The automation landscape has evolved dramatically over the past decade, from simple robotic process automation to increasingly sophisticated intelligent systems. This evolution represents a journey from rule-based automation to brilliant, autonomous systems capable of learning, adapting, and making decisions. Let's explore this progression and understand how Agentic AI transforms business automation.
What is Intelligent Process Automation?
Intelligent Process Automation applies AI and related new technologies, likewise cognitive Automation, computer vision, and machine learning, to Agentic Process Automation. It blends the most advanced technologies used to manage and automate digital processes. It is used as an "assistant to humans" who perform all the manual, repetitive and routine tasks previously performed by their counterparts. This crossroads of emerging technologies produces automation capabilities that drastically improve the business value and give a competitive advantage to the organisation.
With these technologies—especially AI and machine learning—an IPA tool should learn how to change and enhance the process flow to construct an intelligent procedure. With time, it should be able to learn and develop. IPA is essential in automating increasingly significant portions of enterprise employment. IPA enables users to scale up their automation use cases more rapidly and easily and carry out more complex tasks, such as automatically detecting objects on a screen or using technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP).
 Fig 1: Intelligent Automation
Fig 1: Intelligent Automation
The Automation Evolution: From RPA to Intelligent Automation
1. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): The First Step
RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human actions but lacks AI and decision-making capabilities. It follows predefined instructions for structured data processing, making it useful for simple workflows.
Key Features of RPA
-
Rule-Based Execution: Works strictly within predefined workflows and conditions.
-
Task Automation: Automates repetitive processes like data entry and invoice processing.
-
No AI or Learning Capabilities: Cannot adapt to new patterns or unstructured data.
Examples of RPA in Action
-
Data Entry & Processing: Automates transferring structured data across applications.
-
Invoice Processing: Extracts details from invoices and updates records automatically.
-
Email Filtering & Response Automation: Sorts emails and sends predefined responses.
Limitations of RPA
-
Cannot Handle Unstructured Data: Struggles with handwritten documents, voice inputs, and complex images.
-
Lacks Adaptability: Cannot adjust to changes in business processes without reprogramming.
-
No Decision-Making Capabilities: Follows static rules and cannot learn from past tasks.
2. Hyperautomation: Expanding RPA with AI and Analytics
Hyperautomation enhances RPA by integrating AI, machine learning, and process mining to automate complex workflows. It enables systems to dynamically analyze data, learn from patterns, and optimize processes.
Key Technologies in Hyperautomation
-
AI & Machine Learning: Allows automation tools to improve over time and predict outcomes.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables AI to understand and process text for chatbots and document automation.
-
Process Mining: Identifies inefficiencies and suggests optimizations based on workflow analysis.
Examples of Hyperautomation
-
AI-Powered Chatbots: Automates customer interactions with context-aware responses.
-
AI-Driven Intelligent Document Processing: Extracts and categorizes data from invoices, contracts, and emails.
-
Predictive Analytics in Business Operations – Uses historical data to forecast demand and optimize inventory.
How Hyperautomation Improves RPA
-
Automates Complex, Knowledge-Based Tasks – Extends automation to cognitive and analytical workflows.
-
Processes Unstructured Data – Works with text, images, and spoken language.
-
Continuously Learns and Improves – AI models adapt to new business conditions.
3. Intelligent Automation (IA): The Self-Learning System
Intelligent Automation (IA) combines RPA with AI and cognitive automation to create systems that adapt and optimize processes in real time. It eliminates manual intervention and enhances decision-making capabilities.
Key Features of Intelligent Automation
-
Self-Learning Capabilities – Uses machine learning to refine automation over time.
-
Real-Time Adaptation – Adjusts to workflow changes without requiring manual updates.
-
Decision-Making Abilities – Uses AI to process data and recommend the best action.
Examples of Intelligent Automation
-
AI-Based Fraud Detection – Analyzes transaction patterns to identify potential fraud.
-
Healthcare Diagnostics Automation – Assists doctors by analyzing medical scans and patient data.
-
Supply Chain Optimization – Adjusts inventory levels based on predictive demand analysis.
