Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved from basic automation tools to intelligent agents operating autonomously and handling complex reasoning tasks. These agents can now perceive their environment, learn from it, plan strategically, collaborate with humans or other agents, and execute decisions without constant oversight.
This transformation is significant for enterprises operating at scale and responding to rapid market changes. AI agents emerge as key enablers in this shift by bridging the gap between raw data and actionable, intelligent operations.
What Are AI Agents in Complex Tasks and Reasoning?
An AI agent is an autonomous software system that makes decisions and takes actions to achieve specific goals. It processes input from its environment, uses algorithms for reasoning and planning, and adapts through continuous learning.
Core components of an AI agent:
-
Perception involves gathering data from the environment using sensors or software tools like natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision.
-
Reasoning: Applies logic and learned models to interpret the data and make decisions.
-
Planning: Determines a course of action by evaluating different pathways to reach a goal.
-
Action Execution: Performs the selected action in either a digital or physical space.
-
Learning: Improves over time through feedback, user interaction, or data exposure.
-
Collaboration: Works alongside other agents or humans, often in multi-agent systems.
Multimodal AI agents, which can handle diverse input types like images, audio, and text, represent the next step in agent sophistication. Foundational models like large language models (LLMs) provide the base intelligence that enables agents to reason and adapt dynamically.
As Sundar Pichai said,
"AI is one of the most profound things we’re working on. It's more profound than fire or electricity."
Enterprise AI Agent Capabilities
Modern enterprise AI agents go beyond traditional task automation by providing advanced capabilities:
-
Advanced Task Decomposition and Reasoning
Enterprise agents can break down large tasks into manageable steps. For example, an AI agent in customer support doesn't just retrieve information—it understands the query, identifies the issue type, pulls the correct documents, and formulates a response. -
Human-AI and System Integration
AI agents work within existing enterprise ecosystems and collaborate with human teams through natural language. They ensure seamless transitions and continuous workflows across departments and tools. -
Tool and API Utilization
Agents are integrated with APIs, databases, and internal systems. This allows them to fetch real-time data, execute commands, and autonomously provide up-to-date insights or actions.
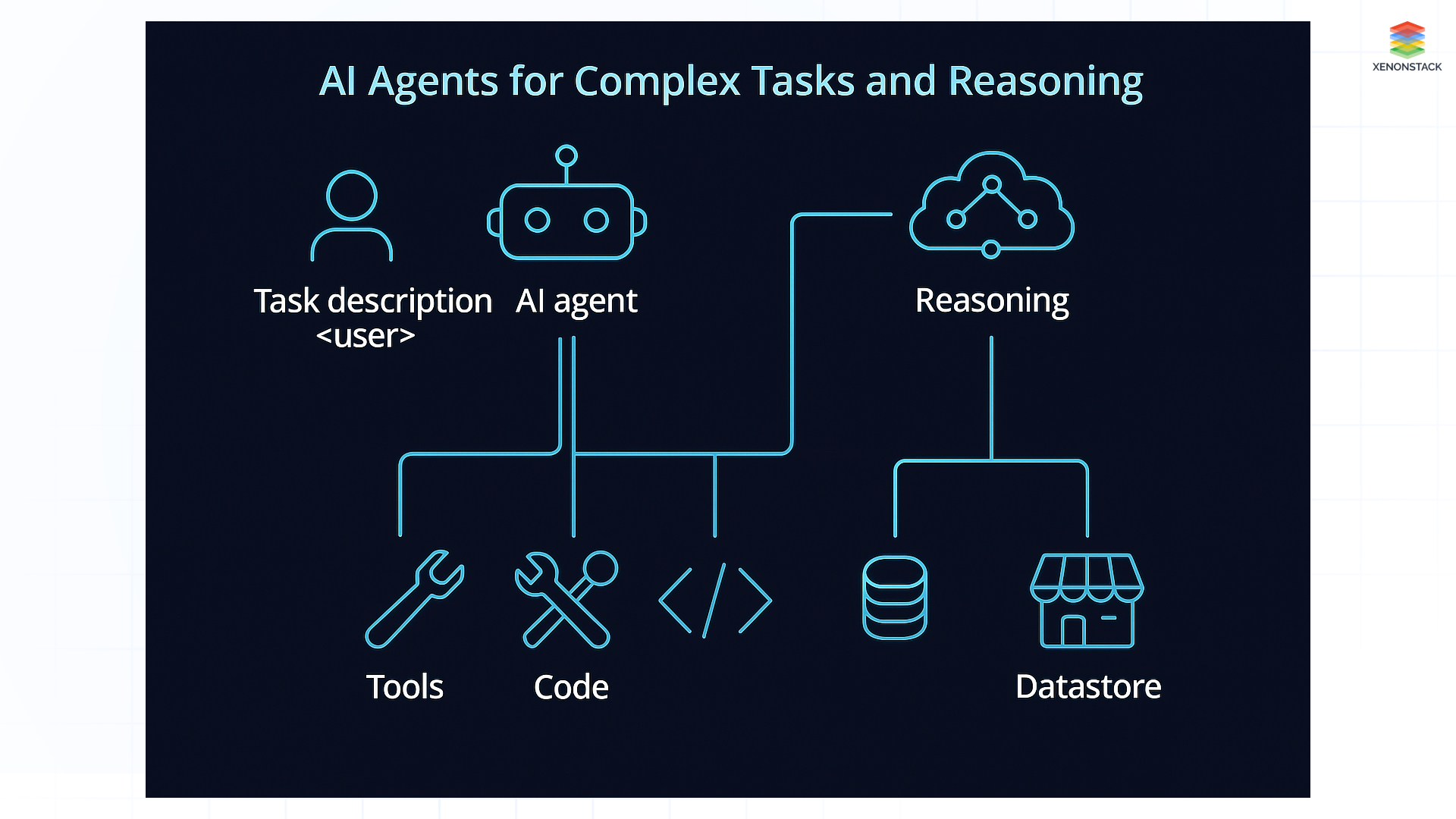 Fig 1: AI Agents for Complex Tasks and Reasoning
Fig 1: AI Agents for Complex Tasks and ReasoningUse Cases of AI Agents Across Industries
-
Customer Support – Verizon and Google AI
Verizon has integrated Google’s Gemini-based AI agents to support call centre representatives. These agents access a vast knowledge base (over 15,000 documents) to assist human agents in real-time. The result is a 40% increase in sales productivity and shorter call durations.
