
Businesses are transforming operations with Autonomous Digital Operations and Enterprise Agentic AI, replacing manual processes with intelligent automation. Traditional IT struggles with complexity, while AI-driven agents enable real-time decision-making, predictive analytics, and self-healing capabilities.
These systems adapt and act with minimal human intervention from IT and cybersecurity to finance and healthcare. This blog explores how Agentic AI and decision intelligence drive agility, efficiency, and smarter enterprise operations.
Historical Perspective of Autonomous Agents
 Fig 1: Historical Perspective of Autonomous Agents
Fig 1: Historical Perspective of Autonomous Agents
1950s: The Conceptual Beginnings
1956: The Dartmouth Conference is considered the birthplace of Artificial Intelligence. This is where the term "Artificial Intelligence" was first coined, setting the stage for the development of autonomous agent technology.
1960s: Early Explorations
- 1966: Shakey the robot, developed by Stanford Research Institute, became one of the first robots capable of somewhat autonomous movement and problem-solving, integrating software and hardware.
1980s: Foundational AI Techniques
- 1980: The development of search algorithms and other pathfinding algorithms laid the groundwork for autonomous navigation, which is crucial for both software and robotic agents.
1990s: Rise of the Internet and Digital Assistants
- 1997: IBM's Deep Blue, a chess-playing computer, defeats world champion Garry Kasparov, showcasing the potential of AI to surpass human intelligence in specific tasks.
- 1997: The appearance of early digital assistants in consumer technology, though primitive, marked the beginning of AI integration into daily life.
2000s: Advanced Robotics and Machine Learning
- 2004: DARPA Grand Challenge, the first competition for autonomous vehicles, spurred significant interest and investment in autonomous vehicle research.
- 2006: Thanks to Geoffrey Hinton and others, the reemergence of neural networks reignited progress in deep learning, significantly advancing AI capabilities.
2010s: AI Goes Mainstream
- 2011: IBM's Watson wins Jeopardy! Demonstrating natural language processing and understanding capabilities beyond simple tasks.
- 2012: Google's DeepMind develops AlphaGo, an AI capable of defeating a professional human player in the complex board game Go. This marks a significant milestone in machine learning and strategic thinking.
- 2016: The launch of autonomous ride-hailing services in select cities introduces the public to the practical use of multiple autonomous agents.
The 2020s: Integration and Expansion
Integrating AI into various sectors, including healthcare, finance, and urban management, shows the versatility and potential of building autonomous agents beyond their initial scope.
Continuous advancements in AI, machine learning, and robotics drive the development of more sophisticated, efficient, and capable task execution agents, promising an exciting future for AI applications.
What are Autonomous Agents?
Autonomous agents are computer systems capable of independent decision-making and acting in their environment without direct human intervention. They are designed to perceive and understand the surroundings and situations, and they will perform actions to complete their tasks. They operate without human control and rely on their internal logic and reasoning capabilities to make decisions. They can learn and adapt to changes in the environment and adjust their work strategies.
Some examples of Autonomous Agents
-
Self-driving cars: By adding sensors and advanced algorithms to navigate roads, these cars can notice their surroundings and decide about direction, speed, and obstacles.
-
Personal assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa can understand user commands and information to perform tasks like setting alarms or booking appointments.
-
Trading robots: These Robots use algorithms to analyse market data, identify trading opportunities, and execute the trades automatically.
-
Game-playing agents: AI-powered characters in video games can learn and adapt their strategies based on their opponent's behaviour.
Why are Autonomous Agents Important?
Autonomous agents are playing an important role in our world by bringing significant benefits in terms of efficiency, safety, exploration, and innovation. Autonomous agents hold significant importance for many reasons:
Increased efficiency and productivity: They can handle repetitive tasks and reduce human efforts, while humans can focus on more complex tasks and operate continuously without breaks; hence, this will increase productivity.
Enhance Safety and Reliability: They can reduce the chances of human error and perform risky tasks where humans are at risk of accidents and injuries. They can perform tasks without taking any breaks and ensure reliable outcomes. Also, they can work for monitoring and efficient management.
