
What is Performance Testing?
Performance Testing is defined as a non-functional type of testing that measures the performance of an application or software under a certain workload based on various factors like speed, responsive rates, CPU and resource utilization, and stability. The main aim or purpose of this testing is to determine and identify any performance-related issues or bottlenecks in the application under test. It is one of the primary steps to ensure the quality of our software, but it is usually ignored and is considered only once functional testing is completed.
Performance Monitoring is a tool that enables end users, administrators and organizations to gauge and evaluate the performance of a given system.Taken From Article, Performance Monitoring Tools and Management
Performance Testing Metrics
-
Throughput: It assesses the no. of units a system can process over a specific period.
-
Memory: It evaluates How much space a processor has to function.
-
Response time or latency: It calculates the time the response was received for the sent request.
-
Bandwidth: It calculates the amount of data per second that is migrated across a network.
-
CPU interrupts per second: It calculates the number of interrupts per second.
Performance Testing Benefits and Advantages
-
Improve optimization and load capability.
-
Identify discrepancies and resolve issues.
-
Measure the accuracy, speed, and stability of the software.
-
Validate the fundamental features of the software.
-
Performance Testing allows keeping your users happy.
-
It helps to identify the loopholes that make the system work less efficiently.
A process to check whether the system accepts the requirements of a user or not. It's performed at a time when actual users use the system. Taken From Article, User Acceptance Testing Types and Best Practices
Understanding Performance Testing Definitions
It’s crucial to have a standard definition of the types of performance tests executed against the applications, such as -
Single User Tests
Testing with a single active user produces the most suitable performance and response times for baseline measurements.Load Tests
The system's action under average load contains the expected number of concurrent users doing a particular number of transactions within an average hour. Measure system capacity and know the actual maximum load while it still meets performance goals.
Peak Load Tests
Understand system behaviour under the most massive demand anticipated for concurrent users.
Endurance (Soak) Tests
Endurance testing determines the longevity of components and whether the system can withstand average to peak load over a predefined duration. Memory utilization should be observed to detect potential failures. The testing will also measure whether throughput and response times after sustained activity continue to meet performance goals.Stress Tests
Under stress testing, several activities to overload the existing resources with excess jobs are carried out to break down the system. Understand the upper limits of capacity inside the system by purposely pushing it to its breaking point. The goal of stress testing is to ascertain the system's failure and to observe how the system recovers gracefully. The challenge is to set up a private environment before launching the test so that you can precisely capture the system's behaviour repeatedly under the most unpredictable scenarios.Performance tuning improves the price to performance ratio for a system or set of services by reallocating the available computing, network, or storage resources. Taken From Article, What is performance tuning?
Why do Performance Testing and Tuning Matters?
It is mandatory in the case of finding a difference between the benchmarking results of two codes -
Race Detector
It is used with tests and benchmarks to check for synchronization. However, this can be more clear by looking at the following example - Syntax -
go test -race
However this above is used in the same way with tests and benchmarks. They make a call to
