
Introduction
Data privacy has become a crucial aspect for companies and customers as well. Over the years, We have been storing more and more information on the internet. This information includes our address, PII, contact details, and information about the websites we visit by allowing websites to read our cache. So this is impossible to deny that details or information of an organization or particular individual is not there on the internet. Now the question arises, is this all safe. Do we have data privacy? How we can make sure that our data is used appropriately. Let's walk through this blog and learn how data privacy works to answer all these questions.
Challenges related to Data Privacy
At user level
- Online tracking: Our behavior is tracked online, and we sometimes consent websites to use cookies. But most of the time, we don't measure up to what degrees cookies are recording our activities.
- Losing control of data: We often visit many websites, and when we give consent to websites to our data, such as cookies, we lose control over how our data is being used beyond the website we interact with.
- Less Transparency: When we visit various websites, It is commonplace that we add our personal information there, like name, age, address, and phone number. And more often, it is the case that the policies are tough to understand how will use this personal data.
- Social Networking Websites: We use social networking sites too much. Although we know how our data is protected, we miss other aspects of privacy, such as: when we are online and for how much time and what we like most. That data can be used without our consent.
At the Organizational level
- Lack of Communication: Organizations Sometimes fail to communicate what data they are using and how they will use it.
- Data Breaches: Data breaches can become the reason for massive data privacy violations if personal data is leaked.
- Insider Threat: Internal Workers or Employees can use personal data inadequately if it is not appropriately protected.
What is Data Privacy?
Data Privacy generally means knowing to what extent, how, where, and with whom someone's data is shared with others. In other words, data privacy talks about how data should be stored, collected, and shared with other companies. Personal data includes PII data, addresses, and someone's behavior online. Data privacy and protection depend on end-users. They should know the rights and privileges of data privacy. The customer's right to consent on how companies can use their data and delete data they share with the company.
Companies often use customer search behavior to increase their revenue and target the targeted audience. So in this fashion, one's data can be sold/given from one organization to another, which is sometimes illegal but still, it happens.
For instance, You search something on the internet and see ads related to that thing the next moment. So even after having a sound understanding of data privacy, one cannot stop the breach completely, though it can be limited to some extent.
Data discovery platforms find data faster if a new joiner within the organization requires data for analysis or to create a machine learning system.Click here to explore the complete guide for Data Discovery
Why do we need Data Privacy?
Data privacy is a fundamental human right, and laws govern these rights. So data privacy is needed when a user is engaging online. They should have trust in how their data is being used. Hence, organizations have to demonstrate data protection to their customers that their data is kept safe to get the users' trust. Data can be misused if users don't have consent over how their data is used and if there is no data protection. So there are mainly two ways of seeing the need for data privacy: at the organizational level: they have to make sure that their user trusts them, and the second aspect is the law. One must follow the data privacy laws discussed later in this blog.
Without data privacy:
- Criminals can use someone's data to harass or defraud them.
- Organizations can sell users' data to advertisers, resulting in unwanted advertisements.
- When a person's activities are tracked and monitored, their personal space is breached.
- Breaching data can ruin the company's reputation.
How we can do Data Privacy?
Some technologies help in achieving data privacy. It might seem like these tools are responsible for data security in some aspects. Well, it's true because data privacy and data security are two sides of the same coin, and we can't separate them. If we try to achieve data protection, we will eventually be moving towards data privacy. These are some of the technologies that help in doing so:
Encryption
Encryption is the process of changing data to a form that looks like random data, which is of no use without the encryption key.
Data Lineage
Making data lineage gives the idea about the whole data path, like from source to destination, and what changes have been done to the data.
Access Control
Access control makes sure that only authorized parties can access the data. Sometimes Access control is combined with DLP(data loss prevention), which stops sensitive data from going out of the network. This is also known as ownership of data which means who can access what data.
Two Factor Authentication
It helps make data more secure as it prevents attackers from accessing the data.
