Since more organizations are turning towards multi-cloud environment, the problem of Cloud Finance is more emerging than ever before. However, using multiple cloud providers’ flexibility and scalability brings issues in cost, budget, and financial responsibilities. That is where the concept of Financial Operations or FinOps steps in. FinOps is the method of uniting finance, technology, and business to work in the cloud. To consistently tackle many of these challenges across different cloud environments., the FOCUS framework guides the FinOps process. Now we will look at how FOCUS is used to understand and standardize FinOps when managing multi-clouds.
Understanding FinOps
To begin with, let’s first understand what FinOps is. In any environment in the cloud, not limited to EC2 instances, FinOps is a system, process, and tool that optimizes cloud financial operations. It focuses on cross-functional teamwork, when it comes to managing the cloud cost in relations to finance, engineering, and the product team. FinOps improves visibility into cloud costs, budgeting, and resource utilization decision-making.
 Fig 1: FinOps Principles
Fig 1: FinOps Principles
Challenges in Multi-Cloud FinOps
Managing finances across multiple cloud platforms introduces various challenges:
-
Cost Visibility: Those specific cloud providers' prices vary, and many are opaque, making it challenging to track overall expenses.
-
Budgeting and Forecasting: Being erratic, the regularities make accurate budgeting a challenge because scale and usage, as well as billing cycles, may differ.
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Finance and engineering are usually two different functions and therefore it may be very difficult for these two to work hand in hand if they have different objectives and key performance indicators.
-
Resource Optimization: Sometimes there are idle assets in one or more clouds, or some assets are extravagantly provided, and their identification is a complex process.
-
Compliance and Governance: The examination of so many different cloud environments and problems of financial compliance can be quite complicated and time-consuming if there are no unified criteria among them.
The Need for Standardization in Multi-Cloud
Every provider employs a unique set of pricing strategies, cost modes and reporting structures, making it difficult to get an overall vision of the expenditure incurred. Therefore, Standardization becomes critical:
- Enhanced Cost Visibility: A unified approach provides for more accurate identification of cloud costs and their subsequent reporting.
-
Improved Budgeting and Forecasting: It is important for organizations to maintain standardized approaches that will enable them to come up with workable budgets across multiple cloud systems.
-
Cross-Functional Alignment: It provides a consistent approach, helps to integrate the work of the finance team and engineering teams together into a unified goal and key performance indicator system.
-
Streamlined Resource Optimization: The major advantage of standardization is that it allows organizations to review the various platforms and see cost-saving measures.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Integrated operations of finances make it easy to deal with compliance and governance standards within an organization.