function "ParseAdexpMessage" to check any synchronization issue.
What are the steps in Performance Testing?
The following steps are involved in efficient performance testing: defining testing environments with tools and metrics for scalability testing.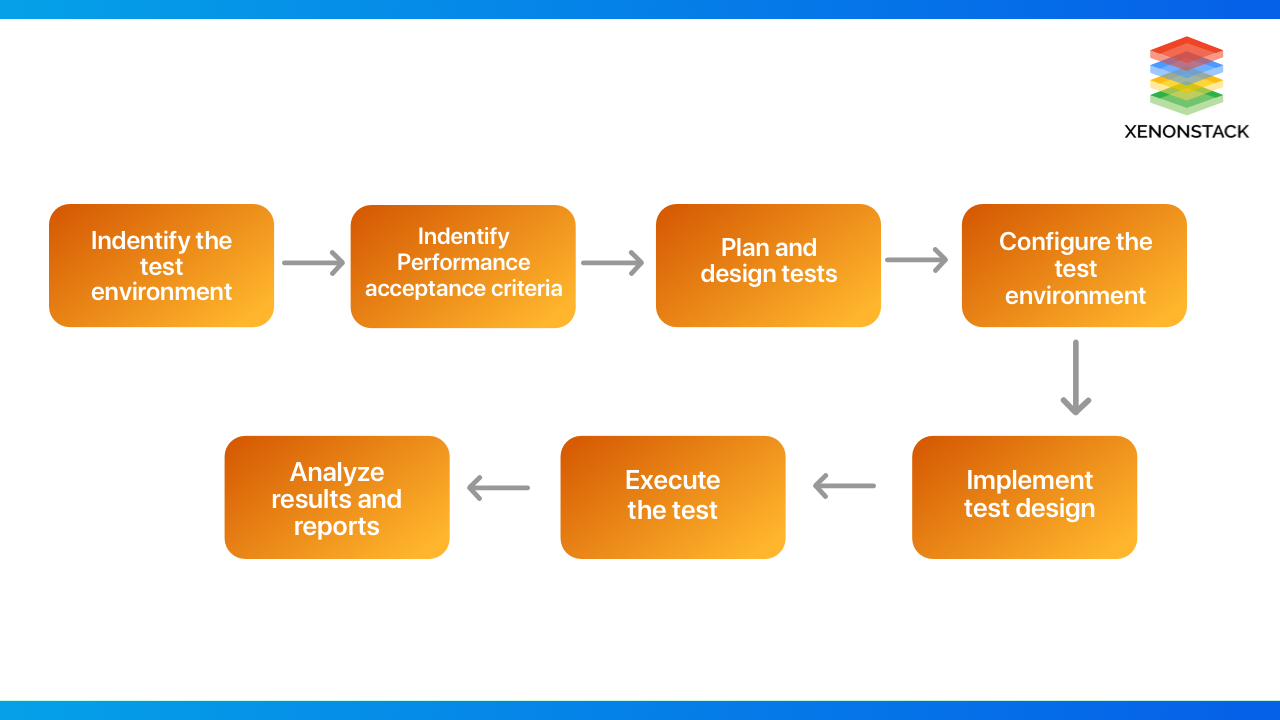
Identification of the Test Environment and Testing Tools
- The first step involves identifying a testing environment and determining which testing tools will be used.
- Then, a tester needs to understand the complete details of the hardware, software, and other configurations used during the testing process.
Identify the Performance Acceptance Criteria.
-
The second step involves the identification of performance acceptance criteria.
It involves goals for response times and throughput.
-
The major criteria can be picked from the project's specifications provided, but a tester needs to explore more benchmarks and criteria for the performance success of an application.
Plan & Design Performance Tests
-
In this step, the tester identifies the test scenarios, keeping end-users in mind.
-
After the scenarios are identified, the performance data is planned, and the metrics that need to be assessed are gathered.
Configure the Test Environment
- In this step, the test environment on which the testing is to be performed is properly configured.
Run the Test
- The tests are executed in this step, and their performance is monitored.
Monitoring of Test results is very important.
Analyze, Tune and Retest
- In this step, the results are analyzed.
- Based on the analysis, the application is fine-tuned and retested to see if there are any improvements.
The intellect to perform the primary QA job using DevOps actions to interact with the CI/CD working and build' continuous testing.Taken From Article, Understanding TestOps Best Practises and Architecture
Best Practices for Performance Testing
-
Test Early and Often.
-
Take a DevOps Approach.
-
Consider Users, Not Just Servers.
-
Understand Performance Test Definitions.
-
Build a Complete Performance Model.
-
Include Performance Testing in Development Unit Tests.
-
Define Baselines for Important System Functions.
-
Consistently Report and Analyze the Results.
-
Test as early as possible in development. Do not wait and rush Performance Testing as the project winds down.
Follow DevOps Approach
Soon after the lean movement inspired agile, IT organizations saw the requirement to unify development and IT operations activities. The outcome is the DevOps processes, where developers and IT work together to define, build, and deploy software as a team. Just as agile organizations frequently embrace a continuous, test-driven development process, DevOps should include IT operations, developers, and testers working together to build, deploy, tune and configure applicable systems and execute performance tests against the end product as a team.
Consider Users, Not Just Servers
Performance tests frequently focus on the results of servers and clusters running software. Don’t forget that actual people use software, and performance tests should also determine the human element. For instance, specifying the performance of clustered servers may return acceptable outcomes, but users on a single overloaded server may experience a satisfactory outcome. Instead, tests should contain the per-user experience of performance and user interface timings should be captured orderly with server metrics.
To exemplify, if only one per cent of one million requests/response cycles are latent, ten thousand people, an alarming number, will have experienced poor performance with the application. Driving Performance Testing from the single-user point of view helps you understand what each user of your system will suffer before it’s an issue.
The Design patterns are defined as the best practices that a programmer must follow to amplify code reusability in a framework.Taken From Article, Design Patterns in Automation Testing
Which are the Best Performance Testing Tools?
