.
-
Continuous monitoring and logging: Tools collect real-time data from IoT devices to help SOC teams learn about them in real-time. Automated logging tools arrange such information so that machine learning algorithms can more easily ascertain whether or not there are threats.
-
Vulnerability Management: The SOC automation of the service includes the IoT vulnerability scan and IoT patch management. As IoT devices are often deployed in different places, these processes must be automated to keep the network safe.
Techniques in SOC Automation for IoT Protection
 Figure 3: Thematic map displaying the SOC automation application areas
Figure 3: Thematic map displaying the SOC automation application areas
-
Machine Learning, including Anomaly Detection
Algorithms are employed so that artificial intelligence is capable of detecting signs of IoT device anomaly. For example, receiving anomalies in a smart thermostat that interfaces with unknown servers or a factory sensor that generates large amounts of traffic are considered to have security issues. Clustering and pattern recognition tools are used widely in SOC and are categorized in the anomaly detection region. -
Artificial Intelligence for Incident Reporting
They said with the help of Artificial Intelligence (AI), SOCs can assess and filter security incidents and rank them according to their severity. A similar purpose exists in SOC automation, where threat intelligence reports are processed using NLP and enriching more alerts for faster threat remediation. -
Security Outreach, Automation, Remediation and Engagement (SOAR)
SOAR platforms combine other security solutions, enable the creation of other processes and structures, and serve as an interface for security events. While there are input automated processes such as alert triaging, hunting, and even remedial steps, if at all they exist in IoT contexts, the SOAR solution minimizes the extent to which humans are involved in such processes. -
Behavioral Analytics
Behavioural analytics establishes typical activities that IoT devices perform and alerts security teams when these devices deviate from the expected standard. Behavioural analysis is particularly useful in detecting zero-day attacks and harnessing unknown vulnerabilities because, compared with signature-based methods, it detects anomalous behaviour.
Equations for SOC Automation in IoT Security
In SOC automation, several formulas are assigned to calculate risk and prioritize incidents.
-
Risk Scoring Formula: One method for deciding which alerts need attention the most is to assign each event an alerting risk score
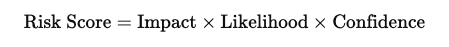
-
Impact assesses how often the event happens, basing its evaluation on the intensity of the impact.
-
Likelihood gives the odds that the event is going to take place.
-
Confidence reflects how much the SOC system believes that the incident is an actual threat.
2. Anomaly Detection Formula: Standard deviations are used in the calculations to check if a behaviour can be considered anomalous or not in the case of anomaly detection. For example:

Where:
- X is the observed value,
- μ is the population mean of normal values.
- σ is the standard deviation.
Z-score suggests deviations and anything above the Z-score out in the dimension is taken as anomalous requiring further scrutinization.
Use cases of SOC automation in IoT Security.
-
Cisco SecureX is a security platform that allows a single point of integration with its threat intelligence tools, IoT Security, and automation to respond to IoT device incidents in real-time. This also means that there are playbooks for mass IoT network SOCs to automate threat detection in large networks.
-
Microsoft Azure Sentinel Azure Sentinel is a cloud SIEM and SOAR developed by Microsoft. Sentinel works alongside machine learning models integrated into it and an anomaly detection system that enables SOC teams to respond to threats in real time across multiple dispersed IoT systems.
-
Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOAR The Cortex XSOAR provided by Palo Alto is a feature-rich SOSR platform that supports a wide range of automation to help SOCs rapidly address IoT threats. Combining threat intelligence and machine learning, Cortex XSOAR provides ongoing and comprehensive threat identification and response across the layered IoT characteristics.
-
Splunk Phantom is one of the most famous SOAR platforms that scales response orchestration in different contexts, including IoT. They offer playbooks for threat intelligence, which enables SOCs to handle IoT security threats at large conveniently through playbooks for incident handling and reporting.
Advantages of SOC Automation
-
Reduced Response Time: SOC automation helps to minimize Time to Detection or much critical Time to Respond; both of which are paramount in IoT where timeliness of a response is sacrosanct.
-
Scalability: With the help of automation, SECs can control and secure a thousand and one IoT devices without requiring a corresponding increase in manpower.
-
Consistency and Accuracy: Professionals argue that documents have reduced the likelihood of erroneous reporting of incidents compared to manual assessment.
-
Cost Efficiency: SOC automation eliminates many manual tasks, and this frees up organizational budget for other significant areas of concern.
 Figure 4: List of different sectors to implement IOT Security
Figure 4: List of different sectors to implement IOT Security
Limitations of SOC Automation
-
Data Overload: The data processed by IoT devices is considerable in volume, and it is difficult to sort through the noise and separate the signal from the noise to respond adequately to it.
-
Device Diversity: Devices within the IoT are not always defined by the same function. Therefore, they control their functions through different protocols, making it impossible to set general protection measures and automatically respond to threats from all devices.
-
Privacy Concerns: When SOC is implemented as an automated process, privacy becomes more of an issue since lots of data are handled to conclude.
-
Resource Constraints on IoT Devices: Networking IoT is another style of IoT in which many devices have limited computational power, which makes direct SOC automation difficult.
Mitigating Challenges of SOC Automation
-
Advanced Filtering and Correlation: The SOC automation platforms can analyze and separate the data with the help of ML algorithms that are designed to cut down the false positives and indicate the actual threats.
-
Standardization and Interoperability: Industry standards in protocols and information security can also be leveraged to overcome the complacent nature of the IoT space, thereby simplifying the centralization of SOC activities.
-
Data Anonymization: Applying data anonymization guarantees that information prone to leakage will be safeguarded during the analysis process, thus solving the data privacy problem.
-
Edge Processing: Performing security data analysis at the edge level in the IoT device has less workload on the IoT devices & also improves real-time threat detection.
SOC automation on IoT security is crucial to advancing IoT networks and threats. Using AI/ML and SOAR features, the SOCs are better positioned to address the IoT environment’s growing intricacies and size, providing near real-time responses, improving results accuracy, and reducing costs. Even though device heterogeneity and data overload remain some of the main issues in the current world, SOC automation proves to be a viable solution for protecting the IoT environment. With the increasing adoption of IoT from various organizations, SOC automation will play a significant role in providing secure, dependable, and scalable IoT systems.
Next Steps for IoT Security
Talk to our experts about implementing compound AI systems and how industries leverage SOC automation for IoT security. By using Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence, organizations become decision-centric, optimizing IT support and operations while enhancing security for connected devices. This approach automates threat detection and response, improving efficiency and responsiveness across departments.



