Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has revolutionized business operations by streamlining workflows, boosting productivity, and reducing operational costs. However, as organizations attempt to scale RPA, governance-related challenges often arise, preventing businesses from fully leveraging the potential of automation technology. These challenges can lead to inefficiencies, security vulnerabilities, and difficulty in scaling RPA across the enterprise without a robust governance framework.
This is where Agentic Process Automation (APA) emerges as a transformative solution. By embedding intelligent workflow orchestration and enabling real-time decision-making systems, APA addresses the limitations of traditional RPA. It integrates dynamic workflows and agentic automation tools to ensure RPA tools remain aligned with business objectives, regulatory compliance, and performance benchmarks.
A detailed comparison of RPA vs APA highlights how APA bridges governance gaps, enhances decision-making in automation, and unlocks the full potential of agentic processes for enterprises.
What is Agentic Process Automation Governance?
Agentic Process Automation (APA) governance refers to the framework and practices that guide the management and optimization of RPA processes using AI-driven decision-making, real-time monitoring, and dynamic adaptation. Unlike traditional RPA governance, which relies on static rule-based systems, APA governance empowers organizations to scale and maintain automation efficiently while ensuring alignment with strategic business objectives.
Through AI-powered agents, APA continuously monitors RPA tools and adjusts workflows, priorities, and resources in real time, enabling proactive management of security, compliance, and operational risks. APA ensures that automation processes are not only efficient but also adaptable to changing business needs, ensuring long-term success and scalability across the organization.
The Role of Agentic Process Automation in Overcoming RPA Challenges
RPA enables organizations to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks such as data entry, invoicing, or customer services. While the operational benefits delivered by RPA are excellent, scaling and maintaining automation across complex business environments introduces challenges. These include governance concerns, alignment with strategic objectives, managing security and compliance risks, and ensuring business continuity.
With Agentic Process Automation (APA), fully-fledged AI-driven agents and machine learning in process automation are integrated into traditional RPA governance. In APA, continuously monitoring RPA processes ensures that dynamic workflows are fine-tuned in real-time. This ensures that autonomous agents in automation remain aligned with business objectives and operational standards. By incorporating adaptive process management and intelligent workflow orchestration, APA significantly reduces risks while increasing productivity, paving the way for the long-term success of automated endeavors.
Key Principles of Agentic Process Automation Governance
Agentic Process Automation (APA) enhances RPA governance by incorporating three key principles:
AI-Driven Decision-Making
APA utilizes AI-driven decision-making to analyze data and make continuous real-time adjustments to RPA processes. By leveraging artificial intelligence, APA automatically optimizes workflows, resolves inefficiencies, and aligns automation efforts with changing business goals, all without requiring manual intervention.
Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring ensures that APA continuously tracks RPA performance, providing constant oversight. This allows businesses to identify issues, like underperforming bots, and take corrective actions promptly, ensuring that RPA remains aligned with business objectives at all times.
Dynamic Adaptation
APA’s dynamic adaptation enables it to adjust workflows, task priorities, and resources based on real-time feedback. Whether responding to market changes or evolving business needs, APA ensures that RPA systems remain flexible and scalable, automatically adapting to maintain efficiency and performance.
These principles together ensure that APA governance keeps RPA systems running smoothly, efficiently, and in sync with business goals.
Real-World Use Cases of Agentic Process Automation Governance
Use Case 1: Optimize RPA Strategy and Governance
Most organizations face inefficiencies and disconnection from broader business goals when scaling RPA initiatives. When RPA tools are deployed across multiple departments, they may operate in silos without regular oversight, leading to redundancies, misaligned priorities, and underperformance. According to McKinsey, 30 percent of RPA projects suffer from poor governance as organizations struggle to maintain a unified automation strategy.
APA directly addresses this challenge by continuously monitoring the performance of RPA tools and making data-driven decisions regarding operations. Unlike static governance models, Agentic Process Automation (APA) uses real-time feedback to adapt activities among AI-driven agents, ensuring automated processes remain in sync with shifting business objectives. As new data enters the system, APA automatically adjusts priorities, reallocates resources, and optimizes dynamic workflows, allowing RPA to scale step-by-step in alignment with the organization’s higher-level strategic goals.
APA’s process-oriented decision-making ensures that RPA tools are consistently fine-tuned to meet strategic objectives. Over time, the automation efforts become more adaptable and scalable, driving long-term success.