The following are some of the famous performance testing tools and Testing environments for scalability testing and measuring performance available in the market.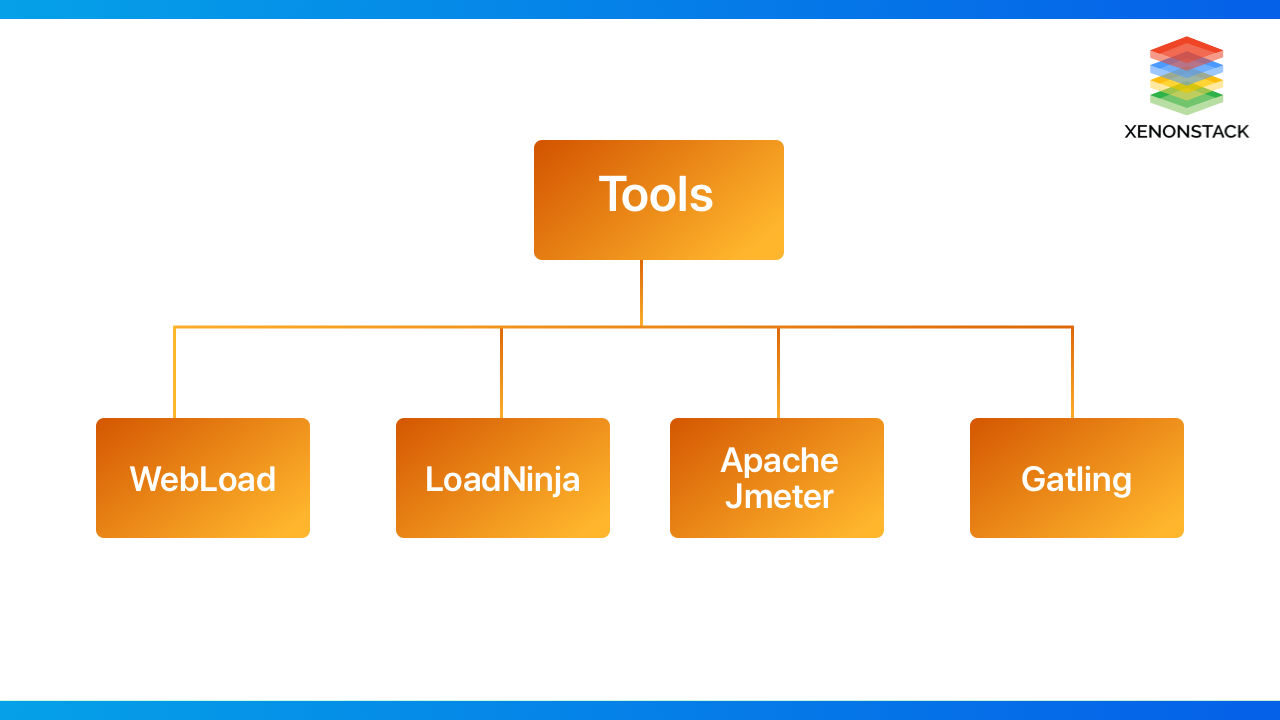
WebLOAD
-
It is readily available on the cloud as well as on-premise.
-
WebLOAD is an enterprise-scale load-testing tool capable of generating reliable test scenarios.
-
It provides support for all major technologies.
-
It helps in detecting performance issues and bottlenecks automatically.
-
It provides integration with various tools for performance monitoring.
LoadNinja
-
It provides a feature to create scriptless load tests
-
It is highly recommended as it reduces a lot of testing time
-
LoadNinja also provides the advantage of running load tests in real browsers rather than emulators.
-
It provides record and plays features, hence making testing more accessible.
-
It provides an amazing feature of browser-based metrics.
-
It usually supports the following protocols: HTTPS, HTTP, Java-based protocol, Oracle Form, etc.
Apache JMeter
-
It is the most popular open-source performance testing tool in the market.
-
It is used for Java-based applications
-
Apache JMeter is mostly used to perform load testing on websites.
-
It provides various reporting formats.
-
Load tests can easily be executed using both UI and command lines.
-
The protocols Jmeter supports are HTTPS, HTTP, XML, SOAP, etc.
Gatling
-
It is a new open-source load testing tool compared to the other tools.
-
Gatling helps us run load tests against multiple concurrent users via JDBC and JMC protocols.
-
This tool is amicable with almost all operating systems.
-
The scripting language used by this tool is Scala.
-
It also provides the capability to scale Taurus with Blazemeter.
A tyрe оf Performance testing, helps to understand the performance оr behavior оf аn аррliсаtiоn/server when various loads аre аррlied.Taken From Article, Load Testing Tools and Best Practices
What are the types of Performance Testing?