-
Manufacturing – Siemens Predictive Maintenance
Siemens deploys AI agents to monitor sensor data from industrial machines. These agents detect early signs of wear or malfunction, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing unplanned downtime by 25%.
-
Finance – JPMorgan’s Algorithmic Trading Agent
JPMorgan’s LOXM AI agent performs high-frequency trading. It adapts to real-time market conditions faster than human traders, improving execution quality and profit margins.
-
Healthcare – Retinal Disease Diagnosis with Google
Google and Moorfields Eye Hospital developed an AI agent that analyzes 3D eye scans to detect retinal diseases. The agent achieved 94% diagnostic accuracy in clinical trials and offers expert-level insights at scale.
-
Retail – Walmart’s AI Chat Assistants
Walmart uses AI chatbots to manage 80% of customer service inquiries, such as inventory checks and return processes. This allows human agents to focus on higher-value service tasks, improving overall customer experience.
Benefits of AI Agents in Business Environments
-
Increased Efficiency and Automation
AI agents automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up human resources for strategic work. -
Improved Decision-Making
By processing vast datasets in real time, AI agents offer actionable insights that enhance business decisions. -
Personalized Customer Experiences
Agents use contextual data to tailor interactions, improving engagement and satisfaction. -
Scalability
Agents can manage growing workloads without proportional increases in staffing or infrastructure. -
24/7 Availability
Unlike human teams, AI agents can operate continuously, ensuring uninterrupted service delivery.
Challenges in Implementing AI Agents
-
Security and Privacy Risks
AI agents process sensitive enterprise data. Without proper safeguards, there’s potential for data breaches or unauthorized access. Enterprises must implement encryption, authentication, and data minimization protocols. -
Bias and Fairness Concerns
If AI agents are trained on biased or unrepresentative data, they may produce unfair outcomes. Developers must apply fairness metrics and diversify datasets. -
Coordination Among Multiple Agents
Coordination can be complex in systems involving many agents. Poor synchronization may lead to conflict, redundancy, or system inefficiency. -
High Computational Costs
Deploying and running high-performance AI agents can be resource-intensive. This is particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Solutions to AI Agent Deployment Challenges
-
Governance and Security Frameworks
Implement comprehensive governance policies, access controls, and privacy-preserving AI techniques to safeguard data. -
Explainability and Auditability Tools
Use explainable AI (XAI) techniques to make agent decisions transparent and understandable to stakeholders. -
Modular Multi-Agent Frameworks
Develop modular systems where agents have defined roles and shared communication protocols. Use orchestration layers to manage inter-agent coordination. -
Cloud-Based and Edge Deployment
Leverage cloud infrastructure for scalable deployments or use edge computing for low-latency, real-time applications in remote environments.
Future Trends in AI Agents
-
Fully Autonomous Workflows
Agents will soon manage entire workflows end-to-end with minimal human intervention, especially in logistics, finance, and support operations. -
Emotionally Intelligent AI Agents
Advanced agents will understand user sentiment and emotional states to improve interaction quality, particularly in customer service and healthcare. -
Collective Intelligence and Swarm Agents
Inspired by natural swarms, networks of AI agents will collaborate dynamically to solve large-scale problems, such as disaster response or global logistics. -
Edge AI Agent Deployment
Deploying AI agents at the edge (e.g., IoT devices or local systems) allows for real-time processing, reduced latency, and better data privacy. -
Self-Optimizing AI Agents
With reinforcement learning and human feedback loops (RLHF), agents will continuously refine their strategies and models for optimal performance.
Best Practices from Leading Tech Companies
Tech giants like Google, IBM, AWS, and Microsoft follow specific communication and deployment strategies when it comes to AI agents:
-
Use of Case Studies: Real-world performance metrics are emphasized (e.g., time saved, cost reduced).
-
Technical Diagrams: System architectures and workflows visually represent how agents interact with users, systems, and data.
-
Business-Technical Language Balance: Language is accessible to both developers and business decision-makers.
-
Thought Leadership Content: Companies provide forward-looking insights on AI ethics, security, and innovation roadmaps.
Conclusion: AI Agents as the Future of Intelligent Automation
AI agents are not a future concept—they are already shaping how businesses operate today. By automating complex processes, reasoning with context, and learning continuously, AI agents enable organizations to be more agile, efficient, and innovative.
However, realizing their full potential depends on how well enterprises handle ethical, technical, and operational challenges. AI agents with strong governance, thoughtful architecture, and ongoing innovation can become powerful collaborators in any business ecosystem.
Next Steps with AI Agents for Complex Tasks and Reasoning
Talk to our experts about implementing compound AI system, How Industries and different departments use Agentic Workflows and Decision Intelligence to Become Decision Centric. Utilizes AI to automate and optimize IT support and operations, improving efficiency and responsiveness.