New possibilities and applications: Autonomous agents can assist humans in their complex tasks, provide real-time data insights, or take autonomous actions based on their understanding of situations.
Innovation and growth: The advancements of autonomous agents contribute to progress in areas like healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, etc. As technology evolves, collaboration between humans and autonomous agents can unlock innovation.
Core Characteristics of Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents possess key characteristics that enable them to operate efficiently without constant human supervision. These attributes—independence, adaptability, proactivity, and goal orientation—allow them to function intelligently in dynamic environments.
-
Independence: Autonomous agents function without direct human intervention, making them ideal for scenarios where real-time human input is impractical. For example, space exploration probes must make independent navigation and data collection decisions since communication delays make remote control impossible.
-
Adaptability: These agents can modify their behaviour based on environmental changes. A great example is an autonomous vehicle that continuously analyzes traffic patterns, road conditions, and unexpected obstacles (like pedestrians or road closures) to adjust its route and speed accordingly.
-
Proactivity: Rather than waiting for commands, autonomous agents anticipate needs and take initiative. Smart thermostats exemplify this by learning household routines and adjusting heating or cooling in advance, ensuring comfort while optimizing energy consumption.
-
Goal-Oriented: Autonomous agents are programmed to achieve specific objectives efficiently. In industrial settings, robots on assembly lines work highly, executing repetitive tasks continuously to meet production targets without the need for breaks.
Types of Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents are crucial in modern AI-driven systems, enabling automation, decision-making, and interaction across various domains. They differ in functionality, from simple reactive systems to advanced learning and social agents, each designed to optimize efficiency and adaptability.
 Fig 2: Types of Autonomous Agents
Fig 2: Types of Autonomous Agents
-
Software Agents: These digital agents operate within virtual environments to perform specific tasks. Examples include virtual assistants like Siri, which answer queries and set reminders, and recommendation systems like Netflix, which suggest content based on user preferences. They enhance automation and personalization in digital platforms.
-
Robotic Agents: These physical agents perform tasks in the real world using sensors and actuators. Examples include Roomba, which autonomously cleans floors, and Tesla’s self-driving cars, which navigate traffic using AI. Such agents improve efficiency in household, industrial, and transportation settings.
-
Hybrid Agents: These agents combine digital intelligence with physical components to function effectively. IoT devices like Nest smart thermostats learn user preferences and adjust home temperatures accordingly. They enable seamless automation by integrating AI-driven software with hardware control systems.
-
Reactive Agents: These agents respond instantly to stimuli without memory or strategic planning. Motion-sensing lights turn on when movement is detected, and basic AI bots react to real-time inputs. While fast and efficient, they lack adaptability and depth of decision-making.
-
Deliberative Agents: These agents use reasoning and planning to make informed decisions. GPS navigation systems analyze real-time traffic and suggest the best route, and AI-powered logistics optimize supply chain operations. They provide intelligent solutions by anticipating outcomes before taking action.
-
Learning Agents: These agents improve their performance over time through experience and ML algorithms. AI chatbots refine responses based on user interactions while self-learning cybersecurity systems detect and counter evolving threats. They continuously adapt to new data, enhancing decision-making and efficiency.
-
Social Agents: These agents interact and collaborate with humans or other AI systems using social intelligence. AI-powered customer service bots understand emotions and adjust responses, while collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans in manufacturing. Their goal is to enhance teamwork, communication, and problem-solving.
By leveraging these different types of autonomous agents, businesses and industries can streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Secure AI Framework Implementation for Enterprise Systems
How Enterprise Agentic AI Transforms Business Operations
Agentic AI transforms enterprise operations by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and optimizing workflows. Organizations can increase efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enhance productivity with AI-driven automation, intelligent process monitoring, and self-learning AI agents. As businesses strive for digital transformation, AI is crucial in streamlining operations and unlocking new growth opportunities.
Agentic AI-driven decision-making for Operational Efficiency
Decision-making is critical to enterprise operations, and AI significantly improves its accuracy and speed. By leveraging predictive analytics, big data processing, and real-time monitoring, AI systems analyze vast amounts of information to generate actionable insights.