How IA Improves Hyperautomation
-
Eliminates Manual Intervention – Automates decision-making without human input.
-
Learns and Adapts – Continuously improves automation accuracy based on historical data.
-
Optimizes Decision-Making – Uses AI insights to streamline business operations.
Intelligent Automation Framework
Intelligent Automation (IA) combines Artificial Intelligence (AI), Agentic Process Automation (APA), and advanced analytics to create self-learning, adaptive systems. It enhances business processes by automating tasks, optimizing workflows, and making data-driven decisions. Here’s how it works:
 Fig 2: Intelligent Automation Framework
Fig 2: Intelligent Automation Framework
-
Data Collection and Processing: IA begins by gathering structured and unstructured data from various sources, such as databases, documents, emails, and sensors. Technologies like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) help extract meaningful information from this data.
-
Process Identification and Automation: Using Process Mining and Task Mining, IA analyzes business workflows to identify repetitive and rule-based tasks. RPA is then deployed to automate these tasks, mimicking human actions like data entry, invoice processing, and email responses.
-
AI-driven decision-making: AI and Machine Learning (ML) analyze historical data to recognize patterns and improve decision-making. For example, an IA system in banking can assess loan applications based on a customer’s financial history, reducing manual review time.
-
Real-Time Adaptation and Optimization: IA continuously learns from real-time data, unlike traditional automation. Agentic AI enables systems to adapt to new scenarios, optimize processes dynamically, and make proactive adjustments without human intervention.
-
Integration with Enterprise Systems: Intelligent Automation connects with existing CRM, ERP, and cloud-based applications, ensuring seamless data exchange across departments. Low-code and no-code platforms allow organizations to implement IA without extensive coding expertise.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: IA systems include analytics dashboards and predictive insights to monitor performance. Businesses can use these insights to refine automation strategies, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation.
Document Processing with Agentic AI
Agentic AI redefines intelligent document processing by enabling autonomous, context-aware workflows that learn, adapt, and collaborate across enterprise systems. Unlike traditional automated document processing or rule-based OCR/RPA, Agentic AI agents combine natural language understanding, reasoning, and decision-making to handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured document processing tasks with unmatched accuracy.
Core Capabilities
-
Autonomous ingestion & classification – Capture and classify documents (invoices, contracts, medical records, compliance forms) from emails, portals, and scans.
-
Contextual extraction & validation – Use multimodal AI to extract fields, validate against enterprise systems, and detect anomalies or fraud in real time.
-
Adaptive integration – Sync instantly with ERP, CRM, and finance tools, streamlining automated document processing across departments.
-
Real-time decisioning – Trigger downstream actions like approvals, claims, payments, or compliance reporting with minimal human touch.
-
Compliance & security – Ensure GDPR/HIPAA adherence with built-in governance and audit trails.
-
Continuous learning – Agents improve over time, adapting to new templates, languages, and evolving business rules.
Business Impact
-
Efficiency: Reduce processing times from days to minutes through intelligent workflows.
-
Scalability: Handle millions of documents across geographies with consistent accuracy.
-
Accuracy: Minimise human error with contextual validation.
-
Cost optimisation: Lower manual processing costs and free resources for high-value work.
-
Industry applications: From healthcare claims and finance invoices to government permits and retail orders, intelligent document processing with Agentic AI enables sector-specific automation.
By orchestrating autonomous agents , Agentic AI elevates document processing into a self-optimizing function that drives agility, compliance, and operational resilience.
What are the Core Technologies involved in IPA?
For Intelligent Automation to function effectively, it integrates the following technologies:

Fig 3: Core Technologies Of IPA
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML enable automation systems to analyze patterns, predict future trends, and make data-driven decisions. They enhance automation by improving accuracy, reducing errors, and optimizing processes in real time.
-
Agentic Process Automation (APA): APA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks by mimicking human actions, reducing manual effort and increasing efficiency. It serves as the execution layer for structured workflows but lacks cognitive capabilities.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language, enabling automation in chatbots, virtual assistants, and intelligent document processing. It helps businesses extract insights from unstructured text data, improving customer interactions.
