What are Coroutines? An Introduction to Asynchronous Programming
A coroutine is a general control structure where flow control is cooperatively passed between two different routines while returning. They are computer program components that generalize subroutines for non-preemptive multitasking, allowing execution to be suspended and resumed. Coroutines are well-suited for implementing familiar program components such as:
-
Cooperative Tasks
-
Exceptions
-
Event Loops (such as those used in GraphQL query resolvers)
-
Iterators
-
Infinite Lists
Developing Android applications is a great option to drive success to your business but, picking up the best programming language is the real dilemma. Click to explore about, Kotlin vs Java
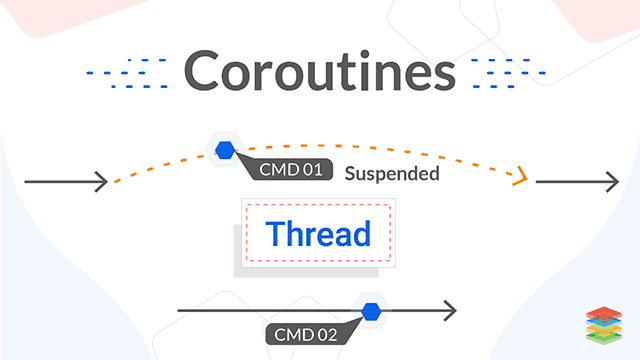
How Do Coroutines Work? Understanding Execution Flow and Scheduling
Coroutines are rescheduled at specific points in the program and do not execute concurrently. Because of this, programs using coroutines can avoid resource locking, which is a common challenge in traditional multithreading. This makes them a key component of event-driven or asynchronous programming patterns, often used in modern frontend frameworks like ReactJS and Angular.
-
In Code-Splitting in ReactJS, coroutines can help manage lazy-loaded components efficiently.
-
In Angular Dependency Injection, coroutines can be used for handling service instantiation and background tasks asynchronously.
Unlike threads, which are preemptively scheduled, coroutines must be explicitly suspended and resumed. This allows them to integrate well with Module Pattern in JavaScript, ensuring efficient memory usage and execution control.
Key Benefits of Coroutines: Performance, Efficiency, and Scalability
The benefits of Coroutines are listed below:
-
Asynchronous Execution – Efficient implementation in asynchronous programming.
-
Functional Programming Integration – Enables functional programming techniques, as seen in Functional Programming vs OOP discussions.
-
Efficient Resource Management – Requires fewer resources compared to traditional threads.
-
Pre-emptive Scheduling – Allows scheduling with less overhead than traditional threading.
-
Optimized Performance – Helps keep the system's resource utilization high.
-
Reduced Resource Locking – Minimizes the need for locks, making applications more efficient.
-
Improved Locality of Reference – Enhances memory access efficiency.
-
Python Support – Plays a key role in Python Functional Programming, where generators and async functions behave similarly to coroutines.
Kotlin Application Container can be deployed either by kubernetes Dashboard or Kubectl (Command line). Click to explore about, Kotlin Application Deployment
Top Use Cases of Coroutines in Modern Software Development
The use cases of coroutines are listed below:
State Machine
State Machine is useful to implement state machines within a single subroutine, where the state is determined by the current entry or exit point of the procedure. This results in the more readable code as compared to the use of goto.
Actor Model
Actor Model is very useful to implement the actor model of concurrency. Each actor has its own procedures, but they give up control to the central scheduler, which executes them sequentially.
Generator
Generator is useful to implement generators which are useful for streams particularly input/output and for traversal of data structures.
Communicating Sequential Process
Communicating sequential process is useful to implement communicating sequential processes where each sub-process is a coroutine. Channel input/output and blocking operation yield coroutines and a scheduler unblock them on completion events.
Reverse Communication
Reverse communication, which is commonly used in mathematical software, is useful to implement, wherein a procedure needs the using process to make a computation.
Coroutines vs. Subroutines vs. Threads
Subroutines are the special cases of coroutines. When subroutines are called, execution begins at the start, and once subroutines exit, it is finished. An instance of a subroutine only returns once, and it does not hold state between invocations. This is very much similar to threads. However, coroutines are cooperatively multitasked while threads are preemptively multitasked. This means that coroutines provide concurrency, not parallelism.
CI is the development practice that automates the integration of source code from different developers working on a single software project. Click to explore about, Java Serverless Microservices
Why Coroutines Are Essential for High-Performance Applications
In order to read a file and parse it while reading into some meaningful data, one can either read it step by step at every line or may also load the entire content in memory, which would not be recommended for large text cases e.g text editors like Microsoft Word. In general, to throw away the stack concept completely, it is needed. And also when we want things to do concurrently i.e. non-preemptive multitasking, we need coroutines for concurrency.
Next Steps in Implementing Coroutines in Your Projects
Talk to our experts about implementing coroutines and asynchronous programming. Learn how industries and different departments use event-driven architectures and functional programming to enhance workflows and decision-making. Utilize coroutines to automate and optimize IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness.