-
Reduced Operational Costs: AI automates manual workflows, reducing reliance on human labour and lowering expenses.
-
Improved Accuracy: AI eliminates human biases and errors by making data-driven decisions.
-
Faster Decision-Making: AI-powered algorithms process data in real time, enabling businesses to react to changing conditions instantly.
-
Scalability: AI can handle complex, enterprise-wide operations, making it ideal for large-scale business environments.
For example, AI-powered financial analysis tools can evaluate historical spending patterns to optimize budget allocation, while AI-driven supply chain models predict demand fluctuations to prevent inventory shortages.
Architectures and Frameworks of Autonomous Agents
Architecture Components
These blueprints define the overall structure and organization of an autonomous agent's functionalities. Here are two common approaches:
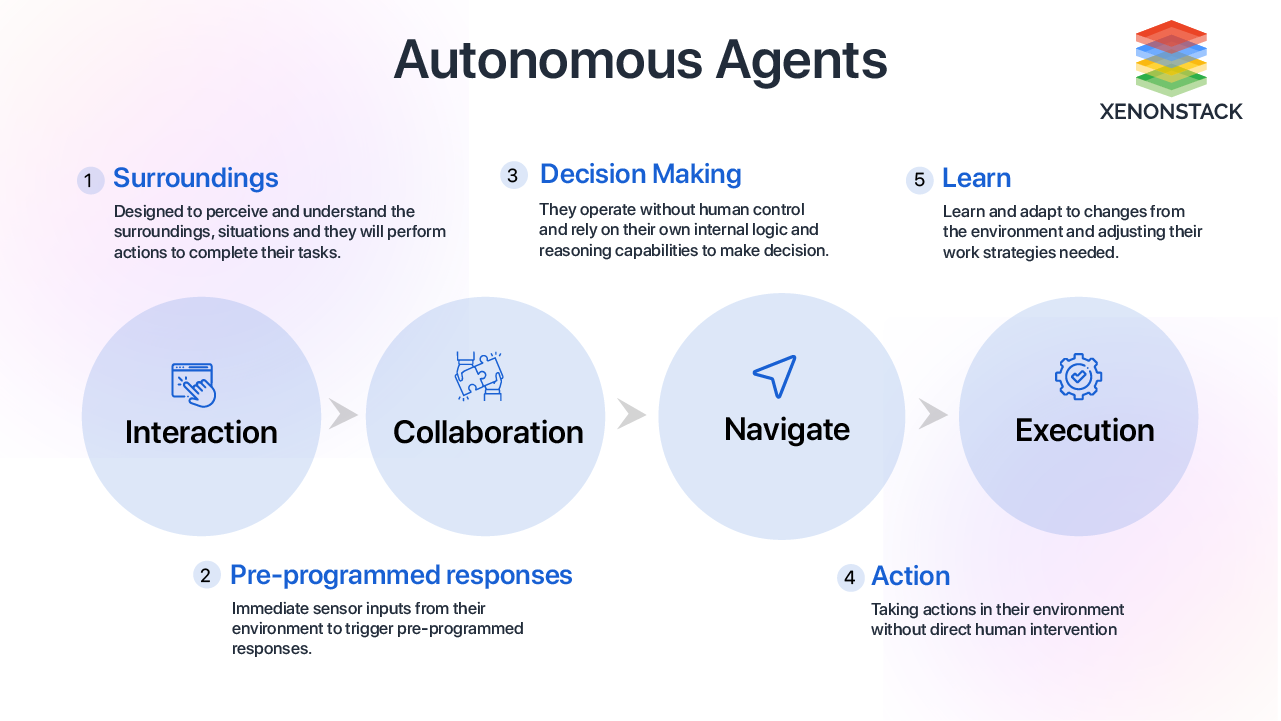
Fig 3: Architecture Components of Autonomous Agents
1. Layered Architecture
This popular approach breaks down the agent's functionalities into distinct layers, each with a specific purpose:
-
Perception Layer: Gathers and processes sensor data (cameras, LiDAR) to understand the environment.
-
Decision-Making Layer: Analyses information, reasons about actions, and chooses the best course of action based on goals.
