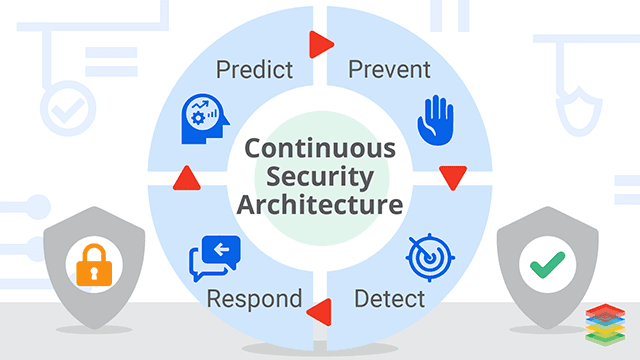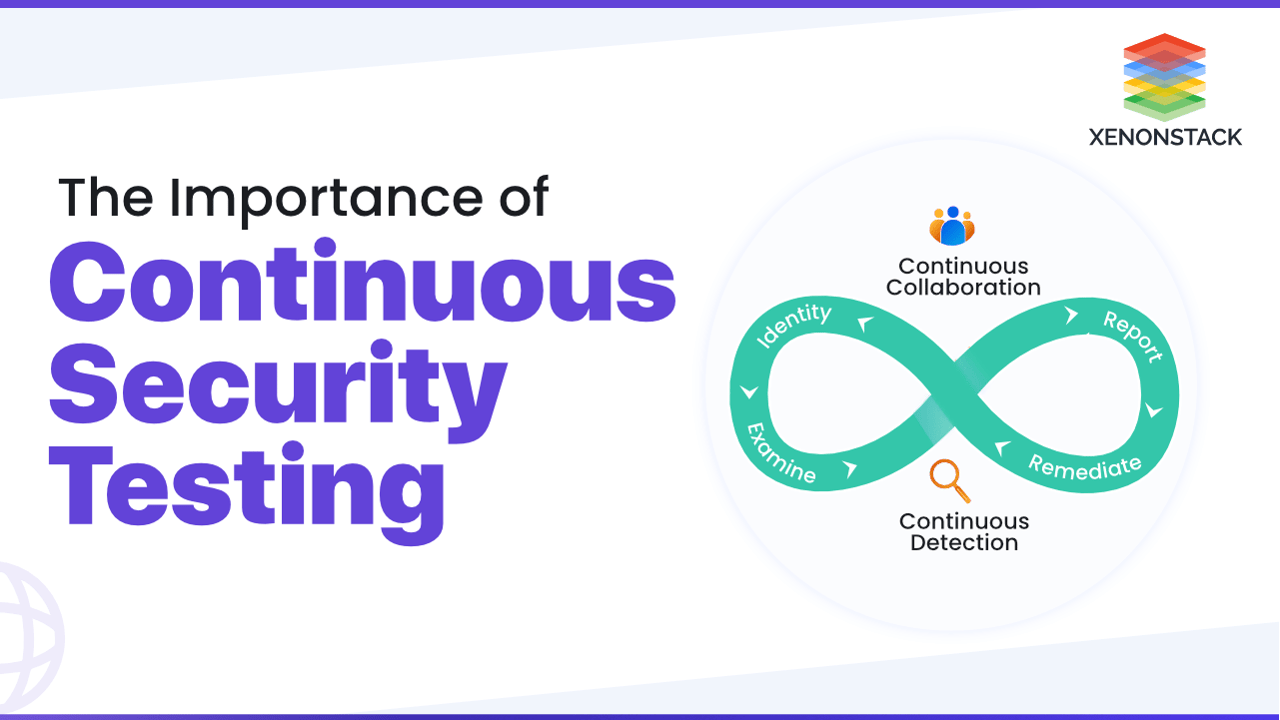
Introduction to the Concept of Security Testing
As the pace of software development accelerates, traditional security testing methods that occur only at the end of a development cycle are becoming inadequate. Continuous Security Testing (CST) addresses this challenge by continuously scanning applications and IT infrastructure to detect vulnerabilities throughout the development process. This proactive approach allows for vulnerabilities to be discovered and addressed early, reducing the likelihood of security breaches while keeping development timelines on track.
Key Benefits of Continuous Security Testing:
-
Early Vulnerability Detection: CST provides real-time insight into vulnerabilities, helping to identify security risks before they escalate.
-
Increased Development Efficiency: By integrating security testing directly into the development workflow, teams can detect and address security issues without slowing down progress.
-
Ongoing Risk Mitigation: Continuous testing ensures that vulnerabilities are promptly identified and resolved, minimizing potential security threats.