-
Process Mining & Analytics: Process Mining analyzes business workflows to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for automation. Combined with analytics, it enables organizations to optimize end-to-end processes rather than automating isolated tasks.
-
Agentic AI (Autonomous AI Agents): Agentic AI uses self-learning AI agents that analyze data, make decisions, and adapt to changing environments without human intervention. These autonomous systems continuously optimize workflows, enhancing automation efficiency and scalability.
Real-World Applications of Agentic AI in Intelligent Automation
From manufacturing and healthcare to insurance and customer service, businesses leverage Agentic AI to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall operational accuracy. Below are key industries where Agentic AI and intelligent automation are making a significant impact: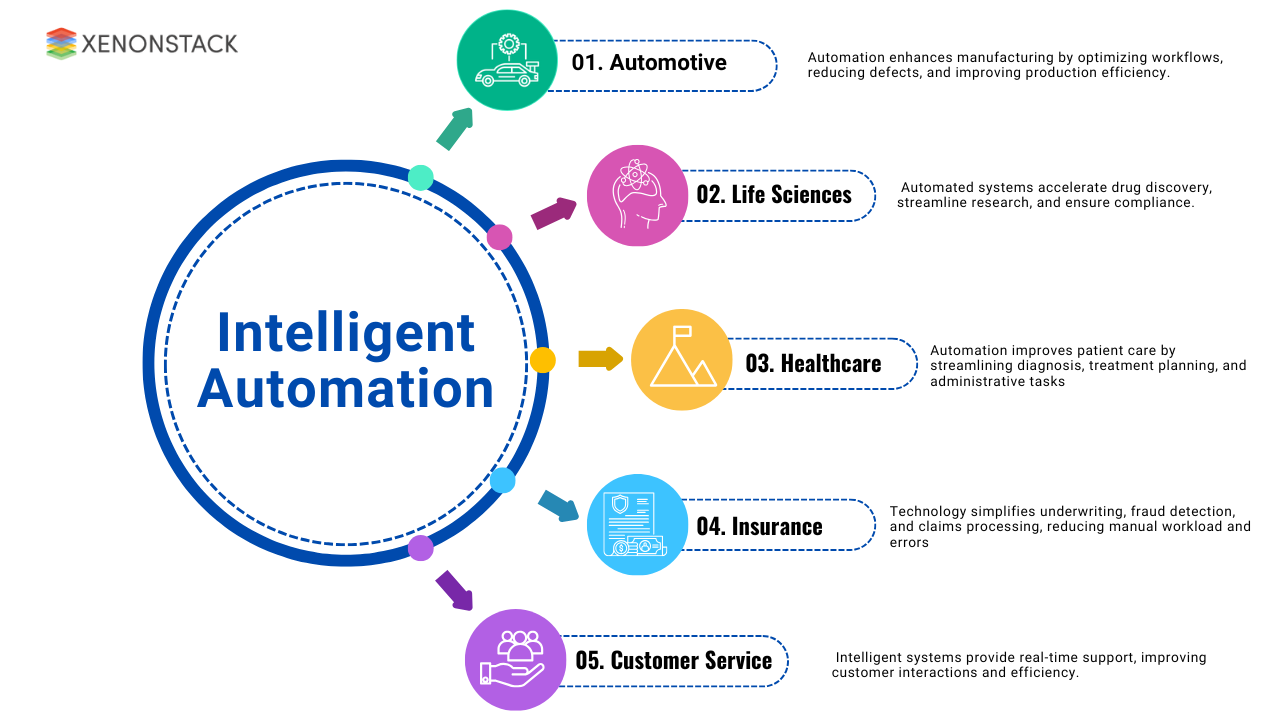
Fig 4: Use Cases of Intelligent Automation
-
Automotive: Automation enhances manufacturing by optimizing workflows, reducing defects, and improving production efficiency. Collaborative robots, like those used by Volkswagen, assist workers in assembly, ensuring precision and reducing physical strain.
-
Life Sciences: Automated systems accelerate drug discovery, streamline research, and ensure compliance. The rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines highlights how technology optimizes clinical trials and regulatory processes.