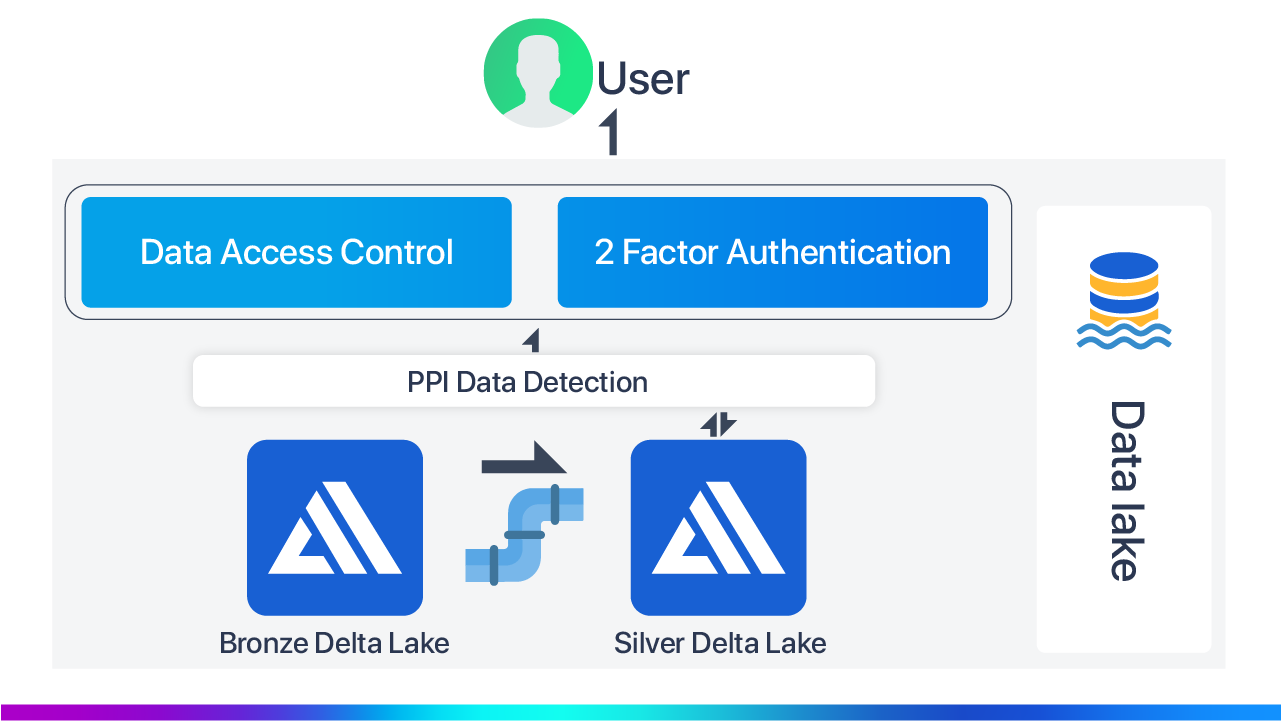
Data Compliances and encoding/encryption of specific fields(PII Detection)
Some tools can help hide or encrypt the data. When we talk about data, it is big data, and we can't do the encryption changes manually. For example, we share data with other organizations, and we don't want them to see PII data out of this data lake. In this case, we can use tools like Apache ranger, Nightfall.
Data Compliance is the method by which organizations ensure that sensitive digital information is stored and organized appropriately (with defined standards and practices) to save data from loss, corruption, or misuse.
Laws that govern data privacy
There are laws for data protection in most countries in the world. This means in every country; there are various laws for data protection. A report submitted to the Department of Health & Human Services, "Records, Computers, and Rights of Citizens (07/01/1973)", proposes universal principles for the protection and privacy of citizen and consumer data:
- For all the data collected, there should be a stated purpose.
- Information collected from an individual cannot be shared with other individuals or organizations unless authorized by the individual's consent or by law.
- Records kept on an individual should be up to date and accurate.
- When data is no longer needed for the stated purpose, they should delete data.
- Sharing personal data to locations where data protection laws are not equivalent is prohibited.
Difference between Data Security and Data Privacy
- Although these two terms are used interchangeably, technically, these two terms are different. One of them cannot survive without the other.
- Data privacy is all about proper usage of customers' data, and Data Security provides the methods and concepts by which we protect this data from third-party or unauthorized access.
- Data security deals with encryption, network security, access control, and how policies get enforced. Whereas, Data privacy is all about consent, policies, and people's right concerning their Personal Information.
- For example: suppose you log in to a website with your password, that's the method of data security, and how that website uses your data defined under data privacy.
Data is a pillar of the organization, so we must follow excellent and simple rules while storing the data. Explore about Augmented Data Quality Best Practices and its Features
Benefits of Data Privacy
Data privacy plays a vital role in the smooth and trustworthy usage of users' information by individuals and organizations. Along with that, there are various advantages of data privacy:
- Law: There are laws for data privacy in almost every country, So to follow those laws, one has to have data privacy policies applied when dealing with data.
- More minor Data Breaches: With the laws enforced for data privacy, organizations have to follow specific rules, and hence data will be more secured, and eventually, there will be fewer data breaches.
- Protecting customers' privacy: Data Privacy involves data protection policies, meaning customers' data is secured, and sensitive information doesn't end up in the wrong hands.
- Maintaining and improving the Brand value: Privacy policies describe how we will use the data. If it is done efficiently, people trust that organization, and hence, brand value increases.
Use Case Scenario
A company collects PII data of its customers or even employees; then it becomes the company's legal responsibility to store this data and how they use it. So basically, defining the who, what, why, and how to store long data defines the data policy that companies must follow.
In a particular scenario, we collect the PII data of customers. Then we do encryption or hide sensitive data from people, defining who will access data.
Suppose we have data stored in our data lake, and from that lake, we put a policy with Apache ranger, which is used to control the user access over the data. So in our use case, As we are storing the phone number, we put a policy where they cannot have access over the phone number column for all the developers.
This tool works manually, defines the user's access level, and defines the column data to be hidden, all that done manually. Still, other tools like presidio can automatically do the data encryption part with trained ML models. Here in our case, hiding a phone number or credit card number can be done automatically on a large set of data.
Conclusion
Data privacy is a method of knowing up to what extent and how we will use our data. For a very long time, We have been putting so much information about ourselves on the internet. It seems like there's our digital duplicate on the internet, and protecting that, data privacy becomes a crucial aspect. Specific laws govern data privacy, but a person needs to know how to use their data.
- Read more about The inception of Augmented Data Management
- Click to explore What is Data Observability?
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