-
Enhanced Security Posture: Regular security assessments improve the overall security of the application by identifying gaps and weaknesses early in development.
What is Continuous Security Testing?
Security testing is a type of software testing that helps reveal the vulnerabilities, threats, and risks in a system. This testing aims to identify all possible loopholes in the software application, leading to the loss of valuable information.
Security testing checks the impact of malicious input operations on the software application. It provides evidence that the software application and the information are safe and reliable.
Different Types of Security Testing You Should Know
Here are seven main types of security testing:
-
Vulnerability Scanning: Vulnerability scanning is performed using automated tools to detect and evaluate vulnerabilities in software.
-
Security Scanning: Security scanning means scanning the security of websites, file-management systems, or networks for vulnerabilities.
-
Penetration Testing: Cybersecurity experts do penetration testing to find any possible vulnerabilities in a computer system. It is the process of simulating a real-life cyber attack.
-
Risk Assessment: Risk assessment detects various assets affected by the cyberattack and the different risks associated with those assets.
-
Security Auditing: A security audit is an assessment of the organization's information system. It tests whether your company's internal and external security meets the security rules.
-
Posture Assessment: Posture Assessment refers to checking the system's security status or the organization's network.
-
Ethical Hacking: Ethical hacking is performed by security experts. It is the process of identifying potential data breaches and network threats. Companies perform such activities to check the system defenses.
-
Static Application Security Testing (SAST): SAST analyzes an application’s source code, bytecode, or binary code to identify vulnerabilities at the earliest stages of development, even before the code is deployed or executed.
-
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): DAST involves testing a running application in real time to detect vulnerabilities that may be exploited during actual usages, such as issues in web applications exposed to external threats.
-
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST): IAST combines elements of both SAST and DAST by analyzing code during runtime, providing deeper insights into application vulnerabilities by monitoring both the application’s behavior and source code simultaneously.
Test automation is the utilization of specialized software to control the execution of tests and the comparison of actual outcomes with predicted results. Click to explore the Best Security Testing Tools for DevOps
The Importance of Continuous Security Testing for Businesses
Continuous security testing is the process of measuring, challenging, and optimizing the effectiveness of an organization's security controls, policy enforcement, and infrastructure configurations. It is now believed to be the best possible practice.
Evolving Cyber Threats
As technology grows, attackers use sophisticated ways to hide their actions from various malware detection tools. Continuous security testing is the most effective way to counter these security threats. It enables you to run regular simulations, optimize security control, and validate the threat intelligence system.
Improved Bug Fixing Process
Bugs can be a big problem if not dealt with in time. The effective solution is to identify the bugs throughout the development process rather than fixing the bugs at the end of the whole process. This can be made possible by continuous Security testing.
Improved Security Awareness
With continuous security testing feedback, developers will be able to identify and rectify their mistakes effectively, resulting in an efficient development process with better overall security. As security practices continuously improve, organizations will benefit both in the short term and in the long term.
Secure Agile Development
Using the agile development process requires qualified personnel. With so many changes being made to the application during the development process, security vulnerabilities can easily be overlooked, and ultimately, these vulnerabilities can be integrated into the product.
However, with continuous security testing, an organization can monitor and analyze each stage of the development process. This allows for the identification and addressing of vulnerabilities during the development process.
Challenges in Implementing Continuous Security Testing
Challenges faced by organizations during continuous security testing:
- Lack of Expertise - The team may be unable to embrace new approaches due to a lack of availability and the skills required to acquire and use new tools and processes.
- Unstable Execution - The organization's existing state of test automation may be unstable and unreliable. The length of time it takes to execute code increases as it grows.
- Environment unavailability - System dependencies frequently make the test environment unavailable, unmanageable, and limited.
- Tool Integration and Compatibility - Organizations often struggle with integrating new security tools into their existing software development environment.
- False Positives and Noise - False positives from security scans and the "noise" generated by unnecessary alerts can overwhelm development teams.
How to Effectively Perform Security Testing in Development?
The security testing needs to be done in the initial stages of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) because it costs a lot more if the security testing is performed after the software execution and deployment stage.
Here's the step-by-step guide for performing security testing at each stage of the software development process.
Step 1. Requirement Stage
The requirement process stage is the first stage of software development. Here, a security analysis of the business needs is done.
Step 2. Design Stage
In the second step, the design stage, security testing will be done to explore the design's risks.
Step 3. Development Stage
In the third stage, the development stage, White box testing along with dynamic and static testing will be performed.
Step 4. Testing Stage (functional testing, integration testing, system testing)
One round of vulnerability scanning will be done, along with the black-box testing.