-
Healthcare: Automation improves patient care by streamlining diagnosis, treatment planning, and administrative tasks. Virtual assistants and advanced processing tools enhance remote consultations, reduce wait times, and improve hospital workflows.
-
Insurance: Technology simplifies underwriting, fraud detection, and claims processing, reducing manual workload and errors. Automated risk assessment ensures precise premium calculations and improves compliance with regulatory requirements.
-
Customer Service: Intelligent systems provide real-time support, improving customer interactions and efficiency. Automated sentiment analysis, ticketing systems, and virtual assistants enhance response times and streamline communication.
-
Business planning: In business intelligence, research, and data analytics fields, intelligent process automation helps to drive growth, future thinking, and strategic positioning. Intelligent automation can track repetitive tasks and locate unproductive areas. Automating tasks that take too much time in a business can free up employee time for more important matters.
What are the Benefits of Intelligent Automation?
- Intelligent automation transforms industries by streamlining processes, improving efficiency, and reducing operational costs. By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses can enhance productivity and adapt to evolving market demands.
-
Maximized Operational Efficiency: Automation eliminates manual inefficiencies, enabling organizations to maintain continuous, uninterrupted operations. By handling routine tasks autonomously, these systems allow human workers to focus on higher-value activities.
-
Enhanced Data-Driven Decision Making: Integrating real-time analytics improves decision-making across business functions. Automated systems can process vast amounts of data and identify patterns that would be difficult for humans to detect.
-
Scalability and Adaptive Automation: Automated solutions enable seamless scaling, ensuring businesses grow without added complexity. These systems handle increasing workloads efficiently, reducing the need for additional resources.
-
Personalized User Experience: By analyzing behavioural patterns, automation tailors interactions for improved customer satisfaction. This leads to more relevant, timely, contextual engagements with customers and employees.
-
Cost Optimization: Automating complex workflows reduces costs by minimizing reliance on manual labour. Organizations can allocate resources more strategically, focusing on innovation and long-term growth.
Intelligent Automation Tools
To successfully implement Intelligent Automation (IA) and Agentic AI, businesses leverage a combination of APA (Agentic Process Automation), AI-driven automation, cognitive AI agents, and workflow orchestration tools. These tools help automate complex business processes, improve decision-making, and enable autonomous operations. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of these tools:
 Fig 5: Intelligent Automation Tools
Fig 5: Intelligent Automation Tools
Open-Source Intelligent Automation Tools
Open-source tools provide flexibility, customization, and cost-effective automation solutions without vendor lock-in. These tools are widely used for workflow automation, AI-driven decision-making, and cognitive automation.
1. Apache Airflow – Workflow Orchestration
Apache Airflow is a workflow automation and orchestration platform designed to schedule, monitor, and manage complex business workflows.
-
Used primarily for data pipeline automation, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, and AI model execution.
-
It allows users to build scalable, repeatable workflows that automate data processing, making it a crucial tool for businesses handling large-scale data operations.
2. Robot Framework – APA for Task Automation
Robot Framework is a powerful, open-source APA (Agentic Process Automation) tool designed for automating repetitive tasks.
-
Supports web testing, API automation, and AI integrations, making it useful for software testing and process automation.
-
Compatible with Selenium, Appium, and REST APIs, allowing seamless testing and workflow execution across multiple platforms.
3. Camunda – Business Process Management (BPM)
Camunda is a BPM (Business Process Management) platform that helps businesses automate, analyze, and optimize workflows.
-
Provides BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) support for mapping and automating business processes.
-
Integrates AI-powered decision-making to streamline approval processes, compliance workflows, and enterprise automation.
4. AutoGPT & BabyAGI – Autonomous AI Agents
AutoGPT and BabyAGI are AI-driven autonomous agents that take intelligent automation to the next level.
-
These tools self-learn and make decisions autonomously, performing tasks such as research automation, data processing, and AI-based workflow execution.
-
Used for automating knowledge-based work, reducing manual intervention in strategic decision-making and operational tasks.