-
Action Layer: This layer executes the chosen action by controlling motors, actuators, or communication interfaces (e.g., sending commands to a robot arm).
-
Learning Layer (Optional): Continuously improves the agent's performance by learning from experience and adapting its behaviour (e.g., reinforcement learning).
2. Behaviour-Based Architectures
This approach decomposes the agent's behaviour into smaller, independent modules called "behaviours." Each behaviour represents a specific task or response (e.g., obstacle avoidance, following a path).
The agent can activate or prioritize different behaviours based on the situation, leading to flexible and adaptable behaviour (e.g., switching from obstacle avoidance to path following when the path is clear).
Frameworks
These tools streamline development by offering pre-made components, libraries, and development environments. Imagine them as toolkits for building autonomous agents. Here's the benefit:
-
Faster Development: Frameworks offer pre-built components like sensor data processing libraries, communication protocols, and even modules for specific algorithms (e.g., learning algorithms). This saves developers time and effort compared to building everything from scratch.
-
Functionality Boost: Frameworks offer added functionalities such as debugging and testing tools, aiding developers in pinpointing and resolving agent behaviour issues.
Popular Frameworks
-
Robotic Operating System (ROS): A widely used open-source framework for robot software development, ROS offers tools for communication, sensor data handling, and device drivers.
-
JaCaMo is a Java-based framework for developing multi-agent systems. It provides functionalities for agent communication, belief representation, and reasoning.
-
Agent Foundation (AF) is a framework offering tools for building knowledge-based agents. It supports logic programming languages for knowledge representation and reasoning.
An Autonomous Agent's Workflow Example
Let's consider an autonomous agent designed to assist with research tasks. Suppose we want the agent to summarize the latest news about "Twitter."
We instruct the agent with the following objective: "Find and summarize the recent news about Twitter."
The agent first breaks down the objective into a series of tasks:
- Search Google for news related to Twitter.
- Read the content of the relevant news articles.
- Summarize the critical information from the articles.
The agent starts by executing the first task, searching Google for Twitter-related news and compiling a list of relevant links.
Next, the agent reviews the original objective and the completed task, recognizing that the next step is to read the content of the gathered news articles. This ensures the agent has the necessary information to fulfil the final task of summarizing the news.
After carefully reading the articles, the agent confirms that the only remaining task is to write a summary. The agent then synthesizes the key points from the news content and delivers the final summary as requested.
Use Cases in Autonomous Agents

Fig 4: Use Cases of Autonomous Agents
Manufacturing
Autonomous agents enhance production efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization. AI-driven robots adjust to dynamic conditions, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Key Use Cases
-
Quality control: AI ensures defect detection and consistency.
-
Predictive maintenance: Prevents unexpected equipment failures.
-
Supply chain management: Optimizes logistics and inventory.
With a projected CAGR of 45%, AI-driven automation is revolutionizing manufacturing and boosting productivity and safety.
Healthcare
AI-powered agents improve patient monitoring, diagnostics, and personalized treatments. Wearable sensors track vitals, while AI analyzes medical images with high precision.
Key Use Cases
-
AI-driven diagnostics – Faster, more accurate disease detection.
-
Personalized treatment plans – AI tailors care based on patient data.
-
Drug discovery – AI speeds up research and clinical trials.
The sector is expected to grow at 40% CAGR, enhancing accessibility and efficiency in healthcare.
Transportation
Autonomous agents drive innovation in self-driving cars, traffic management, and logistics automation. AI-powered systems reduce accidents, optimize routes, and enhance delivery efficiency.
Key Use Cases
-
Autonomous vehicles – Reducing human error in transportation.
-
Drone deliveries – Automating last-mile logistics.
-
Traffic optimization – AI reduces congestion and fuel waste.
With a 38% CAGR, the adoption of AVs and drones is reshaping mobility, though regulatory challenges persist.
Finance & Banking
AI-powered agents automate trading, fraud detection, and customer service, improving financial security and decision-making.
Key Use Cases
-
Algorithmic trading – AI executes optimized investment strategies.
-
Fraud detection – Identifies suspicious transactions in real-time.