Step 5. Implementation Stage
In the implementation stage, vulnerability scanning will be done along with one round of penetration testing.
Step 6. Maintenance Stage
In the last stage, the maintenance stage, an impact analysis of the impact area will be done.
The Test Plan should include the following:
- The testing data should be linked to the security testing.
- Test tools are required for security testing.
- Several test outputs can be analyzed by using various security tools.
- Test cases that rely on security purposes should be written.
To understand more about services and solutions, read more on our Continuous Security Services and Strategy Consulting page.
Best Practices for Automating Continuous Security Testing
Automation comes in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Scans and policies can be manually programmed or pre-programmed. They can also be triggered automatically at code commits or manually initiated. These scans can produce automated remediation and reports or require human intervention.
Here are four approaches to incorporate automated security testing into your software development practices:
-
Run SAST (Static Application Security Testing) to automate security scans for every code change. For ease of assessment, sort the results by the vulnerability's priority level.
-
Depending on the policies in place, scan results should automatically generate a work ticket or problem or stop a build. These results should be presented to the developer for immediate remediation in the workspace or using the IDE to avoid context switching.
-
When code is committed, policies are automatically applied, with the ability to capture and approve exceptions as needed.
-
DAST scans can be used to look for known vulnerabilities in running web applications. In GitLab, you can automate DAST scans by adding the CI task to your existing file or using Auto DAST.
Key Advantages of Implementing Continuous Security Testing
-
Frequent changes in the Security Stack: The IT environment evolves daily, and changes are made regularly, whether network changes, employees leaving or joining the company, or the use of new software. Estimating the impact of these changes on the company's security posture is crucial and helps remove any Security gaps.
-
Cost-Effective IT Operations: Since vulnerabilities are detected earlier, mitigation plans for them can be planned beforehand.
-
Unexpected Breaches Prevention: Continuous security testing helps discover new vulnerabilities periodically, keeping us updated. We don't have to wait for the pen-testing report for vulnerability detection.
-
Boost in Knowledge: New threats emerge daily, so it is essential to stay updated. Continuous security testing provides you with just the opportunity to boost your knowledge about security vulnerabilities.
Reasons Why Enterprises Should Adopt Continuous Security Testing
New Threats Every Day
New strains of malware and potential threats are identified daily. Hence, security controls should be ensured to identify these variants as frequently as possible. Threats may include keyloggers, ransomware, trojans, etc.
Frequent IT Environment Change
Daily operations may affect the organization's security posture. Policy changes, tool updates, new software or applications, and new endpoint additions can create new cracks in the defenses. It is essential to test SIEM for proper alert generation for any security violation.
Evolving Stealth Techniques
It is challenging to detect every new tactic, technique, and procedure. Therefore, it is advised to use behavior-based detection tools or other tools that use machine learning to spot any suspicious behavior when it occurs.
Adhere to Mandatory Compliance
While assisting firms in maintaining excellent cyber hygiene, compliance with data security protection legislation is equally critical. CSM can aid in detecting compliance concerns, which is why it is becoming a more critical aspect of cyber security.
Emerging Trends in Continuous Security Testing
Here are five emerging trends in continuous security testing:
-
Proactive Security Approach: Organizations are increasingly focusing on identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, emphasizing a proactive stance toward security.
-
Integration into SDLC: Continuous security testing is being integrated into the SDLC to ensure that security measures are embedded from the start of development.
-
Threat Modeling: Threat modeling is on the rise. It allows teams to anticipate potential security threats and design defenses accordingly.
-
CI/CD Integration for Security: Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are being enhanced with security checks to address vulnerabilities at every stage of the deployment process.
-
Vulnerability Management: There is an increasing focus on continuous vulnerability management, with regular scans and updates implemented to mitigate risks effectively.
Why Continuous Testing is the Future of Security?
While continuous security testing offers consistent, proactive protection, many companies hesitate to adopt automated security procedures due to familiarity with traditional methods. However, security is critical for every business, and neglecting it can lead to serious risks. With continuous security testing in place, vulnerabilities are identified and addressed early in the development process, ensuring greater overall security with less manual effort. By integrating SAST (Static Application Security Testing) and DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing), organizations can improve their security posture while staying ahead of emerging threats. Businesses that embrace continuous security testing gain a competitive edge, protecting themselves from evolving cyber risks and ensuring long-term success, unlike those relying on outdated, reactive security practices.
Next Steps for Better Security Testing Integration
Connect with our experts to explore how implementing Continuous Security Testing, along with advanced security automation and AI-driven workflows, can help your organization proactively manage vulnerabilities. Leverage continuous testing to enhance your security posture, improve operational efficiency, and ensure faster response times to emerging threats.