5. ProcessMaker – AI-Driven Workflow Automation
ProcessMaker is a low-code workflow automation platform designed for BPM, AI-powered decision-making, and automated document processing.
-
Allows businesses to automate approval processes, invoice processing, and enterprise workflows using AI and automation tools.
-
Supports integration with APA and AI models to enhance business efficiency and reduce operational bottlenecks.
Enterprise-Grade Automation Platforms
Enterprise automation platforms provide scalable, AI-driven solutions for large organizations. These tools are designed for end-to-end automation, integrating AI with business process automation to enable intelligent, data-driven operations.
1. UiPath – AI-Powered APA & Hyperautomation
UiPath is a leading APA and hyperautomation platform used for automating large-scale business processes.
-
This includes intelligent document processing (IDP), which automates data extraction from invoices, contracts, and reports.
-
Offers AI-driven bots that enhance process automation with machine learning-based decision-making.
2. Blue Prism – AI-Driven Enterprise APA
Blue Prism is an enterprise-grade APA solution designed for industries like banking, healthcare, and finance.
-
It combines AI and machine learning with automation to optimize repetitive, data-driven tasks.
-
Supports scalable digital workforce solutions, reducing dependency on human intervention in critical business operations.
3. Automation Anywhere – Cloud-Native APA & AI Integration
Automation Anywhere provides cloud-native APA with advanced AI capabilities.
-
Integrates AI-powered analytics with Bot Insight, enabling businesses to track and optimize automation performance in real-time.
-
Supports AI-driven automation workflows, making it a powerful tool for organizations moving towards intelligent process automation.
4. Microsoft Power Automate – AI-Integrated Low-Code Automation
Microsoft Power Automate is a low-code automation platform that connects with Azure AI services for intelligent decision-making.
-
Allows users to automate workflows across Microsoft 365, Dynamics 365, and third-party applications.
-
Supports AI-driven chatbots, workflow orchestration, and agentic process automation for end-to-end business process automation.
5. IBM Watson Orchestrate – AI-Powered Cognitive Automation
IBM Watson Orchestrate is a cognitive automation tool that leverages Agentic AI for enterprise process automation.
-
Uses natural language understanding (NLU) and machine learning to automate knowledge-based tasks.
-
With minimal human intervention, businesses can automate data-driven decision-making, customer support, and HR processes.
Challenges and Consideration in Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation offers efficiency and scalability but comes with challenges. Ethical concerns arise from AI biases and lack of transparency, while regulatory compliance with laws like GDPR adds complexity. Integrating automation with legacy systems is difficult, and scaling requires continuous optimization.
Security risks, including cyberattacks and data breaches, demand strong protections. Workforce resistance due to job displacement fears highlights the need for upskilling and trust-building. Automation errors can also escalate quickly, making human oversight essential.
A balanced approach—combining AI governance, security, and workforce adaptation—is key to leveraging automation effectively while minimizing risks.
The Future of Intelligent Automation with Agentic AI
The evolution of Agentic AI is expected to drive the emergence of fully autonomous, self-regulating AI ecosystems that:-
Hyper-Autonomous Workflows: Agentic AI will go beyond rule-based automation to make real-time, context-aware decisions, reducing human intervention in business processes.
-
Adaptive Learning & Optimization: Unlike traditional automation, these AI agents continuously learn from interactions and refine their strategies for efficiency and accuracy.
-
Cross-Industry Disruption: From finance (fraud detection, risk assessment) to customer service (AI-powered assistants) and manufacturing (self-adjusting supply chains), Agentic AI will redefine operations.
-
Human-AI Collaboration: Instead of replacing humans, intelligent agents will act as co-pilots, augmenting decision-making and handling repetitive tasks.
-
Ethics & Governance Challenges: With increased autonomy comes the need for robust regulations, bias mitigation, and accountability frameworks.
Next Steps with Intelligent Automation
Talk to our experts about implementing intelligent automation, how industries and different departments leverage AI-driven workflows and decision intelligence to become more decision-centric. Utilize AI to automate and optimize IT support and operations, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)