-
AI-driven financial advising – Provides personalized insights.
The industry, with a 35% CAGR, leverages AI to enhance security, efficiency, and customer engagement.
Energy & Utilities
Autonomous AI improves energy efficiency, grid management, and predictive maintenance in the utilities sector.
Key Use Cases
-
Smart grid management – Optimizes energy distribution.
-
Renewable energy integration – Balances supply with demand.
-
Predictive maintenance – Extends equipment lifespan.
With a 30% CAGR, AI is revolutionizing energy sustainability and resource optimization.
Retail & E-commerce
AI-driven systems personalize shopping experiences, automate logistics, and optimize pricing.
Key Use Cases
-
Personalized recommendations – AI tailors shopping suggestions.
-
Inventory & demand forecasting – Prevents stock shortages.
-
AI chatbots – Enhances customer support.
Projected to grow at 42% CAGR, AI is transforming customer engagement and operational efficiency.
Customer Service
AI-driven agents streamline customer interactions, reducing costs and response times while improving satisfaction.
Key Use Cases
-
Chatbots & virtual assistants – Handle routine queries 24/7.
-
Sentiment analysis – AI understands customer emotions.
-
Support automation – AI optimizes ticket resolution.
AI-driven customer service solutions enhance efficiency, scalability, and personalization across industries.
Benefits of Autonomous Agents
Challenges and Considerations in Autonomous Agents
As autonomous agents become more prevalent, organizations must address key challenges to ensure ethical, secure, and seamless integration. From ethical concerns to regulatory compliance, a structured approach is needed to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
-
Ethical Implications and Responsibility: Autonomous agents raise concerns about accountability, decision-making in critical situations, and job displacement. Ethical guidelines, industry regulations, and workforce reskilling programs are essential to ensure responsible deployment.
-
Security Risks and Data Privacy: AI agents handle vast data, making them vulnerable to cyber threats and breaches. Strong cybersecurity measures, encryption, and compliance with data protection regulations are crucial to safeguarding sensitive information.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Deploying autonomous agents requires overcoming technical and workforce challenges. A phased approach, clear communication, and training programs help ease resistance and ensure smooth adoption.
-
Regulatory and Compliance: Rapid AI advancements often outpace regulations, creating legal uncertainties. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies and designing adaptable AI systems ensure long-term compliance and risk mitigation.
Future of Autonomous Agents
Rapid advancements in AI, machine learning, and robotics are driving the future of autonomous agents, leading to more intelligent, adaptive, and self-governing systems. As industries integrate these agents, they will play a critical role in shaping the next generation of automation and decision-making.
-
Greater Autonomy and Decision-Making: Future autonomous agents will require minimal human oversight, leveraging advanced AI models for complex decision-making. These agents will self-learn, self-optimize, and operate in dynamic environments with higher accuracy and reliability.
-
Expansion Across Industries: Autonomous agents will become essential in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and smart cities. From AI-driven medical diagnostics to self-regulating energy grids, their applications will enhance efficiency and sustainability across sectors.
-
Human-AI Collaboration: AI agents will augment human roles rather than replace them, improving productivity and decision-making. Organizations will focus on collaborative AI, where autonomous agents assist professionals in high-value tasks while handling repetitive processes.
-
Ethical and Regulatory Evolution: With AI playing a bigger role in society, governments and organizations will develop stricter regulations on AI ethics, accountability, and fairness. The future will see global AI governance frameworks ensuring responsible and bias-free AI deployment.
-
Integration with Emerging Technologies: Autonomous agents will integrate with blockchain, IoT, and quantum computing to enhance security, transparency, and computational power. This convergence will redefine industries, from automated supply chains to AI-driven smart contracts.
As autonomous agents evolve, they will drive unprecedented efficiency, innovation, and transformation, shaping a future where AI-powered automation enhances every aspect of business and society.
Next Steps with Autonomous Agents
Talk to our experts about implementing Enterprise Agentic AI for Autonomous Digital Operations. Discover how industries and business functions leverage Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence to become decision-centric enterprises. Harness AI-driven automation to optimize IT support and operations, enhancing efficiency, agility, and responsiveness in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.