Use Case 2: Security and Compliance
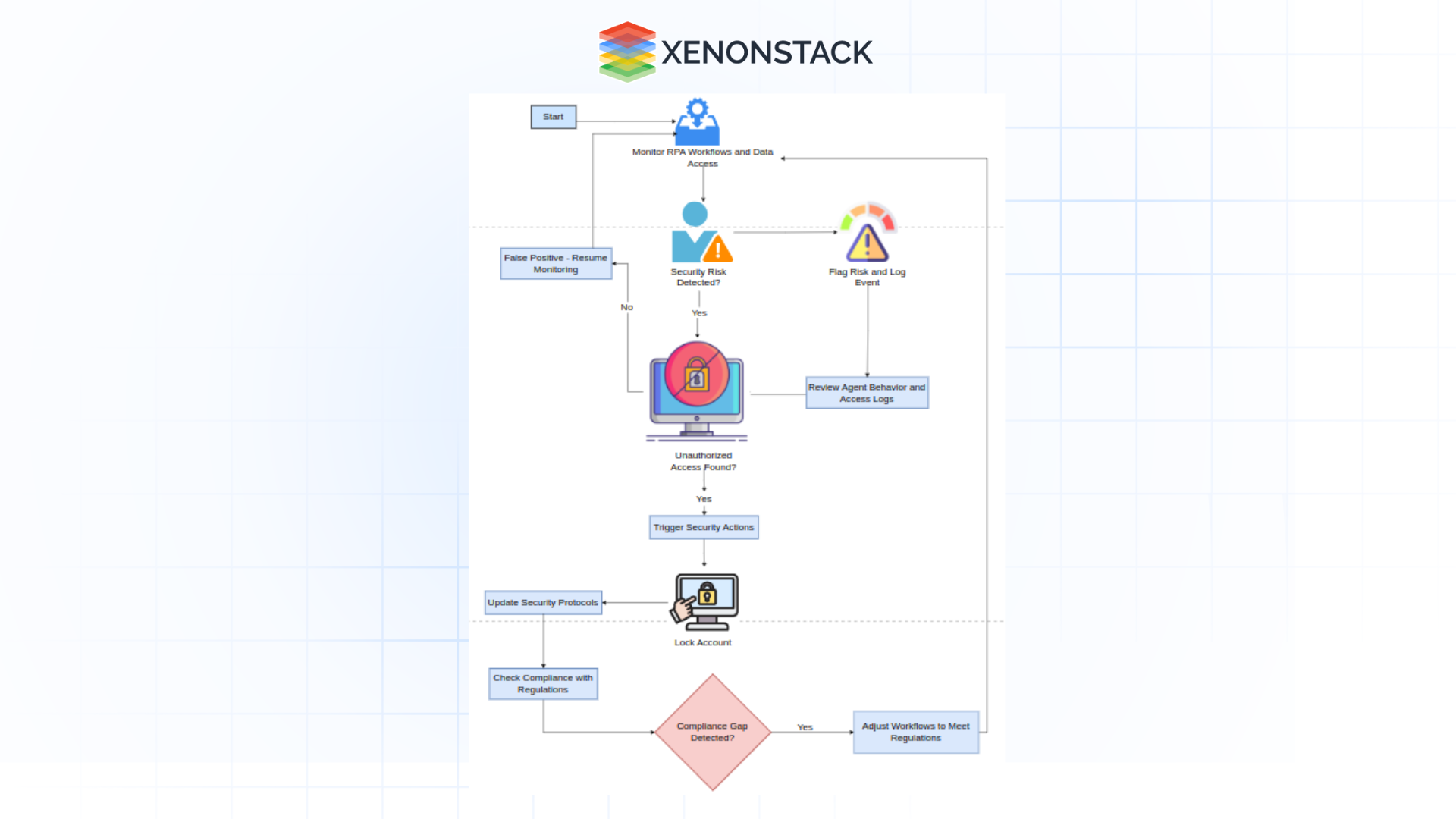 Figure 1: APA Process for Maintaining RPA Security and Compliance
Figure 1: APA Process for Maintaining RPA Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are critical concerns when RPA is applied to domains involving sensitive information, such as healthcare and finance. Without a well-defined governance framework, RPA bots may inadvertently lead to data breaches or legal infractions. According to a 2022 report from the Institute for Robotic Process Automation, 45% of organizations revealed security vulnerabilities during RPA deployment. The two main causes are lack of proper oversight and failure to incorporate security controls into the automation process.
APA addresses these challenges by integrating smart risk management directly into the RPA workflow. While monitoring the activities of AI-driven agents, APA detects potential security risks, such as unauthorized data access or other non-compliant actions. When these risks are identified, APA takes corrective action, including reviews of agent behavior and addressing any flagged issues, ensuring continuous updates to security measures.