-
Scalability: In a larger organization, it is possible to set up a standardized FinOps model so that adding a different cloud provider or service is easily done.
Introducing FOCUS (FinOps Open Cost & Usage Specification)
The FOCUS framework or the FinOps Open Cost & Usage specification offers a set of practices for the management of multi-cloud FinOps. Its main goal is to standardize communication and approach to measure and define costs related to cloud environments.
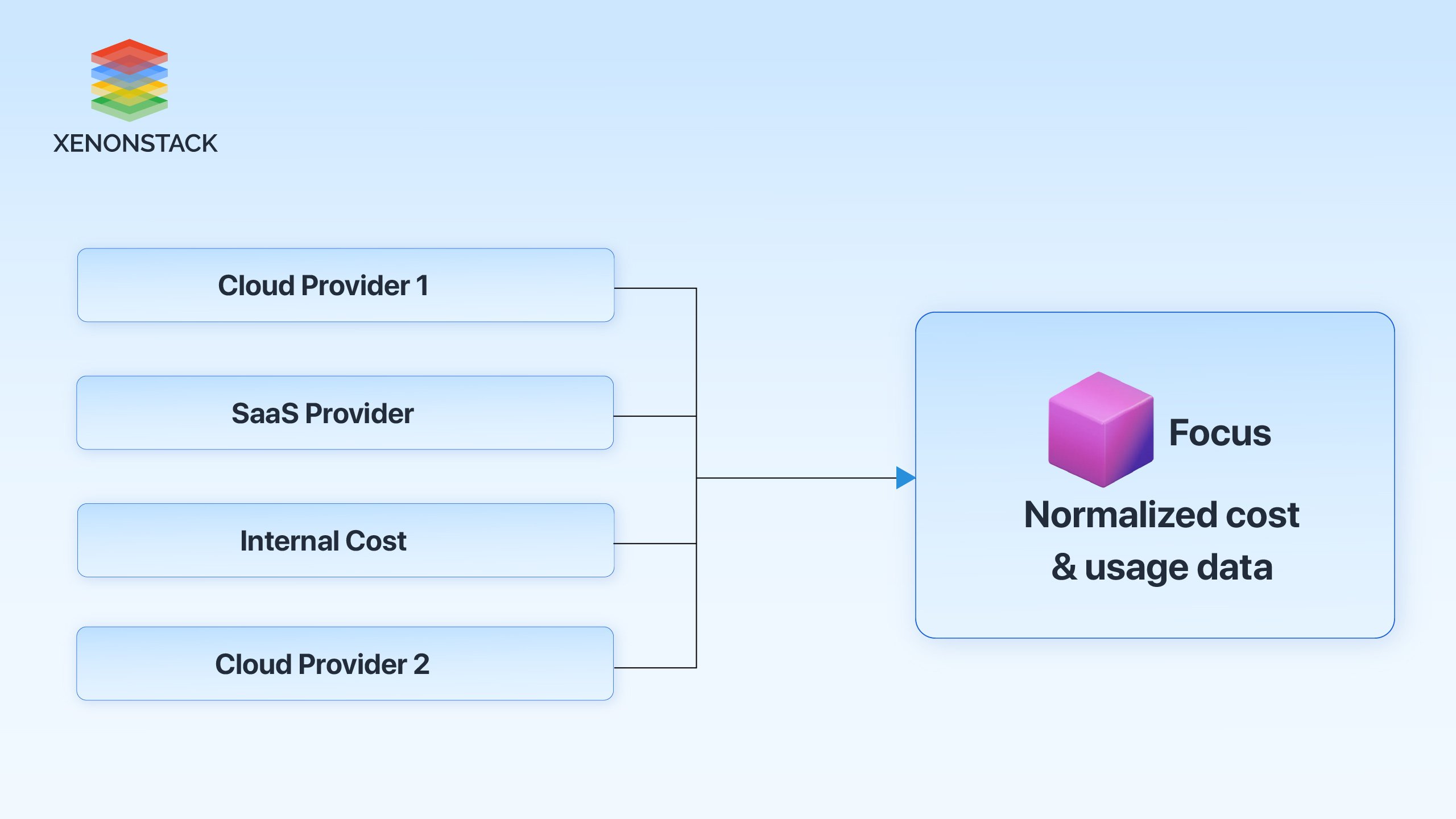 Fig 2: FinOps Open Cost & Usage Specification
Fig 2: FinOps Open Cost & Usage Specification
Key Components of FOCUS
-
Open Specification: FOCUS is deliberately developed as an open specification and can be implemented by any organization regardless of its type and size. Openness fosters cooperation and knowledge of how to do things better between the FinOps community members.
-
Cost Visibility: FOCUS enhances broad cost visibility because it prescribes the way costs are recognized and recorded. This in turn makes it easier to track spending more effectively across multiple platforms within the cloud.
-
Usage Metrics: This framework integrates usage metric as one of the criteria that need to be constantly measured. Thus, having a consistent and coherent manner of tabulating the data usage, the management makes wiser decisions on resource allocation.
-
Collaboration: Minimizing costs and time is achieved through close collaboration of the finance, engineering, and operations departments through FOCUS. It is better to find out major keys that everyone has an understanding about the cost and usage or at the least cloud costs so that collective efforts can be made for effective management of expenditure on cloud.
Implementing FOCUS in Your Organization
To effectively implement the FOCUS framework, organizations should follow these structured steps:
Step 1: Assessment and Planning: When implementing FinOps the first step is to evaluate your current FinOps plan. Find areas where cost visibility and usage metrics are least provided in processes and tools. FOCUS should be incorporated to match the needs of the organization, and the plan should be formulated for its implementation.
Step 2: Establish Open Specifications: Conduct the activities to implement the open specifications described by FOCUS. This is to ensure that the teams working on cloud are fully informed on the language and approach of the evaluation of cost and cloud usage. It is important in order to ensure that there is cohesion between various teams and subgroups.
Step 3: Integrate The Tools: Whenever you want to select a tool, make sure it is compatible with the FOCUS framework and all the cloud providers. Having tools that can enable tagging, tracking, and reporting with the aid of a successful implementation of a solid tracking system will guarantee the tracking of data that has been collected.
Step 4: Standard Reporting Processes: When it comes to reporting, the company should standardize this area and provide written policies on how cost and usage of the cloud should be reported. It is equally important that all the stakeholders are familiar with these processes and that they are featured in the organization’s financial reporting processes.