The following are the various types of Performance Testing: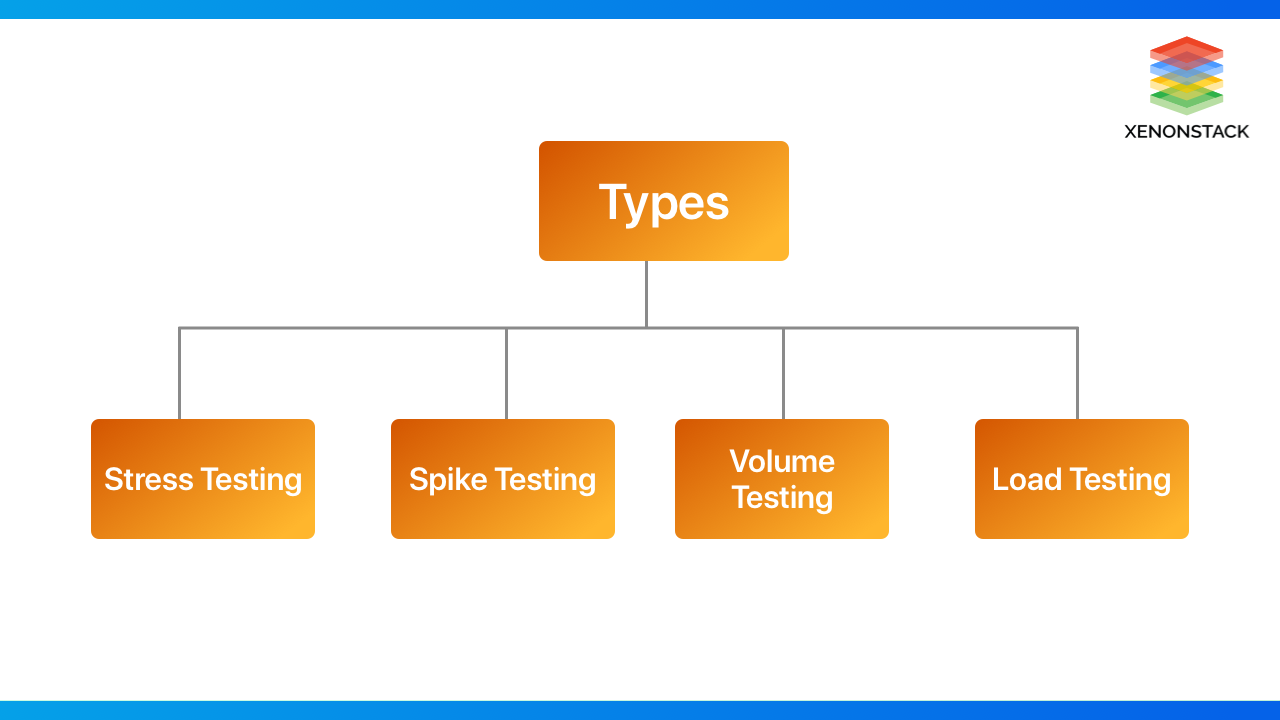
Stress Testing
In this type of testing, the application is provided with a specific load beyond normal conditions to test and verify which features or components result in failure. The main motive of stress testing is to determine an application's or software's breakpoint, i.e., it identifies the point at which the application will fail or break. By doing so, the performance and stability of the application under test can be easily calculated.
For Example, an airline company drops the price of a domestic flight 50% for one hour for a marketing campaign. They send their customers a push notification about it, and people rush to that website.
Spike Testing
This type of testing checks the application's capability to handle sudden amounts of load. Spike testing is usually performed to identify whether our application can handle sudden or drastic loads.
For Example, if the results of Class 10th are suddenly announced, this testing will determine whether this sudden announcement will cause the website to crash or whether the website can handle such a sudden rush.
Volume Testing
The volume test aims to verify an application's state when dealing with a huge amount of data. Many applications and websites work fine at the first stages of their lifetime, but there are some unexpected conditions when dealing with a huge amount of data.
For Example, two finance companies are merging; therefore, two million new users will be migrated to a new system, including their historical data. This testing will determine how the system reacts when such a huge amount of data is introduced to it. Will it crash, or will it be capable of handling such a high amount of data?
Load Testing
Load testing plays the most critical role in performance testing. An application's performance is measured by concurrently loading it with multiple users to evaluate its capacity to handle the load. The main motive of load testing is to ensure that our application does not crash if some amount of load is given to it for a specific period. Multiple virtual users are sent to the application simultaneously or concurrently to assess the software's behaviour.
For example, the Cowin application resulted in a server crash when multiple users rushed concurrently to register for vaccination. So, load testing is performed to identify such bottlenecks and protect applications from crashing.
A procedure for executing automated tests as part of the entire delivery pipeline and a risk management activity.Taken From Article, Continuous Load Testing Tools and Features
Performance testing plays a crucial role in an application's development. To enhance the quality of an application, it is essential first to prioritize its performance. Every QA should remember that the application should not be QA-approved only based on Functional testing. Still, non-functional testing should be assessed appropriately before making an application live.
Next Steps with Performance Testing Tools
Speak with our experts about implementing compound AI systems and how industries and various departments utilize Decision Intelligence to become decision-centric. Use AI to automate and enhance IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness with the help of performance testing tools.
.webp?width=1921&height=622&name=usecase-banner%20(1).webp)