Furthermore, APA adapts to regulatory changes, ensuring that RPA processes stay aligned with new laws and industry requirements. This ability to make real-time decisions guarantees that security and compliance are embedded into the RPA governance model, making costly breaches or violations virtually impossible.
With continuous monitoring and autonomous decision-making, RPA bots remain secure and compliant, allowing businesses to scale their automation efforts without exposing themselves to unnecessary risks.
Use Case 3: Business Continuity and RPA Maintenance
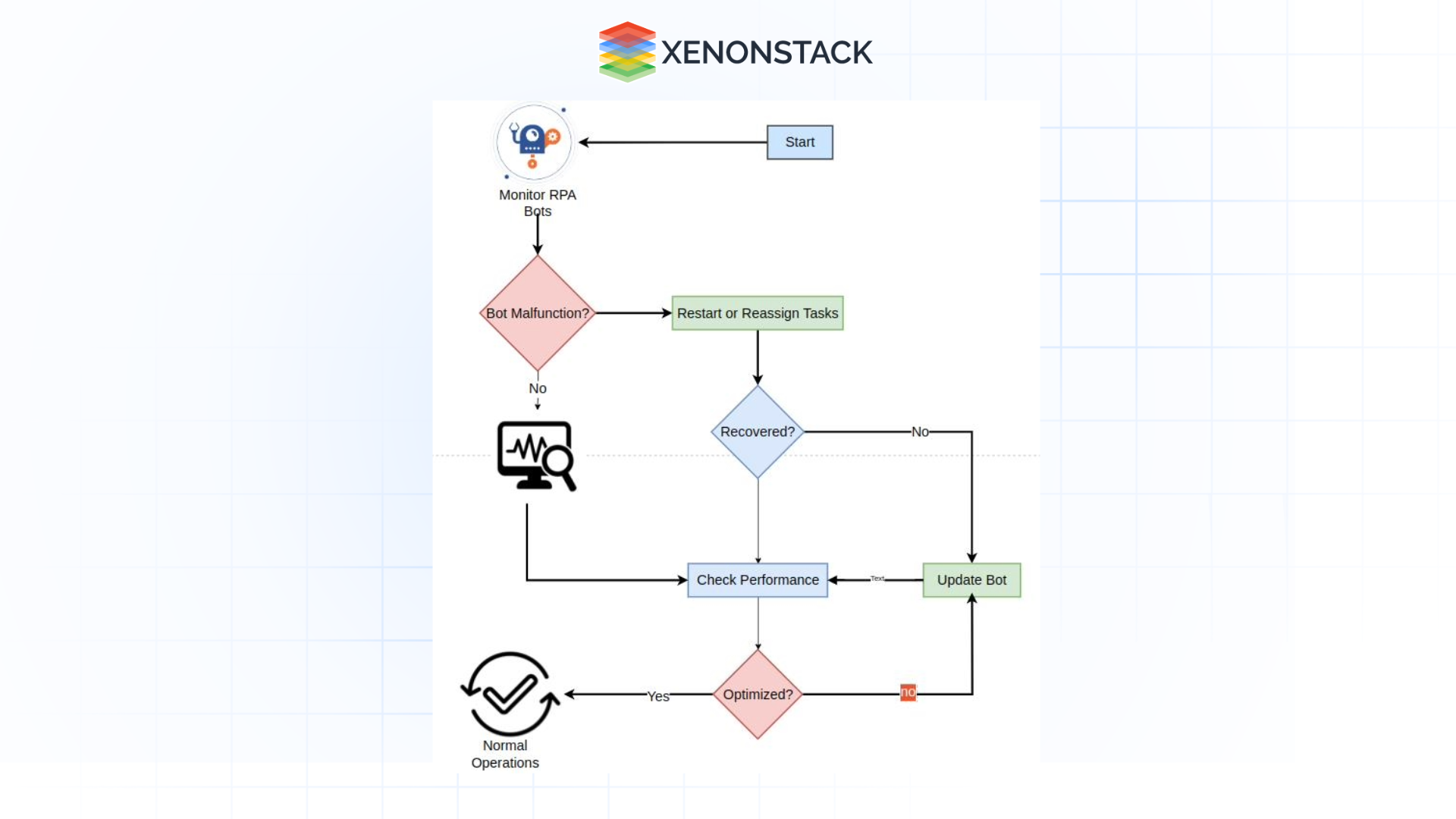 Figure 2: Optimize RPA Bots and Maintenance
Figure 2: Optimize RPA Bots and Maintenance
RPA tool failures can severely disrupt business processes, especially when these tools are performing critical functions. In 2020, 50% of large RPA deployments failed due to insufficient oversight, causing operational disruptions. Without constant monitoring and intelligent automation, RPA bots cannot recover from failures autonomously, resulting in delays to business operations.