Step 5: Train and Educate Teams: The next course of action should be to organize training to ensure that all your teams comprehend what the FOCUS model entails and the effects it will have on cloud financial management.
Step 6: Monitor: Another focus of this plan is on the constant assessment of the rate of successful FOCUS implementation. The feedback be taken commonly from regard stakeholders to enhance the processes as well as performances.
Benefits of Adopting FOCUS
Implementing the FOCUS framework can lead to several significant benefits for organizations:
- Increased Cost Efficiency: When a specific structure of cost capture and report is implemented, it will be easier for an organization to manage its costs so that general expenditure is minimized.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing teams with more information about the costs and usage of a product or service they can better allocate resources efficiently.
- Improved Accountability: FOCUS makes sure that every team is practicing Cloud cost control, and in the end, every team becomes responsive.
- Greater Agility: FOCUS allows organizations to respond more flexibly to emerging trends in cloud costs, and the consumption patterns, which in turn facilitates long range planning and forecasting.
- Strengthened Collaboration: FOCUS encourages cross-functional harmony between the finance, engineering, and operations departments with programmatic goals and directions for cloud financial management.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Major financial risks relating to cloud adoption can be managed when SOPs and KPIs are developed; this approach helps to recognize these risks at an early stage.
-
Data-Driven Culture: Implementing FOCUS creates a culture of focus on financial data to drive decision making instead of relying more on feelings or intuitions.

FOCUS Use Cases
Here are some compelling use cases of FOCUS:
Cost Distribution
Many organisations deal with the problem of inappropriately charging cloud costs to various departments or projects. FOCUS allows for practices of tagging and reporting that makes it easier to conduct charge back strategies. In turn, finance teams can use consistent metrics to split costs among different business units as well as guarantee a specific amount of cost responsibility.
Budgeting and Forecasting
The evaluation of costs in multi-cloud relationships can only be done by understanding the budgetary trends of the past as well as the requirements for the future. The FOCUS methodology helps organizations introduce some degree of consistency in data collection related to usage, thereby helping finance teams develop reasonable projections. This way, companies are able to create much more realistic plans of payments that correspond to their needs.
Cost Optimization Initiatives
The problem of finding potential cost savings when accessing multiple cloud providers is challenging. Through FOCUS, the organizations' usage metrics can be compared with the industry benchmarks for spending on the resources. This benchmarking allows for creating awareness of areas where cost optimization programmes like rightsizing resources or implementing reserved instances can adequately be done.
Financial Reports and Analysis
With the use of FOCUS, organizations have the capacity to produce accurate and integrated financial reports which collect data from several cloud systems. By viewing cloud expenses in a single pool, spending is easily understood, and more insights can be gained in order to make more informed strategic decisions in regard to costs.
Risk Control and Regulatory Compliance
When it comes to applications designed for Multi-Cloud environments, the question of compliance with financial regulations can become rather an issue. FOCUS helps organizations to implement and maintain compliance by providing organizations with a framework for the necessary processes for cloud expense tracking and reporting. This is because by practicing consistent methodologies, organizations are able to reduce risk exposed to cases of fraudulent financial reporting or sudden emergent expenditure.
Cross-Functional Teamwork
Ultimately, FinOps depends on the cooperation between two functional areas that are usually distinct: finance and engineering. The practical benefit realized by using FOCUS is that it helps to establish a glossary by which every actor can consider costs and usage metrics. For example, engineering teams can offer insights on resource utilization at the project level, while financial teams can provide cost estimates. This facilitates alignment of goals and plans because everyone agrees to be accountable for them.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Optimizing multi-cloud FinOps is the best practice organizations need to adopt if they are aiming to optimize their operations. The FOCUS structure—FinOps Open Cost & Usage Specification helps to reach this goal. Through collaboration, achieving the right cost model, determining the consumption and sharing the findings organizations can put together the fundamentals of a good FinOps that provide value and accountability.
Such techniques as FOCUS should be implemented, as organizations continue with the Cloud Adoption to improve financial transparency and cogency. Through implementing the FOCUS framework, businesses are also able to effectively manage their cloud expenses while simultaneously enabling their employees to make cost-efficient choices that will help support their organizations’ purposes of innovation and growth.

 Fig 1: FinOps Principles
Fig 1: FinOps Principles Fig 2: FinOps Open Cost & Usage Specification
Fig 2: FinOps Open Cost & Usage Specification