APA addresses this by continuously monitoring the health of RPA bots and detecting issues before they lead to full system failures. When a bot malfunctions, APA automatically initiates recovery processes, such as restarting the tool, rebalancing task prioritization, or reassigning tasks to other bots, all with minimal downtime. Furthermore, APA performs regular bot maintenance, ensuring that RPA processes remain efficient and up-to-date.
Continuous health and performance management of RPA bots ensures smooth-running automated processes, facilitating uninterrupted business operations.
Best Practices for Agentic Process Automation Governance
Challenges in Agentic Process Automation Governance and Their Solutions
Scalability Inefficiencies
Many RPA deployments face the problem of scaling poorly across organizations, especially when business objectives are not well aligned with the tools.
Solution
Dynamic Governance in APA maximizes the effectiveness of the RPA process by ensuring it is aligned with business objectives, which enhances scalability and operational efficiency.
Security and Compliance Risks
Companies running RPA bots on sensitive data host security risks or risks of non-compliance with regulations.
Solution
Proactive Security and Compliance in APA ensures real-time checks are built into the process to monitor security and compliance, protecting bots and ensuring they remain compliant with relevant regulations.
Operational Downtime
Downtime occurs when bot failures are not detected due to a lack of continuous monitoring.
Solution
Autonomous Bot Management in APA provides nearly zero downtime by autonomously managing bot maintenance and recovery, ensuring that RPA processes run smoothly with minimal disruption.
Discover how Agentic AI is transforming businesses by optimizing automation governance. Visit this page to explore the full potential of APA and how it can drive smarter decision-making and security.
Top Benefits of Agentic Process Automation Governance
Agentic Process Automation (APA) offers a range of key benefits that significantly enhance RPA effectiveness, scalability, and security. These advantages include:
-
Align RPA with Business Objectives: APA dynamically adjusts RPA tool activities as organizational priorities evolve, ensuring continuous alignment with strategic goals, enhancing business outcomes, and intelligent automation.
-
AI Decision-making Capacity: The AI-driven system within APA automatically identifies and resolves inefficiencies, eliminating operational redundancies and bottlenecks and driving better performance through machine learning and intelligent workflows.
-
Scalability: APA’s adaptive capabilities enable the intelligent expansion of RPA to support continuous growth, providing businesses with scalable automation that can grow alongside organizational needs.
-
Proactive Risk Mitigation: APA uses AI to automatically detect vulnerabilities and takes proactive measures to mitigate them, ensuring a secure environment for automated processes and reducing potential security breaches.
-
Constant Compliance: With real-time updates to align with regulatory changes, APA ensures that RPA processes always comply with evolving laws and industry standards, minimizing the risk of fines and reputational damage.
-
Secure Data: Throughout the automation process, APA continuously monitors and manages access to confidential data, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected at every stage, which strengthens overall data security.
-
Reduced Downtime: Through autonomous decision-making, APA ensures that RPA bots continue running without interruptions by proactively identifying issues and resolving them swiftly, minimizing downtime.
-
Proactive Maintenance: APA tracks areas requiring updates or optimizations, preventing performance decay and keeping RPA tools running efficiently over time.
-
Enhanced Recovery Capability: In case of a malfunction, APA quickly initiates recovery procedures, minimizing business disruption and enabling rapid recovery, ensuring continuous operation and uptime.
The Future of Agentic Process Automation Governance
Agentic Process Automation (APA) is the next-generation change in the way businesses govern and scale their RPA efforts. By incorporating AI-driven decision-making into RPA governance, APA enables the real-time optimization of automation processes while proactively managing security and compliance risks. It ensures continuous operation of business processes, offering enhanced efficiency, security, and scalability.
As businesses continue to increase their reliance on automation, APA’s smart governance will become increasingly vital in unlocking the full potential of RPA. APA will play a crucial role in risk reduction and providing long-term value to RPA, ultimately driving business success.
Next Steps in Implementing Agentic Process Automation Governance
Talk to our experts about implementing APA governance, how industries and different departments use Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence to become decision-centric. Utilizes APA to automate and optimize IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness.


